Abstract
Purpose. In this study, P-glycoprotein (P-gp) mediated efflux of simvastatin (SV), simvastatin acid (SVA), and atorvastatin (AVA) and inhibition of P-gp by SV, SVA, and AVA were evaluated to assess the role of P-gp in drug interactions.
Methods. P-gp mediated efflux of SV, SVA, and AVA was determined by directional transport across monolayers of LLC-PK1 cells and LLC-PK1 cells transfected with human MDR1. Inhibition of P-gp was evaluated by studying the vinblastine efflux in Caco-2 cells and in P-gp overexpressing KBV1 cells at concentrations of SV, SVA, and AVA up to 50 μM.
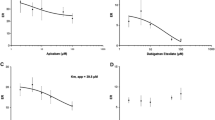
Results. Directional transport studies showed insignificant P-gp mediated efflux of SV, and moderate P-gp transport [2.4-3.8 and 3.0-6.4 higher Basolateral (B) to Apical (A) than A to B transport] for SVA and AVA, respectively. Inhibition studies did not show the same trend as the transport studies with SV and AVA inhibiting P-gp (IC50 ∼25-50 μM) but SVA not showing any inhibition of P-gp.
Conclusions. The moderate level of P-gp mediated transport and low affinity of SV, SVA, and AVA for P-gp inhibition compared to systemic drug levels suggest that drug interactions due to competition for P-gp transport is unlikely to be a significant factor in adverse drug interactions. Moreover, the inconsistencies between P-gp inhibition studies and P-gp transport of SV, SVA, and AVA indicate that the inhibition studies are not a valid means to identify statins as Pgp substrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
T. R. Pedersen, K. Berg, and T. J. Cook. et. al. Safety and tolerability of cholesterol lowering with simvastatin during 5 years in the Scandinavian Survival Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 156:2085-2092 (1996).
R. F. Reinoso, A. Sanchez Navarro, M. J. Garcia, and J. R. Prous. Pharmacokinetic interactions of Statins. Methods Find Exp. Clin. Pharamacol. 23:541-566 (2001).
M. Igel, T. Sudhop, and K. vonBergman. Metabolism and drug interactions of 3-hydroxy-3methylglutaryl coenzyme A-reductase inhibitors (statins). Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 57:357-364 (2001).
P. D. Thompson, P. Clarkson, and R. H. Karas. Statin Associated Myopathy. JAMA 289:1681-1690 (2003).
T. Prueksaritanont, B. Ma, and C. Tang. et. al. Metabolic interactions between mibefradil and HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: an in vitro investigation with human liver preparations. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 47:291-298 (1999).
T. Prueksaritanont, C. Tang, Y. Qui, L. Mu, R. Subramanian, and J. H. Lin. Effects of fibrates on metabolism of statins in human hepatocytes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 839:1280-1287 (2002).
P. H. Siedlik, S. C. Olson, B. B. Yang, and R. H. Stern. Erythromycin coadministration increases plasma atorvastatin concentrations. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 39:501-504 (1999).
E. Wang, C. N. Casciano, R. P. Clement, and W. W. Johnson. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) characterized as direct inhibitors of P-glycoprotein. Pharm. Res. 18:800-806 (2001).
K. Bogman, A.-K. Peyer, M. Torok, E. Kusters, and J. Drewe. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and P-glycoprotein modulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 132:1183-1192 (2001).
T. Sakaeda, K. Takara, and M. Kakumoto. et. al. Simvastatin and lovastatin, but not pravastatin, interact with MDR1. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 54:419-423 (2002).
A. H. Schinkel. The physiological function of drug-transporting P-glycoproteins. Semin. Cancer Biol. 8:161-170 (1997).
Z. C. Gatmaitan and I. M. Arias. Structure and function of P-glycoprotein in normal liver and small intestine. Adv. Pharamcol 24:77-97 (1993).
F. Thiebaut, T. Tsuruo, H. Hamada, M. M. Gottesman, I. Pastan, and M. C. Willingham. Immunohistochemical localization in normal tissues of different epitopes in the multidrug transport protein P170: evidence for localization in brain capillaries and cross-reactivity of one antibody with a muscle protein. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 37:159-164 (1989).
C. Cordon-Cardo. O'brien JP, Boccia J, Casals D, Bertino JR, and Melamed MR Expression of multidrug resistance gene product (P-glycoprotein) in human normal and tumor tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 38:1277-1287 (1990).
X. Wu, L. R. Whitfeild, and B. H. Stewart. Atorvastatin transport in Caco-2 cell model: Contribution of P-glycoprotein and Proton-monocarboxylic acid transporter. Pharm. Res. 17:209-215 (2000).
M. Yamazaki, W. E. Neway, and T. Ohe. Chen I-Wu, Rowe JF, Hochman JH, Chiba M, and Lin JH. In vitro substrate identification studies for P-glycoprotein-mediated transport: Species difference and predictability of in vivo results. J. Pharamacol. Exp. Ther. 296:723-735 (2001).
D. W. Shen, C. Cardarelli, J. Hwang, M. Cornwell, N. Richert, S. Ishii, I. Pastan, and M. M. Gottesman. Multiple drug-resistant human KB carcinoma cells independently selected for high-level resistance to colchicine, adriamycin, or vinblastine show changes in expression of specific proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 26bd1:7762-7770 (1986).
A. H. Schinkel, E. Wagenaar, L. VanDeemter, C. A. A. M. Mol, and P. Borst. Absence of mdr1a P-glycoprotein in mice affects tissue distribution and pharmacokinetics of dexamethasone digoxin and cyclosporin A. J. Clin. Invest. 96:1698-1705 (1995).
H. Lennernas. Clinical pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 42:1141-1160 (2003).
J. W. Polli, S. A. Wring, J. E. Humphreys, L. Huang, J. B. Morgan, L. O. Webster, and C. S. Serabjit-Singh. Rational use of P-glycoprotein assays in drug discovery. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 299:620-628 (2001).
S. Scala, N. Akhmed, U. S. Rao, K. Paull, L. B. Lan, B. Dickstein, J. S. Lee, G. H. Elgemeie, W. D. Stein, and S. E. Bates. P-glycoprotein substrates and antagonists cluster into two distinct groups. Mol. Pharmacol. 51:1024-1033 (1997).
Zocor product insert. Physicians Desk Reference 56th edition. 2002; 2219-2223.
J. V. Asperen, O. van Tellingen, A. H. Schinkel, and J. H. Beijnen. Comparative pharmacokinetics of vinblastine after a 96-hour continuous infusion in wild-type and mice lacking mdr1a P-glycoprotein. J. Pharmacol. And Exp. Therap. 289:329-333 (1999).
R. B. Kim, M. F. Fromm, C. Wandel, B. Leake, A. J. J. Wood, D. M. Roden and G. R. Wilkinson. The drug transporter P-glycoprotein limits oral absorption and brain entry of of HIV-1 protease inhbitors. J. Clin. Invest. 101:289-294 (1998).
A. H. Schinkel, E. Wagenaar, C. A. Mol, and L. van Deemter. P-glycoprotein in the blood-brain barrier of mice influences the brain penetration and pharmacological activity of many drugs. J. Clin. Invest. 97:2517-2524 (1996).
D. Nakai, R. Nakagomi, Y. Furuta, T. Tokui, T. Abe, T. Ikeda, and K. Nishimura. Human liver specific anion transporter, LST-1, mediates uptake of pravastatin by human hepatocytes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap. 297:861-867 (2001).
K. Nezasa, K. Higaki, M. Takeuchi, M. Nakano, and M. Koike. Uptake of rosuvastatin by isolated rat hepatocytes: comparison with pravastatin. Xenobiotica 33:379-388 (2003).
Y. Shitara, T. Itoh, H. Sato, A. P. Li, and Y. Sugiyama. Inhibition of transporter-mediated hepatic uptake as a mechanism for drug-drug interaction between cerivastatin and cyclosporin A. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 304:610-616 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hochman, J.H., Pudvah, N., Qiu, J. et al. Interactions of Human P-glycoprotein with Simvastatin, Simvastatin Acid, and Atorvastatin. Pharm Res 21, 1686–1691 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHAM.0000041466.84653.8c
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHAM.0000041466.84653.8c