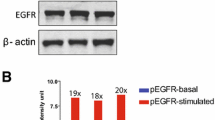
Abstract
Purpose
Mevalonate metabolites are vital for a variety of key cellular functions with the biosynthetic products including cholesterol and farnesyl and geranylgeranyl isoprenoids. Inhibition of this pathway using lovastatin induces a potent apoptotic response in a specific subset of human tumor-derived cell lines, including head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC). In this study, we evaluated the potential of a number of chemotherapeutics that demonstrate activity in HNSCC, including an inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) to potentiate the cytotoxic effects of lovastatin.
Methods
We evaluated the cytotoxic effects of combining a variety of chemotherapeutics with lovastatin using the MTT assay and flow cytometry. The MCF-7 lovastatin-resistant breast adenocarcinoma cell line and the lovastatin-sensitive HNSCC cell lines SCC9 and SCC25 were tested. Expression levels of EGFR and ligand activated EGFR following lovastatin treatment were analyzed by Western blotting.
Results
Pretreatment or concomitant treatment of 10 μM lovastatin did not significantly augment the effects of a variety of chemotherapeutic agents tested in these cell lines. Co-administration with actinomycin D or cycloheximide, drugs that inhibit RNA and protein synthesis, respectively, inhibited lovastatin-induced apoptosis in these cell lines. This suggests a requirement for the cellular functions disrupted by these chemotherapeutic agents in lovastatin-induced apoptosis of HNSCC cells. In contrast to the chemotherapeutics analyzed, the AG1478 tyrosine kinase inhibitor of the EGFR demonstrated additive cytotoxic effects in combination with lovastatin in HNSCC cells. Mevalonate metabolites may regulate EGFR function, suggesting that lovastatin may inhibit the activity of this receptor. Indeed, lovastatin treatment inhibited EGF-induced autophosphorylation of the EGFR in the SCC9 and SCC25 cell lines. Pretreatment of SCC9 and SCC25 cell lines for 24 h with 10 μM lovastatin, conditions that demonstrated significant inhibition of EGF-induced EGFR autophosphorylation, induced significant additive effects in combination with AG1478.
Conclusion
These results demonstrated the ability of EGFR pathway inhibitors to potentiate lovastatin-induced apoptosis and suggested that lovastatin may target the EGFR pathway in HNSCC cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HNSCC:
-
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- EGFR:
-
epidermal growth factor receptor
- 5-FU:
-
5-fluorouracil
- HMG-CoA:
-
3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A
- ActD:
-
actinomycin D
- CHX:
-
cycloheximide
References
Agarwal B, Bhendwal S, Halmos B, Moss SF, Ramey WG, Holt PR (1999) Lovastatin augments apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic agents in colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 5:2223–2229
Arteaga CL, Johnson DH (2001) Tyrosine kinase inhibitors-ZD1839 (Iressa). Curr Opin Oncol 13:491–498
Atula T, Silvoniemi P, Kurki T, Varpula M, Grenman R (1997) The evaluation and treatment of the neck in carcinoma of the oral cavity. Acta Otolaryngol [Suppl 5] 29:223–225
Bishayee S (2000) Role of conformational alteration in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) function. Biochem Pharmacol 60:1217–1223
Bishayee A, Beguinot L, Bishayee S (1999) Phosphorylation of tyrosine 992, 1068 and 1086 is required for conformational change of the human epidermal growth factor receptor c-terminal tail. Mol Biol Cell 10:525–536
Boring C, Squire TS, Tong T (1992) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 42:19–38
Boring CC, Squire TS, Tong T, Montgomery S (1994) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 44:7–26
Cohen SM, Lippard SJ (2001) Cisplatin: from DNA damage to cancer chemotherapy. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 67:93–130
Corsini A, Maggi FM, Catapano AL (1995) Pharmacology of competitive inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase. Pharmacol Res 31:9–27
Darzynkiewicz Z, Bruno S, Del Bino G, Gorczyca W, Hotz MA, Lassota P, Traganos F (1992) Features of apoptotic cells measured by flow cytometry. Cytometry 13:795–808
Dimitroulakos J, Yeger H (1996) HMG-CoA reductase mediates the biological effects of retinoic acid on human neuroblastoma cells: lovastatin specifically targets P-glycoprotein-expressing cells. Nat Med 2:326–333
Dimitroulakos J, Nohynek D, Backway KL, Hedley DW, Yeger H, Freedman MH, Minden MD, Penn LZ (1999) Increased sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemias to lovastatin-induced apoptosis: a potential therapeutic approach. Blood 93:1308–1318
Dimitroulakos J, Ye LY, Benzaquen M, Moore MJ, Kamel-Reid S, Freedman MH, Yeger H, Penn LZ (2001) Differential sensitivity of various pediatric cancers and squamous cell carcinomas to lovastatin-induced apoptosis: therapeutic implications. Clin Cancer Res 7:158–167
Dimitroulakos J, Marhin WH, Tokunaga J, Irish J, Gullane P, Penn LZ, Kamel-Reid S (2002) Microarray and biochemical analysis of lovastatin-induced apoptosis of squamous cell carcinomas. Neoplasia 4:337–346
Dumontet C, Sikic BI (1999) Mechanisms of, action of and resistance to antitubulin agents: microtubule dynamics, drug transport, and cell death. J Clin Oncol 17:1061–1070
Feleszko W, Jakobisiak M (2000) Lovastatin augments apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic agents in colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 6:1198–1199
Feleszko W, Mlynarczuk I, Balkowiec-Iskra EZ, Czajka A, Switaj T, Stoklosa T, Giermasz A, Jakobisiak M (2000) Lovastatin potentiates antitumor activity and attenuates cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin in three tumor models in mice. Clin Cancer Res 6:2044–2052
Feleszko W, Mlynarczuk I, Olszewska D, Jalili A, Grzela T, Lasek W, Hoser G, Korczak-Kowalska G, Jakobisiak M (2002) Lovastatin potentiates antitumor activity of doxorubicin in murine melanoma via an apoptosis-dependent mechanism. Int J Cancer 100:111–118
Fisher DE (1994) Apoptosis in cancer therapy: crossing the threshold. Cell 78:539–542
Forastiere AA, Shank D, Neuberg D, Taylor SGt, DeConti RC, Adams G (1998) Final report of a phase II evaluation of paclitaxel in patients with advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group trial (PA390). Cancer 82:2270–2274
Gibbs JB, Oliff A, Kohl NE (1994) Farnesyltransferase inhibitors: Ras research yields a potential cancer therapeutic. Cell 77:175–178
Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1990) Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature 343:425–430
Grem JL (2000) 5-Fluorouracil: forty-plus and still ticking. A review of its preclinical and clinical development. Invest New Drugs 18:299–313
Gschwind A, Zwick E, Prenzel N, Leserer M, Ullrich A (2001) Cell communication networks: epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation as the paradigm for interreceptor signal transmission. Oncogene 20:1594–1600
Herbst RS (2002) ZD1839: targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 11:837–849
Hoffmann T, Hafner D, Ballo H, Haas I, Bier H (1997) Antitumor activity of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies and cisplatin in ten human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma lines. Anticancer Res 17:4419–4425
Hunninghake DB (1992) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Curr Opin Lipidol 3:22–28
Kawata S, Yamasaki E, Nagase T, Inui Y, Ito N, Matsuda Y, Inada M, Tamura S, Noda S, Imai Y, Matsuzawa Y (2001) Effect of pravastatin on survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. A randomized controlled trial. Br J Cancer 84:886–891.
Kelland LR, McKeage MJ (1994) New platinum agents. A comparison in ovarian cancer. Drugs Aging 5:85–95
Keyomarsi K, Sandoval L, Band V, Pardee AB (1991) Synchronization of tumor and normal cells from G1 to multiple cell cycles by lovastatin. Cancer Res 51:3602–3609
Kim SY, Han IS, Yu HK, Lee HR, Chung JW, Choi JH, Kim SH, Byun Y, Carey TE, Lee KS (1998) The induction of P450-mediated oxidation of all-trans retinoic acid by retinoids in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Metabolism 47:955–958
Koutsoukos AD, Rubinstein LV, Faraggi D, Simon RM, Kalyandrug S, Weinstein JN, Kohn KW, Paull KD (1994) Discrimination techniques applied to the NCI in vitro anti-tumour drug screen: predicting biochemical mechanism of action. Stat Med 13:719–730
Lamont EB, Vokes EE (2001) Chemotherapy in the management of squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Lancet Oncol 2:261–269
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J (2000) The EGF receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene 19:6550–6565
Monks A, Scudiero DA, Johnson GS, Paull KD, Sausville EA (1997) The NCI anti-cancer drug screen: a smart screen to identify effectors of novel targets. Anticancer Drug Des 12:533–541
Partik G, Hochegger K, Schorkhuber M, Marian B (1999) Inhibition of epidermal-growth-factor-receptor-dependent signalling by tyrphostins A25 and AG1478 blocks growth and induces apoptosis in colorectal tumor cells in vitro. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 125:379–388
Penn LZ (2001) Apoptosis modulators as cancer therapeutics. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2:684–692
Piacentini M, Fesus L, Melino G (1993) Multiple cell cycle access to the apoptotic death programme in human neuroblastoma cells. FEBS Letts 320:150–154
Pinto HA, Jacobs C (1991) Chemotherapy for recurrent and metastatic head and neck cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 5:667–686
Pruitt K, Der CJ (2001) Ras and Rho regulation of the cell cycle and oncogenesis. Cancer Lett 171:1–10
Raymond E, Chaney SG, Taamma A, Cvitkovic E (1998) Oxaliplatin: a review of preclinical and clinical studies. Ann Oncol 9:1053–1071
Seabra MC, Mules EH, Hume AN (2002) Rab GTPases, intracellular traffic and disease. Trends Mol Med 8:23–30
Slieker LJ, Martensen TM, Lane MD (1988) Biosynthesis of the epidermal growth factor receptor: post-translational glycosylation-independent acquisition of tyrosine kinase autophosphorylation activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 153:96–103
Takai Y, Sasaki T, Matozaki T (2001) Small GTP-binding proteins. Physiol Rev 81:153–208.
Thibault A, Samid D, Tompkins AC, Figg WD, Cooper MR, Hohl RJ, Trepel J, Liang B, Patronas N, Venzon DJ, Reed E, Myers CE (1996) Phase 1 study of lovastatin, an inhibitor of the mevalonate pathway, in patients with cancer. Clinical Cancer Res 2:483–491
Trimmer EE, Essigmann JM (1999) Cisplatin. Essays Biochem 34:191–211
van Gog FB, Brakenhoff RH, Stigter-van Walsum M, Snow GB, van Dongen GA (1998) Perspectives of combined radioimmunotherapy and anti-EGFR antibody therapy for the treatment of residual head and neck cancer. Int J Cancer 77:13–18
Vokes EE, Weichselbaum RR, Lippman SM, Hong WK (1993) Head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 328:184–194
Wittes RE, Cvitkovic E, Shah J, Gerold FP, Strong EW (1977) CIS-Dichlorodiammineplatinum(II) in the treatment of epidermoid carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer Treat Rep 61:359–366
Zhu XF, Liu ZC, Xie BF, Li ZM, Feng GK, Yang D, Zeng YX (2001) EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG1478 inhibits cell proliferation and arrests cell cycle in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 169:27–32
Acknowledgements
Support from Cancer Care Ontario (JD) and the Ottawa Regional Cancer Centre Foundation (JD) is greatly appreciated. We wish to thank Sean Hopkins and Dr. Samy El-Sayed for helpful discussions and critically reviewing this manuscript. We wish to thank Apotex and the Ottawa Regional Cancer Centre Pharmacy for generously providing reagents used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mantha, A.J., McFee, K.E., Niknejad, N. et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy potentiates lovastatin-induced apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 129, 631–641 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-003-0490-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-003-0490-2