Abstract
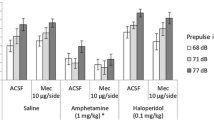
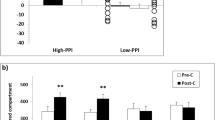
Previous studies have demonstrated that dopamine (DA) agonists disrupt sensorimotor gating as measured by prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle response (ASR) in rats; other reports suggest that this stimulant-induced disruption of PPI may reflect drug-induced increases in ASR amplitude rather than changes in sensorimotor gating. In the current study, 6-hydroxydopamine lesions that depleted dopamine from the nucleus accumbens, olfactory tubercles and anterior striatum reversed the disruption of PPI caused by amphetamine (AMPH), but did not disrupt AMPH potentiation of ASR baseline. These findings strongly suggest that increased mesolimbic DA activity is one substrate of the AMPH-induced disruption of PPI; in contrast, AMPH potentiation of baseline startle amplitude may be independent of mesolimbic DA activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braff D, Stone C, Callaway E, Geyer M, Glick I, Bali L (1978) Prestimulus effects on human startle reflex in normals and schizophrenics. Psychophysiology 15:339–343
Crow T, Cross A, Johnson J, Johnstone E, Owen F, Owens D, Poulter M (1984) Catechol-amines and schizophrenia: an assessment of the evidence. In: Catecholamines: neuropharmacology and central nervous system. Liss, New York, pp 11–20
Davis M (1988) Apomorphine,d-amphetamine, strychnine and yohimbine do not alter prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex. Psychopharmacology 95:151–156
Geyer MA, Mansbach RS (1989) Disruption of prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle in rats by phencyclidine and MK801. Schizophr Res 2:186
Graham F (1975) The more or less startling effects of weak prestimuli. Psychophysiology 12:238–248
Kehne JH, Sorenson CA (1978) The effects of pimozide and phenoxybenzamine pretreatments on amphetamine and apomorphine potentiation of the acoustic startle response in rats. Psychopharmacology 58:137–144
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1988) Dopaminergic stimulation disrupts sensorimotor gating in the rat. Psychopharmacology 94:507–514
Swerdlow NR, Geyer M, Braff D, Koob GF (1986a) Central dopamine hyperactivity in rats mimics abnormal acoustic startle in schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 21:23–33
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA, Vale WW, Koob GF (1986b) Corticocotropin-releasing factor (CRF) potentiates acoustic startle in rats: blockade by chlordiazepoxide. Psychopharmacology 88:147–152
Wong D, Wagner H, Tune L, Dannals R, Pearlson G, Links J, Tamminga C, Broussolle E, Ravert H, Wilson A, Toung J, Malat J, Williams J, O'Tuama L, Snyder S, Kuhar M, Gjedde A (1986) Positron emission tomography reveals elevated D2 dopamine receptors in drug-naive schizophrenics. Science 234:1558–1563
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swerdlow, N.R., Mansbach, R.S., Geyer, M.A. et al. Amphetamine disruption of prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle is reversed by depletion of mesolimbic dopamine. Psychopharmacology 100, 413–416 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244616
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244616