Summary
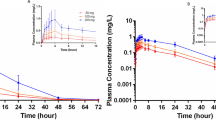
A single oral dose of clonidine 300 µg was administered to 8 healthy, normotensive subjects and the time course of its plasma concentrations was followed for 24 h. The plasma concentration of clonidine rose to a peak of 1.17±0.12 ng/ml at about 2 h: the absorption half-life was 0.6±0.2 h. Elimination followed first order kinetics with a half-life of 7.7±2.0 h. The correlation between the two most common side-effects of clonidine, sedation and dryness of the mouth, with the time course of its plasma concentrations was highly significant, p<0.01. All the subjects complained of severe sedation. During continuous administration of clonidine (75 µg t.i.d.) for one week a steady state serum level of 0.30–0.35 ng/ml was achieved. One 75 µg tablet of clonidine raised the serum level to about 0.69±0.13 ng/ml in two hours. After cessation of dosing, the serum level declined with a half-life of 7.5±1.5 h. The urinary excretion of unchanged clonidine was found to be about onethird of the administered dose in 24 h during continuous administration and in the first 24 h after the single oral dose.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kobinger, W., Walland, A.: Investigations into the mechanism of the hypotensive effect of 2-(2,6-dichlorophenylamino)-2-imidazoline HCl. Europ. J. Pharmacol.2, 155–162 (1967)
Bousquet, P.: Localisation of the central cardiovascular action of the clonidine. Brit. J. Pharmacol.49, 573–579 (1973)
Zaimis, E.: On the pharmacology of Catapress (St. 155). In: Catapress in hypertension (ed. M.E. Conolly), pp 222–226. London: Butterworth 1970
Conolly, M. E., Briant, R. H., George, C. F., Dollery, C. T.: A crossover comparison of clonidine and metyldopa in hypertension. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.4, 222–227 (1972)
Putzeys, M. R., Hoobier, S. W.: Comparison of clonidine and methyldopa on blood pressure and side-effects in hypertensive patients. Amer. Heart J.83, 464–468 (1972)
Rand, M. J., Rush, M., Wilson, S.: Some observations on the inhibition of salivation by ST 155. Europ. J. Pharmacol.5, 168–172 (1969)
Laverty, R., Taylor, K. M.: Behavioural and biochemical effects of 2-(2,6-dichlorophenylamino)-2-imidazoline hydrochloride (ST 155) on the central nervous system. Brit. J. Pharmacol.35, 253–264 (1969)
Dollery, C. T., Davies, D. S., Draffan, G. H., Dargie, H. J., Pean, C. R., Reid, J. L., Clare, R. A., Murray, S.: Clinical pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of clonidine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.19, 11–17 (1976)
Cho, A. K., Curry, S.: The physiological disposition of 2-(2,6-dichlorophenylamino)-2-imidazoline. Biochem. Pharmacol.18, 511–520 (1969)
Rehbinder, D.: The metabolism of clonidine. In: Catapress in hypertension (ed. M. E. Conolly) pp 227–233. London: Butterworth 1970
Draffan, G. H., Clare, R. A., Murray, S., Bellward, G. D., Davies, D. S., Dollery, C. T.: The determination of clonidine in human plasma. Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Mass Spectrometry in Biochemistry and Medicine, Sardinia, Italy, June 1975
Ehrhardt, J. D.: Métabolisme du catapressan. Action hypotensive du 4-hydroxycatapressan. Thérapie27, 947–954 (1972)
Edlund, P-O., Paalzow, L. K.: Pharmakokinetics of clonidine determined by gas liquid chromatography. XV Scandinavian Congress of Physiology, Århus, abstr. 170, p. 116 (1976)
Rehbinder, D., Deckers, W.: Untersuchungen zur Pharmakokinetik und zum Metabolismus des 2-(2,6-Dichlorphenylamino)-2-imidazolin-hydrochlorid (St 155). Arzneim. Forschung19, 169–176 (1969)
Bock, K. D., Heimsoth, V., Merguet, P., Shoenermark, J.: Klinische und Klinische-experimentelle Untersuchungen mit einer neuen blutdrucksenkenden Substanz, Dichlorphenylaminoimidazolin. Dtsch. Med. Wschr.91, 1761–1772 (1966)
Michel, D., Zimmermann, W., Nasschi, A., Seraphim, P.: Erste Beobachtungen über einen antihypertensiven Effet von 2-(2,6-dichlorophenylamino)-2-imidazolin-hydrochloride am Menschen. Dtsch. Med. Wschr.91, 1540–1547 (1966)
NG, D. D., Phelau, E. L., McGregor, D. D., Laverty, R., Taylor, K. M., Sir Smirk, H.: Properties of Catapress, a new hypotensive drug: A preliminary report. New Zealand med. J.66, 864–870 (1967)
Raftos, J., Bauer, G. E., Lewis, R. G. et al.: Clonidine in the treatment of severe hypertension. Med. J. Aust.1, 786–793 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keränen, A., Nykänen, S. & Taskinen, J. Pharmacokinetics and side-effects of clonidine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 13, 97–101 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00609752
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00609752