Abstract
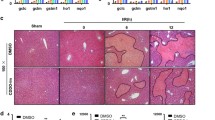
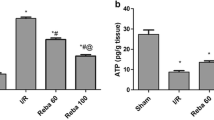
Liver injury is known to often progress even after the hepatotoxicant is dissipated. The hydrolytic enzyme calpain, which is released from dying hepatocytes, destroys the surrounding cells and results in progression of injury. Therefore, control of calpain activation may be a suitable therapeutic intervention in cases of fulminant hepatic failure. This study evaluated the effects of a potent cell-permeable calpain inhibitor, MDL28170, and its mechanisms of action on thioacetamide (TAA)-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. We found that MDL28170 significantly decreased mortality and change in serum transaminase after TAA administration. The necroinflammatory response in the liver was also suppressed. Furthermore, a significant suppression of hepatocyte apoptosis could be found by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick-end labeling assay. The upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), both of which are known to mediate the propagation of inflammation, was abolished. MDL2810 also effectively blocked hepatic stellate cell activation, which is assumed to be the early step in liver fibrosis. These results demonstrated that MDL28170 attenuated TAA-induced acute liver failure by inhibiting hepatocyte apoptosis, abrogating iNOS and TNF-α mRNA upregulation and blocking hepatic stellate cell activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khalidi JA, Czaja AJ. Current concepts in the diagnosis, pathogenesis, and treatment of autoimmune hepatitis. Mayo Clin Proc 76:1237–1252;2001.
Aragon B, Poussard S, Dulong S, Touyarot K, Dargelos E, Brustis JJ, Levieux D, Ducastaing A, Cottin P. Protein kinase C alpha is a calpain target in cultured embryonic muscle cells. Mol Cell Biochem 231:97–106;2002.
Azam M, Andrabi SS, Sahr KE, Kamath L, Kuliopulos A, Chishti AH. Disruption of the mouse mu-calpain gene reveals an essential role in platelet function. Mol Cell Biol 21:2213–2220;2001.
Bedda S, Laurent A, Conti F, Chereau C, Tran A, Tran-Van Nhieu J, Jaffray P, Soubrane O, Goulvestre C, Calmus Y, Weill B, Batteux F. Mangafodipir prevents liver injury induced by acetaminophen in the mouse. J Hepatol 39:765–772;2003.
Bruck R, Aeed H, Shirin H, Matas Z, Zaidel L, Avni Y, Halpern Z. The hydroxyl radical scavengers dimethylsulfoxide and dimethylthiourea protect rats against thioacetamide-induced fulminant hepatic failure. J Hepatol 31:27–38;1999.
Chen ZF, Schottler F, Lee KS. Neuronal recovery after moderate hypoxia is improved by the calpain inhibitor MDL28170. Brain Res 769:188–192;1997.
Cheng J, Imanishi H, Liu W, Iwasaki A, Ueki N, Nakamura H, Hada T. Inhibition of the expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin in human hepatic stellate cell line, L190, by a selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor, NS-398. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 297:1128–1134;2002.
Cuzzocrea S, McDonald MC, Mazzon E, Mota-Filipe H, Centorrino T, Terranova ML, Ciccolo A, Britti D, Caputi AP, Thiemermann C. Calpain inhibitor I reduces colon injury caused by dinitrobenzene sulphonic acid in the rat. Gut 48:478–488;2001.
Cuzzocrea S, McDonald MC, Mazzon E, Siriwardena D, Serraino I, Dugo L, Britti D, Mazzullo G, Caputi AP, Thiemermann C. Calpain inhibitor I reduces the development of acute and chronic inflammation. Am J Pathol 157:2065–2079;2000.
Daniel KG, Anderson JS, Zhong Q, Kazi A, Gupta P, Dou QP. Association of mitochondrial calpain activation with increased expression and autolysis of calpain small subunit in an early stage of apoptosis. Int J Mol Med 12:247–252;2003.
Diez-Fernandez C, Sanz N, Bosca L, Hortelano S, Cascales M. Involvement of nitric oxide synthesis in hepatic perturbations induced in rats by a necrogenic dose of thioacetamide. Br J Pharmacol 121:820–826;1997.
Dogru-Abbasoglu S, Balkan J, Kanbagli O, Cevikbas U, Aykac-Toker G, Uysal M. Amino-guanidine, an inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, plus N-acetylcysteine treatment reduce the lipopolysaccharide-augmented hepatotoxicity in rats with cirrhosis. Hum Exp Toxicol 21:359–364;2002.
Dooley S, Hamzavi J, Breitkopf K, Wiercinska E, Said HM, Lorenzen J, Ten Dijke P, Gressner AM. Smad7 prevents activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis in rats. Gastroenterology 125:178–192;2003.
Gilligan DM, Sarid R, Weese J. Adducin in platelets: Activation-induced phosphorylation by PKC and proteolysis by calpain. Blood 99:2418–2426;2002.
Hayami S, Ikeda K, Sun F, Tanaka K, Kojo S. Increase of caspase-3 activity in rat liver and plasma by thioacetamide. Biochem Pharmacol 58:1941–1943;1999.
Hon WM, Lee KH, Khoo HE. Nitric oxide in liver diseases: Friend, foe, or just passerby? Ann NY Acad Sci 962:275–295;2002.
Kim KH, Bae JH, Cha SW, Han SS, Park KH, Jeong TC. Role of metabolic activation by cytochrome P450 in thioacetamide-induced suppression of antibody response in male BALB/c mice. Toxicol Lett 114:225–235;2000.
Kohli V, Madden JF, Bentley RC, Clavien PA. Calpain mediates ischemic injury of the liver through modulation of apoptosis and necrosis. Gastroenterology 116:168–178;1999.
Laroux FS, Pavlick KP, Hines IN, Kawachi S, Harada H, Bharwani S, Hoffman JM, Grisham MB. Role of nitric oxide in inflammation. Acta Physiol Scand 173:113–118;2001.
Lee WR. Acute liver failure. N Engl J Med 329:1862–1872;1993.
Leifeld L, Fielenbach M, Dumoulin FL, Speidel N, Sauerbruch T, Spengler U. Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression in fulminant hepatic failure. J Hepatol 37:613–619;2002.
Limaye PB, Apte UM, Shankar K, Bucci TJ, Warbritton A, Mehendale HM. Calpain released from dying hepatocytes mediates progression of acute liver injury induced by model hepatotoxicants. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 191:211–226;2003.
Liu X, Schnellmann RG. Calpain mediates progressive plasma membrane permeability and proteolysis of cytoskeleton-associated paxillin, talin, and vinculin during renal cell death. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:63–70;2003.
Lokuta MA, Nuzzi PA, Huttenlocher A. Calpain regulates neutrophil chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4006–4011;2003.
Margeli AP, Skaltsas SD, Spiliopoulou CA, Mykoniatis MG, Theocharis SE. Hepatic stimulator substance activity in the liver of thioacetamide-intoxicated rats. Liver 19:519–525;1999.
Mookerjee RP, Sen S, Davies NA, Hodges SJ, Williams R, Jalan R. Tumour necrosis factor alpha is an important mediator of portal and systemic haemodynamic derangements in alcoholic hepatitis. Gut 52:1182–1187;2003.
Okuyama H, Nakamura H, Shimahara Y, Araya S, Kawada N, Yamaoka Y, Yodoi J. Overexpression of thioredoxin prevents acute hepatitis caused by thioacetamide or lipopolysaccharide in mice. Hepatology 37:1015–1025;2003.
Rahman TM, Hodgson HJ. The effects of early and late administration of inhibitors of inducible nitric oxide synthase in a thioacetamide-induced model of acute hepatic failure in the rat. J Hepatol 38:583–590;2003.
Rami A, Ferger D, Krieglstein J. Blockade of calpain proteolytic activity rescues neurons from glutamate excitotoxicity. Neurosci Res 27:93–97;1997.
Sindram D, Kohli V, Madden JF, Clavien PA. Calpain inhibition prevents sinusoidal endothelial cell apoptosis in the cold ischemic rat liver. Transplantation 68:136–140;1999.
So EC, Wong KL, Huang TC, Tasi SC, Liu CF. Tetramethylpyrazine protects mice against thioacetamide-induced acute hepatotoxicity. J Biomed Sci 9:410–414;2002.
Taniguchi K, Umeshita K, Sakon M, Miyoshi H, Tokunaga M, Ariyoshi H, Yamano T, Kaneda Y, Monden M. Suppression of oxidative stress-induced hepatocyte injury by calpain antisense. J Surg Res 111:23–27;2003.
Waris G, Livolsi A, Imbert V, Peyron JF, Siddiqui A. Hepatitis C virus NS5A and subgenomic replicon activate NF-κB via tyrosine phosphorylation of IκBα and its degradation by calpain protease. J Biol Chem 278:40778–40787;2003.
Yang R, Gallo DJ, Baust JJ, Uchiyama T, Watkins SK, Delude RL, Fink MP. Ethyl pyruvate modulates inflammatory gene expression in mice subjected to hemorrhagic shock. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 283:G212-G221;2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, CH., Chen, YJ., Lee, TH. et al. Protective effect of MDL28170 against thioacetamide-induced acute liver failure in mice. J Biomed Sci 11, 571–578 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02256121
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02256121