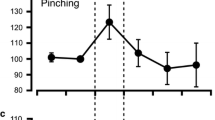
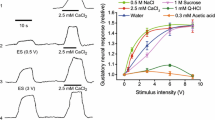
Summary
-
1.
Bradykinin (BKN) and Serotonin (5-HT) are endogeneous substances yielded from injured tissue and evoke pain reactions in man and animals when brought into the skin even in small quantities. In order to test which nervous elements mediate the sensations evoked by these “local hormones” we studied the spike responses of single afferent fibres in cutaneous nerves of the cat's hind leg upon intraarterial administration of small doses (5–30 μg) of 5-HT and BKN.
-
2.
Thick myelinated, thin myelinated, and unmyelinated fibres could be excited by both substances. A further classification of the fibres was done according to the receptor types supplied by them. Among the unmyelinated fibres we tested, al receptor classes were activated by 5-HT and BKN, but among the myelinated fibres only definite groups of receptors proved to be responsive, i.e. the slowly adapting low and high threshold mechanoreceptors with thin myelinated afferents and the slowly adapting mechanoreceptors supplied by thick myelinated fibres.
-
3.
The spike responses started 10–2- sec after injection and persisted up to 4 min in units not firing spontaneously. Discharge frequencies usually were much lower than upon physical stimulation of the receptors.
-
4.
Repeated injection of the same agent at a rate as low as 1:15 min abolished the response to it. However this tachyphylaxis was found not to diminish the effect of the other substance. This might be an indication of an action of BKN and 5-HT on different pharmacological receptors on the nervous membranes.
-
5.
BKN injections were found to enhance the spike discharges of unmyelinated nocipeptive fibres upon noxious radiant heat stimulation for a period of 2–5 min after a single injection of 5–30 μg. It was concluded therefrom that this agent might play a role in the hyperpathia of inflamed skin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck, P. W., Handwerker, H. O., Zimmermann, M.: Nervous outflow from the cat's foot during noxious radiant heat stimulation. Brain Res.67, 373–386 (1974)
Besson, J. M., Conseiller, C., Hamann, K., Maillard, M. C.: Modifications of dorsal horn cell activities in the spinal cord, after intraarterial injection of bradykinin. J. Physiol. (Lond.)221, 189–205 (1972)
Bessou, P., Burgess, P. R., Perl, E. R., Taylor, C. B.: Dynamic properties of mechanoreceptors with unmyelinated (C) fibres. J. Neurophysiol.34, 116–131 (1971)
Bessou, P., Perl, E. R.: Response of cutaneous sensory units with unmyelinated fibres to noxious stimuli. J. Neurophysiol.32, 1025–1043 (1969)
Brown, A. G., Iggo, A.: A quantitative study of cutaneous receptors and afferent fibres in the cat and rabbit. J. Physiol. (Lond.)193, 707–733 (1967)
Burgess, P. R., Perl, E. R.: Myelinated afferent fibres responding specially to noxious stimulation of the skin. J. Physiol. (Lond.)190, 541–562 (1967)
Burgess, P. R., Petit, D., Warren, R. M.: Receptor types in cat hairy skin supplied by myelinated fibres. J. Neurophysiol.31, 833–848 (1968)
Chapman, L. F., Ramos, A. O., Goodell, H., Wolff, H. G.: Neurohumoral features of afferent fibres in man. Their role in vasodilatation, inflammation and pain. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.)4, 617–650 (1961)
Collier, H. O. J.: Introduction to the actions of kinins and prostaglandins.Proc. roy. Soc. Med.64, 1–4 (1971)
Eisen, V.: Modes of formation of human plasma kinins. University of London Thesis submitted for degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Medicine (1961)
Elliot, D. F., Lewis, G. P., Horton, E. W.: The isolation of bradykinin, a plasmakinin, from oxblood. Biochem. J.74, 15–16P (1960)
Erlanger, J., Gasser, H. S.: Electrical signs of nervous activity. Philadelphia: University Press 1937
Fjällbrant, N., Iggo, A.: The effect of histamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine and acetylcholine on cutaneous afferent fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)156, 578–590 (1961)
Fock, S., Franz M., Mense, S.: Discharges in unmyelinated muscle afferents of the cat following intra-arterial application of bradykinin. Pflügers Arch.339, R87 (1973)
Garcia Leme, J., Hamamura, L., Roche e Silva, M.: Effect of anti-proteases and hexadimethrine bromide on the release of a bradykinin-like substance during heating (46° C) of the rat paws. Brit. J. Pharmacol.40, 294–309 (1970)
Hunt, C. C.,McIntyre, A. K.: Properties of cutaneous touch receptors in cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)153, 88–98 (1960)
Iggo, A.: Cutaneous heat and cold receptors with slowly conducting (C) afferent fibres. Quart. J. exp. Physiol.44, 362–370 (1959)
Iggo, A.: Cutaneous mechanoreceptors with afferent C-fibres.J. Physiol. (Lond.)152, 337–353 (1960)
Jänig, W., Schmidt, R. F., Zimmermann, M.: Single unit responses and the total afferent outflow from the cat's footpad upon mechanical stimulation. Exp. Brain Res.6, 100–115 (1968)
Keele, C. A.: Schmerzerzeugende Substanzen. In: Schmerz und Schmerztherapie, D. Gross et al. (Eds.) Stuttgart: Hippokrates 1971
Keele, C. A., Armstrong, D.: Substances producing pain and itch. London: Edward Arnold 1964
Lim, R. K. S., Guzman, F.: Manifestations of pain in analgesic evaluation in animals and man. In: Pain, A. Soulairac et al. (Eds.) London-New York: Academic Press 1968
Lloyd, D. P. C.: Neuron patterns controlling transmission of ipsilateral hind limb reflexes in cat. J. Neurophysiol.6, 293–315 (1943)
Paintal, A. S.: Effects of drugs on vertebrate mechanoreceptors. Pharmacol. Rev.16, 341–380 (1964)
Sicuteri, F.: Vaso-neuroactive substances and their implication in vascular pain. In: Research and clinical studies in headache. Basel: Karger 1967
Taira, N., Nakayama, K., Hashimoto, K.: Vocalisation response of puppies to intraarterial administration of bradykinin and other algesic agents, and mode of action of blocking agents. Tohoku J. exp. Med.96, 365 (1968)
Werle, E.: Über körpereigene schmerzerzeugende Substanzen unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Plasmakinine. In: Schmerz, Grundlagen—Pharmakologie —Therapie, R. Janzen et al. (Eds). Stuttgart: Thieme 1972
Winkelmann, R. K.: Kinins from human skin. In: The skin senses, D. R. Kenshalo (Ed.). Springfield, Ill.: Ch. C. Thomas 1968
Zilliken, F.: “The pain producing substance”. Hageman-Faktor und die Aktivierung von Gerinnungs- und Kininsystemen. In: Schmerz, Grundlagen—Pharmakologie —Therapie, R. Janzen et al. (Eds.). Stuttgart: Thieme 1972
Zotterman, Y.: Studies in the peripheral nervous mechanism of pain. Acta med. scand.80, 185–242 (1933)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beck, P.W., Handwerker, H.O. Bradykinin and serotonin effects on various types of cutaneous nerve fibres. Pflugers Arch. 347, 209–222 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00592598
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00592598