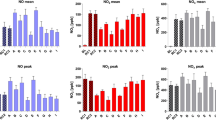
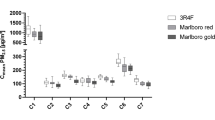
Abstract
ATMOSPHERIC pollution by carbon monoxide (CO), mainly derived from the motor-car, has given rise to worldwide concern in recent years. In an attempt to limit this form of pollution legislation has been introduced, both in the US1 and Britain2, to control the level of CO emitted by the exhaust of the internal combustion engine. The cost of such measures would be high, both in terms of engine modification and the inevitably increased fuel consumption. The question arises: What would be the probable effect of such measures on man ?
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Federal Register, 37, No. 221, part 2 (1972).
Motor Vehicles (Construction and Use), Regulation 33A (HMSO, 1973).
Holland, R. A. B., Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 174, 154–171 (1970).
Robinson, E., and Robbins, R. C., Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 174, 89–95 (1970).
Waller, R. E., Commins, B. T., and Lawther, P. J., Br. J. industr. Med., 22, 128–138 (1965).
Chovin, P., and Truffert, L., Proc. Health Effects of Carbon Monoxide Environmental Pollution, Luxembourg, 1973, 151–194 (Office for Official Publication of European Communities, Luxembourg, 1974).
Commins, B. T., and Lawther, P. J., Br. J. industr. Med., 22, 139–144 (1965).
Lily, R. E. C., Cole, P. V., and Hawkins, L. H., Br. J. industr. Med., 29, 454–457 (1972).
Sjöstrand, T., Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest., 1, 201–214 (1949).
Haarke, H. P., Baars, A., Frahm, B., Peters, H., and Schultz, Ch., Int. Arch Arbits Med., 29, 323–339 (1972).
Wynder, E. L., and Hoffman, D., Tobacco and Tobacco Smoke, Studies in Experimental Carcinogenesis (Academic, New York, 1967).
Lawther, P. J., and Commins, B. T., Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 174, 135–147 (1970).
Astrup, P., Br. med. J., iv, 447–452 (1972).
Wald, N., Haward, S., Smith, P. G., and Kjeldson, K., Br. med. J., i, 761–765 (1973).
Anderson, J. G., Automotive Design Engin., 17, 12–13 (1974).
Royal College of Physicians, Smoking and Health Now (Pitman Medical, London, 1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
COLE, P. Comparative effects of atmospheric pollution and cigarette smoking on carboxyhaemoglobin levels in man. Nature 255, 699–701 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/255699a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/255699a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.