Abstract
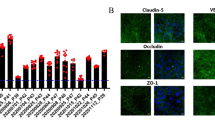
Solute and macromolecular transport studies may elucidate nutritional requirements and drug effects in healthy and diseased peripheral nerves. Endoneurial endothelial cells are specialized microvascular cells that form the restrictive blood-nerve barrier (BNB). Primary human endoneurial endothelial cells (pHEndECs) are difficult to isolate, limiting their widespread availability for biomedical research. We developed a simian virus-40 large T-antigen (SV40-LTA) immortalized human BNB cell line via stable transfection of low passage pHEndECs and observed continuous growth in culture for >45 population doublings. As observed with pHEndECs, the immortalized BNB endothelial cells were Ulex Europaeus agglutinin-1-positive and endocytosed low density lipoprotein, but lost von Willebrand factor expression. Glucose transporter-1, P-glycoprotein (P-gp), γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (γ-GT), large neutral amino acid transporter-1 (LAT-1), creatine transporter (CRT), and monocarboxylate transporter-1 (MCT-1) mRNA expression were retained at all passages with loss of alkaline phosphatase (AP) expression after passages 16–20. Compared with an SV40-LTA immortalized human blood-brain barrier endothelial cell line, there was increased γ-GT protein expression, equivalent expression of organic anion transporting polypeptide-C (OATP-C), organic anion transporter 3 (OAT-3), MCT-1, and LAT-1, and reduced expression of AP, CRT, and P-gp by the BNB cell line at passage 20. Further studies demonstrated lower transendothelial electrical resistance (~181 vs. 191 Ω cm2), equivalent permeability to fluoresceinated sodium (4.84 vs. 4.39 %), and lower permeability to fluoresceinated high molecular weight (70 kDa) dextran (0.39 vs. 0.52 %) by the BNB cell line. This cell line retained essential molecular and biophysical properties suitable for in vitro peripheral nerve permeability studies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aird W (2007a) Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res 100:158–173
Aird W (2007b) Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: II. Representative vascular beds. Circ Res 100:174–190
Allt G, Lawrenson J (2000) The blood-nerve barrier: enzymes, transporters and receptors—a comparison with the blood-brain barrier. Brain Res Bull 52:1–12
Argall K, Armati P, Pollard J (1994) A method for the isolation and culture of rat peripheral nerve vascular endothelial cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 5:413–417
Bell M, Weddell A (1984) A descriptive study of the blood vessels of the sciatic nerve in the rat, man and other mammals. Brain 107:871–898
Burckhardt G, Burckhardt BC (2011) In vitro and in vivo evidence of the importance of organic anion transporters (OATs) in drug therapy. Handb Exp Pharmacol 201:29–104. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-14541-4_2
Courtay C, Oster T, Michelet F, Visvikis A, Diederich M, Wellman M, Siest G (1992) Gamma-glutamyltransferase: nucleotide sequence of the human pancreatic cDNA. Evidence for a ubiquitous gamma-glutamyltransferase polypeptide in human tissues. Biochem Pharmacol 43:2527–2533
Froehner S, Davies A, Baldwin S, Lienhard G (1988) The blood-nerve barrier is rich in glucose transporter. J Neurocytol 17:173–178
Gallo R, Dorschner R, Takashima S, Klagsbrun M, Eriksson E, Bernfield M (1997) Endothelial cell surface alkaline phosphatase activity is induced by IL-6 released during wound repair. J Invest Dermatol 109:597–603
Hawkins R, O’Kane R, Simpson I, Viña J (2006) Structure of the blood-brain barrier and its role in the transport of amino acids. J Nutr 136:218S–226S
He X, Ee PL, Coon JS, Beck WT (2004) Alternative splicing of the multidrug resistance protein 1/ATP binding cassette transporter subfamily gene in ovarian cancer creates functional splice variants and is associated with increased expression of the splicing factors PTB and SRp20. Clin Cancer Res 10:4652–4660. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0439
Hsiang B, Zhu Y, Wang Z, Wu Y, Sasseville V, Yang WP, Kirchgessner TG (1999) A novel human hepatic organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP2). Identification of a liver-specific human organic anion transporting polypeptide and identification of rat and human hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor transporters. J Biol Chem 274:37161–37168
Kanda T, Iwasaki T, Yamawaki M, Ikeda K (1997) Isolation and culture of bovine endothelial cells of endoneurial origin. J Neurosci Res 49:769–777
Konig J, Cui Y, Nies AT, Keppler D (2000) A novel human organic anion transporting polypeptide localized to the basolateral hepatocyte membrane. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 278:G156–G164
Latker C, Shinowara N, Miller J, Rapoport S (1987) Differential localization of alkaline phosphatase in barrier tissues of the frog and rat nervous systems: a cytochemical and biochemical study. J Comp Neurol 264:291–302
Malmgren L, Olsson Y (1980) Differences between the peripheral and the central nervous system in permeability to sodium fluorescein. J Comp Neurol 191:103–107. doi:10.1002/cne.901910106
Man S, Ubogu E, Williams K, Tucky B, Callahan M, Ransohoff R (2008) Human brain microvascular endothelial cells and umbilical vein endothelial cells differentially facilitate leukocyte recruitment and utilize chemokines for T cell migration. Clin Dev Immunol 2008:384982
Mizisin AP, Weerasuriya A (2011) Homeostatic regulation of the endoneurial microenvironment during development, aging and in response to trauma, disease and toxic insult. Acta Neuropathol 121:291–312. doi:10.1007/s00401-010-0783-x
Murphy H, Bakopoulos N, Dame M, Varani J, Ward P (1998) Heterogeneity of vascular endothelial cells: differences in susceptibility to neutrophil-mediated injury. Microvasc Res 56:203–211. doi:10.1006/mvre.1998.2110
Ohtsuki S, Tachikawa M, Takanaga H, Shimizu H, Watanabe M, Hosoya K, Terasaki T (2002) The blood-brain barrier creatine transporter is a major pathway for supplying creatine to the brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:1327–1335
Olsson Y (1990) Microenvironment of the peripheral nervous system under normal and pathological conditions. Crit Rev Neurobiol 5:265–311
Orte C, Lawrenson J, Finn T, Reid A, Allt G (1999) A comparison of blood-brain barrier and blood-nerve barrier endothelial cell markers. Anat Embryol (Berl) 199:509–517
Poduslo J, Curran G, Berg C (1994) Macromolecular permeability across the blood-nerve and blood-brain barriers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5705–5709
Reina M, López A, Villanueva M, de Andrés J, León G (2000) Morphology of peripheral nerves, their sheaths, and their vascularization. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim 47:464–475
Reina M, López A, Villanueva M, De Andrés J, Machés F (2003) The blood-nerve barrier in peripheral nerves. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim 50:80–86
Rondaij M, Bierings R, Kragt A, van Mourik J, Voorberg J (2006) Dynamics and plasticity of Weibel-Palade bodies in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:1002–1007
Saito T, Zhang Z, Ohtsubo T, Noda I, Shibamori Y, Yamamoto T, Saito H (2001) Homozygous disruption of the mdrla P-glycoprotein gene affects blood-nerve barrier function in mice administered with neurotoxic drugs. Acta Otolaryngol 121:735–742
Sano Y, Shimizu F, Nakayama H, Abe M, Maeda T, Ohtsuki S, Terasaki T, Obinata M, Ueda M, Takahashi R, Kanda T (2007) Endothelial cells constituting blood-nerve barrier have highly specialized characteristics as barrier-forming cells. Cell Struct Funct 32:139–147
Schwartz B, Vicart P, Delouis C, Paulin D (1991) Mammalian cell lines can be efficiently established in vitro upon expression of the SV40 large T antigen driven by a promoter sequence derived from the human vimentin gene. Biol Cell 73:7–14
Sharom FJ (2011) The P-glycoprotein multidrug transporter. Essays Biochem 50:161–178. doi:10.1042/bse0500161
Shimizu F, Sano Y, Abe MA, Maeda T, Ohtsuki S, Terasaki T, Kanda T (2011) Peripheral nerve pericytes modify the blood-nerve barrier function and tight junctional molecules through the secretion of various soluble factors. J Cell Physiol 226:255–266. doi:10.1002/jcp.22337
Stins M, Badger J, Sik Kim K (2001) Bacterial invasion and transcytosis in transfected human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Microb Pathog 30:19–28
Takahashi K, Sawasaki Y, Hata J, Mukai K, Goto T (1990) Spontaneous transformation and immortalization of human endothelial cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 26:265–274
van Leeuwen EB, Veenstra R, van Wijk R, Molema G, Hoekstra A, Ruiters MH, van der Meer J (2000) Characterization of immortalized human umbilical and iliac vein endothelial cell lines after transfection with SV40 large T-antigen. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 11:15–25
van Mourik J, Romani de Wit T, Voorberg J (2002) Biogenesis and exocytosis of Weibel-Palade bodies. Histochem Cell Biol 117:113–122
VanWert AL, Gionfriddo MR, Sweet DH (2010) Organic anion transporters: discovery, pharmacology, regulation and roles in pathophysiology. Biopharm Drug Dispos 31:1–71. doi:10.1002/bdd.693
Véga C, Poitry-Yamate C, Jirounek P, Tsacopoulos M, Coles J (1998) Lactate is released and taken up by isolated rabbit vagus nerve during aerobic metabolism. J Neurochem 71:330–337
Yano K, Gale D, Massberg S, Cheruvu P, Monahan-Earley R, Morgan E, Haig D, von Andrian U, Dvorak A, Aird W (2007) Phenotypic heterogeneity is an evolutionarily conserved feature of the endothelium. Blood 109:613–615
Yosef N, Xia R, Ubogu E (2010) Development and characterization of a novel human in vitro blood-nerve barrier model using primary endoneurial endothelial cells. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69:82–97
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Dr. Monique Stins for providing THBMECs. This work was supported by a Baylor College of Medicine New Investigator Start-Up Award (2007–2011). The Neuromuscular Immunopathology Research Laboratory is currently supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants R21 NS073702, R21 NS078226, and R01 NS075212. The content is solely the responsibility of the author and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH. The funding sources had no involvement in the conduct of the research, manuscript preparation, data collection/analyses, or the decision to submit this work for publication.
Conflict of interest
There are no financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yosef, N., Ubogu, E.E. An Immortalized Human Blood-Nerve Barrier Endothelial Cell Line for In Vitro Permeability Studies. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33, 175–186 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-012-9882-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-012-9882-7