Abstract
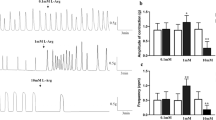
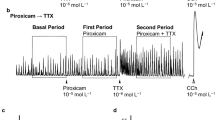
The aim of our study was to further investigatethe pathophysiological mechanism underlying idiopathicchronic constipation (ICC), a disorder of colonicmotility. A possible alteration of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission and also the roleof inhibitory neurotransmitters such as nitric oxide(NO), 5′-adenosine triphosphate (ATP), andvasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) has been evaluatedon preparations of distal colon from patients with or withoutICC. The isometric tension was recorded from isolatedcircular muscle strips of both experimental groupsduring pharmacological and electrical field stimulation (EFS). The contractile response obtained byacetylcholine (ACh 20 μM), EFS (20 Hz, 20 V, 1 msec,pulse trains lasting 1 min) and substance P (SP 1 μM)was significantly lower in ICC than in controlpreparations. The effect of inhibitory nonadrenergic,noncholinergic innervation was evaluated using EFS atlow frequencies (0.5-8 Hz), after cholinergic andsympathetic blockade with atropine (3 μM) andguanethidine (3 μM). The maximum relaxation valueexpressed as percentage of inhibition of SP-inducedcontraction was significantly higher in ICC than incontrol preparations (87 ± 2.4 and 67 ±6.3, respectively; P < 0.05). Experiments with substances thatantagonize or reduce the effect of putative inhibitorymediators (VIP 6-28, apamin andNG-nitro-L-arginine) suggest that analteration in NO and ATP release is present in ICC preparations. In particularat a higher inhibitory frequency NO-mediated relaxationis enhanced in ICC vs control, supporting the hypothesisthat excessive NO production may be involved in pathophysiological mechanism ofconstipation.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
McKirdy HC: Novel autonomic neurotransmitters and upper gastrointestinal function. Pharmacol Ther 38: 429-452, 1988
Boeckxstaens GE, Pelckmans PA, Herman AG, Van Maercke YM: Involvement of nitric oxide in inhibitory innervation of the human isolated colon. Gastroenterology 104: 690-697, 1993
Ke ef KD, Du C, Ward SM, McGregor B, Sanders KM: Enteric inhibitory neural regulation of human colonic circular muscle: role of nitric oxide. Gastroente rology 105: 1009-1016, 1993
Bassotti G, Chiarioni G, Vantini I: Anore ctal manometric abnormalities and colonic propulsive impairment in patients with seve re chronic idiopathic constipation. Dig Dis Sci 39:1558-1564, 1994
Burleigh DE: Evidence for a functional cholinergic deficit in human colonic tissue re se cted for constipation. J Pharm Pharmacol 40:55–57, 1988
Bassotti G, Chiarioni G, Imbimbo BP, Betti C, Bonfante F, Vantini I, Morelli A, Whitehead WE: Impaired colonic motor response to cholinergic stimulation in patients with seve re chronic idiopathic (slow transit type ) constipation. Dig Dis Sci 38:1040-1045, 1993
Slater BJ, Varma JS, Gillespie JI: Abnormalitie s in the contractile properties of colonic smooth muscle in idiopathic slow transit constipation. Br J Surg 84:181–184, 1997
Vanderwinden JM, Mailleux P, Schiffmann SN, Vande rhae-ghen JJ, De Lae t MH: Nitric oxide synthase activity in infantile hype rtrophic pyloric stenosis. N Engl J Med 327: 511–515, 1992
Mearin F, Mourelle M, Guarner F, Salas A, Moncada S, Malagelada JR: Absence of nitric oxide synthase in the gastroesophage al junction of patients with achalasia. Gastroente rology 104: A550, 1993
Vanderwinden JM, De Lae t MH, Schiffmann SN, Mailleux P, Lowenste in CJ, Snyder SH, Vanderhaeghen JJ: Nitric oxide synthase distribution in the enteric nervous system of Hirschsprung' s disease. Gastroenterology 105: 969-973, 1993
Park HJ, Kamm MA, Abbasi AM, Talbot IC: Immunohistochemical study of the colonic muscle and innervation in idiopathic chronic constipation. Dis Colon Rectum 38: 509-513, 1995
Cortesini C, Cianchi F, Infantino A, Lise M: Nitric oxide synthase and VIP distribution in enteric nervous system in idiopathic chronic constipation. Dig Dis Sci 40: 2450-2455, 1995
Milner P, Crowe R, Kamm MA, Lennard-Jones JE, Burnstock G: Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide leve ls in sigmoid colon in idiopathic constipation and dive rticular disease. Gastroente rology 99: 666-675, 1990
Koch TR, Carney JA, Go L, Go VLW: Idiopathic chronic constipation is associated with decre ased colonic vasoactive intestinal peptide. Gastroenterology 94: 300-310, 1988
Schouten WR, ten Kate FJW, de Graaf EJR, Gilberts ECAM, Simons JL, Klück P: Visceral neuropathy in slow-transit constipation: An immunohistochemical investigation with monoclonal antibodies against neurofilament. Dis Colon Re ctum 36: 1112–1117, 1993
Hoyle CH, Kamm MA, Lennard-Jones JE, Burnstock G: An in vitroele ctrophysiological study of the colon from patients with idiopathic chronic constipation. Clin Auton Re s 2(5): 327–333, 1992
Chaussade S, Roche H, Khyari A, Couturier D, Guerre J: Mésure du temps de transit colique: De scription and validation d'une nouvelle technique. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 10: 385–389, 1986
Altomare DF, Rinaldi M, Martinelli E, Mitolo CI: Grading the seve rity of chronic idiopathic constipation. Tech Coloproctol 4: 27–28, 1996
Krishnamurthy S, Schuffler MD, Rohrmann CA, Pope CE: Severe idiopathic constipation is associated with a distinctive abnormality of the colonic mye nteric plexus. Gastroenterology 88: 26-34, 1985
Costa M, Furne ss JB, Llewllyn-Smith D, Cuello AC: Projections of substance-P containing neurons within the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience 6: 411, 1981
Wood JD: Physiology of the enteric nervous system. InPhysiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. LR Johnson (ed). New York, Rave n Press, 1994, p 490
Abrahamsson H: Non-adrenergic non-choline rgic nervous control of gastrointestinal motility patterns. Arch Int Pharmacodyn The r 280: 50-61, 1986
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitolo-Chieppa, D., Mansi, G., Rinaldi, R. et al. Cholinergic Stimulation and Nonadrenergic, Noncholinergic Relaxation of Human Colonic Circular Muscle in Idiopathic Chronic Constipation. Dig Dis Sci 43, 2719–2726 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026615730533
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026615730533