Abstract
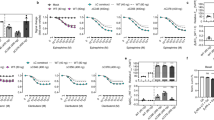
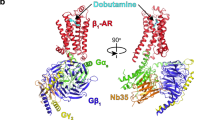
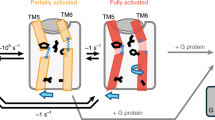
With more than 800 members, the G protein–coupled receptor family constitutes the largest group of membrane proteins involved in signal transduction. Until the end of last year, high-resolution three-dimensional structures were available for only one of them—the light receptor rhodopsin. Recently the structure of the β2-adrenergic receptor has been obtained, and it revealed interesting differences with the structure of rhodopsin. Analyses of these differences raise important questions about the binding modes of diffusible ligands in the receptor and allow formulation of testable hypotheses about the structural determinants linking drug binding to specific signaling responses. The three-dimensional structure derived from the β2-adrenergic receptor crystal has been used to virtually dock ligands with distinct activities. The different binding modes of these ligands, which correlated with their reported efficacy profiles, suggest that it could be possible to predict the structural determinants of drug signaling efficacies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benovic, J.L., Shorr, R.G.L., Caron, M.G. & Lefkowitz, R.J. The mammalian β2-adrenergic receptor: purification and characterization. Biochemistry 23, 4510–4518 (1984).
Rasmussen, S.G. et al. Crystal structure of the human beta2 adrenergic G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature 450, 383–387 (2007).
Cherezov, V. et al. High-resolution crystal structure of an engineered human β2-adrenergic G protein-coupled receptor. Science 318, 1258–1265 (2007).
Rosenbaum, D.M. et al. GPCR engineering yields high-resolution structural insights into β2-adrenergic receptor function. Science 318, 1266–1273 (2007).
Salom, D. et al. Crystal structure of a photoactivated deprotonated intermediate of rhodopsin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 16123–16128 (2006).
Palczewski, K. et al. Crystal structure of rhodopsin: a G protein-coupled receptor. Science 289, 739–745 (2000).
Bockaert, J., Fagni, L., Dumuis, A. & Marin, P. GPCR interacting proteins (GIP). Pharmacol. Ther. 103, 203–221 (2004).
Lohse, M.J., Benovic, J.L., Codina, J., Caron, M.G. & Lefkowitz, R.J. β-Arrestin: a protein that regulates β-adrenergic receptor function. Science 248, 1547–1550 (1990).
Shenoy, S.K. & Lefkowitz, R.J. Multifaceted roles of β-arrestins in the regulation of seven-membrane-spanning receptor trafficking and signalling. Biochem. J. 375, 503–515 (2003).
Shenoy, S.K. et al. β-Arrestin-dependent, G protein-independent ERK1/2 activation by the β2 adrenergic receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 1261–1273 (2006).
Daaka, Y., Luttrell, D.K. & Lefkowitz, R.J. Switching of the coupling of the β2-adrenergic receptor to different G proteins by protein kinase A. Nature 390, 88–91 (1997).
Azzi, M. et al. β-Arrestin-mediated activation of MAPK by inverse agonists reveals distinct active conformations for G protein-coupled receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 11406–11411 (2003).
Galandrin, S., Oligny-Longpre, G. & Bouvier, M. The evasive nature of drug efficacy: implications for drug discovery. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 28, 423–430 (2007).
Ghanouni, P. et al. Functionally different agonists induce distinct conformations in the G protein coupling domain of the β2 adrenergic receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 24433–24436 (2001).
Swaminath, G. et al. Probing the β2 adrenoceptor binding site with catechol reveals differences in binding and activation by agonists and partial agonists. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 22165–22171 (2005).
Gales, C. et al. Probing the activation-promoted structural rearrangements in preassembled receptor-G protein complexes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 778–786 (2006).
Roth, C.B., Hanson, M.A. & Stevens, R.C. Stabilization of the human β2-adrenergic receptor TM4–TM3-TM5 helix interface by mutagenesis of Glu122(3.41), a critical residue in GPCR structure. J. Mol. Biol. 376, 1305–1319 (2008).
Serrano-Vega, M.J., Magnani, F., Shibata, Y. & Tate, C.G. Conformational thermostabilization of the β1-adrenergic receptor in a detergent-resistant form. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 877–882 (2008).
Costa, T., Ogino, Y., Munson, P.J., Onaran, H.O. & Rodbard, D. Drug efficacy at guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein-linked receptors: thermodynamic interpretation of negative antagonism and of receptor activity in the absence of ligand. Mol. Pharmacol. 41, 549–560 (1992).
Samama, P., Cotecchia, S., Costa, T. & Lefkowitz, R.J. A mutation-induced activated state of the β2-adrenergic receptor. Extending the ternary complex model. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 4625–4636 (1993).
Chidiac, P., Hebert, T.E., Valiquette, M., Dennis, M. & Bouvier, M. Inverse agonist activity of β-adrenergic antagonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 45, 490–499 (1994).
Samama, P., Pei, G., Costa, T., Cotecchia, S. & Lefkowitz, R.J. Negative antagonists promote an inactive conformation of the β2- adrenergic receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 45, 390–394 (1994).
Bond, R.A. & Ijzerman, A.P. Recent developments in constitutive receptor activity and inverse agonism, and their potential for GPCR drug discovery. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 27, 92–96 (2006).
Milligan, G. Constitutive activity and inverse agonists of G protein-coupled receptors: a current perspective. Mol. Pharmacol. 64, 1271–1276 (2003).
Rovati, G.E., Capra, V. & Neubig, R.R. The highly conserved DRY motif of class A G protein-coupled receptors: beyond the ground state. Mol. Pharmacol. 71, 959–964 (2007).
Watson, C. et al. The use of stimulus-biased assay systems to detect agonist-specific receptor active states: implications for the trafficking of receptor stimulus by agonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 58, 1230–1238 (2000).
Kenakin, T. Agonist-receptor efficacy. II. Agonist trafficking of receptor signals. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 16, 232–238 (1995).
Baker, J.G., Hall, I.P. & Hill, S.J. Agonist and inverse agonist actions of β-blockers at the human β 2-adrenoceptor provide evidence for agonist-directed signaling. Mol. Pharmacol. 64, 1357–1369 (2003).
Galandrin, S. & Bouvier, M. Distinct signaling profiles of β1 and β2 adrenergic receptor ligands towards adenylyl cyclase and mitogen-activated protein kinase reveals the pluridimensionality of efficacy. Mol. Pharmacol. 70, 1575–1584 (2006).
Yao, X. et al. Coupling ligand structure to specific conformational switches in the β2-adrenoceptor. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2, 417–422 (2006).
Janz, J.M. & Farrens, D.L. Rhodopsin activation exposes a key hydrophobic binding site for the transducin α-subunit C terminus. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 29767–29773 (2004).
Raimondi, F., Seeber, M., Benedetti, P.G. & Fanelli, F. Mechanisms of inter- and intramolecular communication in GPCRs and G proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 4310–4325 (2008).
Valiquette, M., Parent, S., Loisel, T.P. & Bouvier, M. Mutation of tyrosine-141 inhibits insulin-promoted tyrosine phosphorylation and increased responsiveness of the human β2- adrenergic receptor. EMBO J. 14, 5542–5549 (1995).
Karoor, V. & Malbon, C.C. Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 stimulates phosphorylation of the β2-adrenergic receptor in vivo on sites distinct from those phosphorylated in response to insulin. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 29347–29352 (1996).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to C. Le Gouill and A. Marinier for useful discussions, and to the Canadian Institute for Health Research Team in GPCR Allosteric Regulation (CTiGAR), the Direction Générale des Technologies de l'Information et des Communications (DGTIC) of the Université de Montréal and the NMR platform of Institute for Research in Immunology and Cancer (IRIC) for providing access to their servers for simulation and docking.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Audet, M., Bouvier, M. Insights into signaling from the β2-adrenergic receptor structure. Nat Chem Biol 4, 397–403 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.97
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.97
This article is cited by
-
Expression pattern and clinical significance of beta 2-adrenergic receptor in oral squamous cell carcinoma: an emerging prognostic indicator and future therapeutic target
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2022)
-
In Silico Study of the Structurally Similar ORL1 Receptor Agonist and Antagonist Pairs Reveal Possible Mechanism of Receptor Activation
The Protein Journal (2014)
-
Development of 7TM receptor-ligand complex models using ligand-biased, semi-empirical helix-bundle repacking in torsion space: application to the agonist interaction of the human dopamine D2 receptor
Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design (2013)
-
The complexity of G-protein coupled receptor-ligand interactions
Science China Chemistry (2013)
-
Homology model and docking studies on porcine β2 adrenoceptor: description of two binding sites
Journal of Molecular Modeling (2011)