Abstract
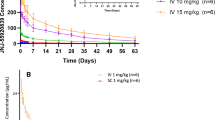
The pharmacokinetics of and biologic response modification by recombinant human interferon-βser (rIFN-βser) were evaluated in 12 healthy male volunteers. Subjects received a single intravenous (iv) injection of 90 × 106 IU of rIFN-βser followed by a single or eight consecutive daily 90 × 106 IU subcutaneous (sc) doses. Blood samples collected after the iv, first sc, and last sc doses and prior to each sc dose were assayed for interferon antiviral activity and the inter-feron-inducible marker neopterin. Following iv administration, serum interferon concentrations generally declined biexponentially, with a mean serum clearance of 0.76 ± 0.28 L/hr-kg, a mean steady-state volume of distribution of 2.88 ± 1.81 L/kg, and a mean terminal half-life of 4.29 ± 2.29 hr as determined by noncompartmental analysis. Following sc administration, absorption of rIFN-βser was prolonged, with serum concentrations generally below 100 IU/mL. No accumulation of rIFN-βser in serum was noted after eight daily sc injections. In contrast, serum neopterin levels did not increase above baseline levels until 12 hr after iv dosing and 24 hr after sc dosing. The mean increase in serum neopterin at 24 hr post iv injection was significantly greater than that at 24 hr post sc dosing.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. V. Mark, S. D. Lu, A. Creasey, R. Yamamoto, and L. Lin. Site-specific mutagenesis of the human fibroblast interferon gene: A structure-function analysis of the protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:5662–5666 (1984).
D. Mark, R. Drummond, A. Creasey, L. Lin, B. Khosrovi, B. Edwards, D. Groveman, J. Joseph, M. Hawkins, and E. Borden. A synthetic mutant interferon beta for clinical trial. In T. Kishida (ed.), Proceedings of the International Symposium on Interferons, Kyoto, Japan, 1983, pp. 167–172.
P. Triozzi and J. Rinehart. The role of interferon-beta in cancer therapy. Cancer Surv. 8:799–808 (1989).
B. Y. Rubin and S. L. Gupta. Differential efficacies of human type I and type II interferons as antiviral and antiproliferative agents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:5928–5932 (1980).
E. C. Borden, I. B. Rosenzweig, and G. I. Byrne. Interferons: From virus inhibitor to modulator of amino acid and lipid metabolism. J. Interferon Res. 7:591–596 (1987).
G. Sarna, M. Pertcheck, R. Figlin, and B. Ardalan. Phase I study of recombinant β ser 17 interferon in the treatment of cancer. Cancer Treat. Rep. 70:1365–1372 (1986).
V. Ratanatharathorn, C. Karanes, M. Al-Sarraf, J. Kish, J. Ensley, R. Pazdur, S. Martino, J. Young, P. Rish, M. Konrad, and P. Galioky. Phase I trial of serine substituted recombinant DNA beta interferon (β-IFN). Proc. AACR 26:274 (1985).
J. Rinehart, L. Malspeis, D. Young, and J. Neidhart. Phase I/II trial of human recombinant β-interferon serine in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 46:5364–5367 (1986).
D. Goldstein, K. M. Sielaff, B. E. Storer, R. R. Brown, S. P. Datta, P. L. Witt, A. P. Teitelbaum, R. V. Smalley, and E. C. Borden. Human biologic response modification by interferon in the absence of measurable serum concentrations: A comparative trial of subcutaneous and intravenous interferon-β serine. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 81:1061–1068 (1989).
E. C. Borden, M. J. Hawkin, K. M. Sielaff, B. M. Storer, J. D. Schiesel, and R. V. Smalley. Clinical and biological effects of recombinant β-interferon administered intravenously daily in phase I trial. J. Interferon Res. 8:357–366 (1988).
G. Schoeden, J. Troppmair, A. Fontana, C. Huber, H. C. Curtius, and A. Niederwieser. Biosynthesis and metabolism of pterins in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and leukemia lines of man and mouse. Eur. J. Biochem. 166:303–310 (1987).
G. Bitterlich, G. Szabo, E. R. Werner, C. Larcher, D. Fuchs, A. Hausen, G. Reibnegger, T. F. Schulz, J. Troppmair, H. Wachter, and M. P. Dierich. Selective induction of mononuclear phagocytes to produce neopterin by interferons. Immunobiology 176:228–235 (1988).
C. Huber, J. R. Batchelor, D. Fuchs, A. Hausen, A. Lang, D. Niederwieser, G. Reibnegger, P. Swetly, J. Troppmair, and H. Wachter. Immune response-associated production of neopterin: Release from macrophages primarily under control of interferon-gamma. J. Exp. Med. 160:310–316 (1984).
J. Troppmair, K. Nachbaur, M. Herold, W. Aulitsky, H. Tilg, G. Gastl, P. Bieling, B. Kotlan, R. Flener, B. Mull, W. O. Aulitsky, H. Rokos, and C. Huber. In vitro and in vivo studies on the induction of neopterin biosynthesis by cytokines, alloantigens and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Clin. Exp. Immunol. 74:392–397 (1988).
P. Kern and M. Dietrich. Increase in serum neopterin levels in patients receiving recombinant interleukin-2 and recombinant interferon αA. In H. Wachter, H. C. Curtius, and W. Pfleiderer (eds.), Biochemical and Clinical Aspects of Pteridines, de-Gruyter, Berlin-New York, 1985, pp. 335–340.
W. Aulitsky, G. Gastl, W. E. Aulitsky, K. Nachbaur, B. Lanske, G. Kemmler, R. Flener, J. Frick, and C. Huber. Interferon γ for the treatment of metastatic renal cancer: Dose dependent stimulation and downregulation of beta-2-microglobulin and neopterin responses. Immunobiology 176:85–95 (1987).
W. E. Aulitsky, H. Tilg, M. Herold, M. Berger, W. Vogel, G. Judmaier, G. Gastl, B. Mull, R. Flener, J. Wiegele, E. Pichler, H. Denz, E. Boheim, W. K. Aulitsky, and C. Huber. Enhanced serum levels of β-2-microglobulin, neopterin, and interferon γ in patients treated with recombinant tumor necrosis factor α. J. Interferon Res. 8:655–664 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiang, J., Gloff, C.A., Yoshizawa, C.N. et al. Pharmacokinetics of Recombinant Human Interferon-βser in Healthy Volunteers and Its Effect on Serum Neopterin. Pharm Res 10, 567–572 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018902120023
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018902120023