Abstract
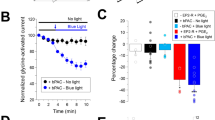
Despite the crucial role that prostaglandins (PGs) have in the sensitization of the central nervous system to pain, their cellular and molecular targets leading to increased pain perception have remained elusive. Here we investigated the effects of PGE2 on fast synaptic transmission onto neurons in the rat spinal cord dorsal horn, the first site of synaptic integration in the pain pathway. We identified the inhibitory (strychnine-sensitive) glycine receptor as a specific target of PGE2. PGE2, but not PGF2α, PGD2 or PGI2, reduced inhibitory glycinergic synaptic transmission in low nanomolar concentrations, whereas GABAA, AMPA and NMDA receptor-mediated transmission remained unaffected. Inhibition of glycine receptors occurred via a postsynaptic mechanism involving the activation of EP2 receptors, cholera-toxin-sensitive G-proteins and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Via this mechanism, PGE2 may facilitate the transmission of nociceptive input through the spinal cord dorsal horn to higher brain areas where pain becomes conscious.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doubell, T. P., Mannion, R. J. & Woolf, C. J. in Textbook of Pain (eds. Wall, P. D. & Melzack, R.) 165–181 (Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, Scotland, 1999).
Yaksh, T. L., Hua, X. Y., Kalcheva, I., Nozaki-Taguchi, N. & Marsala, M. The spinal biology in humans and animals of pain states generated by persistent small afferent input. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 7680–7686 (1999).
O'Banion, M. K. Cyclooxygenase-2: molecular biology, pharmacology, and neurobiology. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 13, 45–82 (1999).
Vane, J. R., Bakhle, Y. S. & Botting, R. M. Cyclooxygenases 1 and 2. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 38, 97–120 (1998).
Kumazawa, T., Mizumura, K. & Koda, H. Involvement of EP3 subtype of prostaglandin E receptors in PGE2-induced enhancement of the bradykinin response of nociceptors. Brain Res. 632, 321–324 (1993).
Vanegas, H. & Schaible, H. Prostaglandins and cyclooxygenases in the spinal cord. Prog. Neurobiol. 64, 327–363 (2001).
Samad, T. A. et al. Interleukin-1 β-mediated induction of Cox-2 in the CNS contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Nature 410, 471–475 (2001).
Ichitani, Y., Shi, T., Haeggstrom, J. Z., Samuelsson, B. & Hokfelt, T. Increased levels of cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA in the rat spinal cord after peripheral inflammation: an in situ hybridization study. Neuroreport 8, 2949–2952 (1997).
Beiche, F., Scheuerer, S., Brune, K., Geisslinger, G. & Goppelt-Struebe, M. Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA in the rat spinal cord following peripheral inflammation. FEBS Lett. 390, 165–169 (1996).
Guhring, H. et al. Suppressed injury-induced rise in spinal prostaglandin E2 production and reduced early thermal hyperalgesia in iNOS-deficient mice. J. Neurosci. 20, 6714–6720 (2000).
Fuxe, K. & Agnati, L. F. Volume Transmission in the Brain: Novel Mechanisms for Neural Transmission (Raven, New York, 1991).
Matsumura, K. et al. Mapping of prostaglandin E2 binding sites in rat brain using quantitative autoradiography. Brain Res. 581, 292–298 (1992).
Kawamura, T. et al. Expression of prostaglandin EP2 receptor mRNA in the rat spinal cord. Life Sci. 61, 2111–2116 (1997).
Beiche, F., Klein, T., Nusing, R., Neuhuber, W. & Goppelt-Struebe, M. Localization of cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 receptor EP3 in the rat lumbar spinal cord. J. Neuroimmunol. 89, 26–34 (1998).
Nakamura, K. et al. Immunohistochemical localization of prostaglandin EP3 receptor in the rat nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 421, 543–569 (2000).
Donaldson, L. F., Humphrey, P. S., Oldfield, S., Giblett, S. & Grubb, B. D. Expression and regulation of prostaglandin E receptor subtype mRNAs in rat sensory ganglia and spinal cord in response to peripheral inflammation. Prostaglandins 63, 109–122 (2001).
Baba, H., Kohno, T., Moore, K. A. & Woolf, C. J. Direct activation of rat spinal dorsal horn neurons by prostaglandin E2. J. Neurosci. 21, 1750–1756 (2001).
Yaksh, T. L. & Malmberg, A. B. in Textbook of Pain (eds. Wall, P. D. & Melzack, R.) 165–200 (Churchill Livingston, Edinburgh, Scotland, 1994).
Narumiya, S., Sugimoto, Y. & Ushikubi, F. Prostanoid receptors: structures, properties, and functions. Physiol Rev. 79, 1193–1226 (1999).
Kiriyama, M. et al. Ligand binding specificities of the eight types and subtypes of the mouse prostanoid receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 122, 217–224 (1997).
Boie, Y. et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of the four rat prostaglandin E2 prostanoid receptor subtypes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 340, 227–241 (1997).
Kaslow, H. R. & Burns, D. L. Pertussis toxin and target eukaryotic cells: binding, entry, and activation. FASEB J. 6, 2684–2690 (1992).
Ribeiro-Neto, F. A. et al. ADP-ribosylation of membrane components by pertussis and cholera toxin. Methods Enzymol. 109, 566–572 (1985).
Smart, T. G. Regulation of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitter-gated ion channels by protein phosphorylation. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 7, 358–367 (1997).
Eguchi, N. et al. Lack of tactile pain (allodynia) in lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 726–730 (1999).
Minami, T. et al. Allodynia evoked by intrathecal administration of prostaglandin F2 alpha to conscious mice. Pain 50, 223–229 (1992).
Malmberg, A. B. & Yaksh, T. L. Cyclooxygenase inhibition and the spinal release of prostaglandin E2 and amino acids evoked by paw formalin injection: a microdialysis study in unanesthetized rats. J. Neurosci. 15, 2768–2776 (1995).
Yang, L. C., Marsala, M. & Yaksh, T. L. Characterization of time course of spinal amino acids, citrulline and PGE2 release after carrageenan/kaolin-induced knee joint inflammation: a chronic microdialysis study. Pain 67, 345–354 (1996).
Vaello, M. L., Ruiz-Gomez, A., Lerma, J. & Mayor, F. Jr. Modulation of inhibitory glycine receptors by phosphorylation by protein kinase C and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 2002–2008 (1994).
Kuhse, J., Betz, H. & Kirsch, J. The inhibitory glycine receptor: architecture, synaptic localization and molecular pathology of a postsynaptic ion-channel complex. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 5, 318–323 (1995).
Gosselin, R. E., Hodge, H. C., Smith, R. P. & Gleason, M. N. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products 4th edn. (Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, 1976).
Beyer, C., Roberts, L. A. & Komisaruk, B. R. Hyperalgesia induced by altered glycinergic activity at the spinal cord. Life Sci. 37, 875–882 (1985).
Yaksh, T. L. Behavioral and autonomic correlates of the tactile evoked allodynia produced by spinal glycine inhibition: effects of modulatory receptor systems and excitatory amino acid antagonists. Pain 37, 111–123 (1989).
Perper, J. A. Fatal strychnine poisoning—a case report and review of the literature. J. Forensic. Sci. 30, 1248–1255 (1985).
Becker, C. M. Convulsants acting at the inhibitory glycine receptor. Handbook Exp. Pharmacol. 102, 539–575 (1992).
Arena, J. M. Poisoning: Toxicity, Symptoms, Treatments 4th edn. (C. C. Thomas, Springfield, Illinois, 1979).
Zieglgänsberger, W. & Herz, A. Changes of cutaneous receptive fields of spino-cervical-tract neurones and other dorsal horn neurones by microelectrophoretically administered amino acids. Exp. Brain Res. 13, 111–126 (1971).
Okuda-Ashitaka, E. et al. Nocistatin, a peptide that blocks nociceptin action in pain transmission. Nature 392, 286–289 (1998).
Zeilhofer, H. U., Muth-Selbach, U., Guhring, H., Erb, K. & Ahmadi, S. Selective suppression of inhibitory synaptic transmission by nocistatin in the rat spinal cord dorsal horn. J. Neurosci. 20, 4922–4929 (2000).
Minami, T., Okuda-Ashitaka, E., Nishizawa, M., Mori, H. & Ito, S. Inhibition of nociceptin-induced allodynia in conscious mice by prostaglandin D2 . Br. J. Pharmacol. 122, 605–610 (1997).
Brandon, E. P. et al. Hippocampal long-term depression and depotentiation are defective in mice carrying a targeted disruption of the gene encoding the RI β subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 8851–8855 (1995).
Malmberg, A. B. et al. Diminished inflammation and nociceptive pain with preservation of neuropathic pain in mice with a targeted mutation of the type I regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Neurosci. 17, 7462–7470 (1997).
Minami, T. et al. Involvement of primary afferent C-fibres in touch-evoked pain (allodynia) induced by prostaglandin E2 . Eur. J. Neurosci. 11, 1849–1856 (1999).
Nishihara, I., Minami, T., Watanabe, Y., Ito, S. & Hayaishi, O. Prostaglandin E2 stimulates glutamate release from synaptosomes of rat spinal cord. Neurosci. Lett. 196, 57–60 (1995).
Liebel, J. T., Swandulla, D. & Zeilhofer, H. U. Modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission by nociceptin in superficial dorsal horn neurones of the neonatal rat spinal cord. Br. J. Pharmacol. 121, 425–432 (1997).
Dodt, H.-U. & Zieglgänsberger, W. Infrared videomicroscopy: a new look at neuronal structure and function. Trends Neurosci. 17, 453–458 (1994).
Ceranik, K. et al. A novel type of GABAergic interneuron connecting the input and the output regions of the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 17, 5380–5394 (1997).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 353/A8 to H.U.Z. and SFB/B15 to W.L.N.) and a stipend from the Graduiertenkolleg GRK 22 to S.L. The authors thank C.-M. Becker, K. Brune and P.W. Reeh for critically reading the manuscript and S. Gabriel, K. Löschner and H. Symowski for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadi, S., Lippross, S., Neuhuber, W. et al. PGE2 selectively blocks inhibitory glycinergic neurotransmission onto rat superficial dorsal horn neurons. Nat Neurosci 5, 34–40 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn778
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn778
This article is cited by
-
Excitatory and inhibitory neuronal signaling in inflammatory and diabetic neuropathic pain
Molecular Medicine (2023)
-
AAV-glycine receptor α3 alleviates CFA-induced inflammatory pain by downregulating ERK phosphorylation and proinflammatory cytokine expression in SD rats
Molecular Medicine (2023)
-
Development of opioid-induced hyperalgesia depends on reactive astrocytes controlled by Wnt5a signaling
Molecular Psychiatry (2023)
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying the actions of arachidonic acid-derived prostaglandins on peripheral nociception
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2020)
-
Modulation of glycine receptor single-channel conductance by intracellular phosphorylation
Scientific Reports (2020)