Abstract
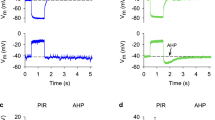
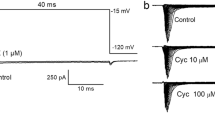
High-voltage-activated (HVA) Ca-channel currents in chick sensory neurons were characterized by dihydropyridine compounds (DHPs) and ω-conotoxin GVIA (ωCTX) using patch-clamp methods. In single-channel recordings, two HVA-currents were identified by their single-channel conductances, 13 pS and 25 pS in 110 mM BaCl2. DHPs selectively affected the large-conductance channel. ωCTX (5 μM), on the other hand, irreversibly eliminated only the small-conductance channel, while the large-conductance channel was either unaffected or only transiently blocked. In whole-cell recordings the macroscopic HVA-current was completely and irreversibly blocked by ωCTX but insensitive to DHPs in 60% of the cells. This current presumably was carried by the 13 pS channel. In the remaining cells, a part of the HVA-current (10%, SD=11%) was either unaffected or transiently blocked by ωCTX and was sensitive to DHPs. This current presumably was carried by the 25 pS channel. Inactivation of both macroscopic current component was incomplete during a 150 ms long depolarization. Our data suggest that the HVA-currents in chick sensory neurons are carried by two distinct Ca-channels that are differentially affected by ωCTX and DHPs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong CM, Matteson DR (1985) Two distinct populations of calcium channels in a clonal line of pituitary cells. Science 227:65–67
Abe T, Saisu H (1987) Identification of the receptor for ω-conotoxin in brain. J Biol Chem 262:9877–9882
Bean BP (1984) Nitrendipine block of cardiac calcium channels: High-affinity binding to the inactivated state. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:6388–6392
Boll W, Lux HD (1985) Action of organic antagonists on neuronal calcium currents. Neurosci Lett 56:335–339
Carbone E, Lux HD (1984) A low-voltage-activated, fully inactivating Ca-channel in vertebrate sensory neurones. Nature 310:501–502
Carbone E, Lux HD (1987) Single low-voltage-activated calcium channels in chick and rat sensory neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 386:571–601
Cruz LJ, Olivera BM (1986) Calcium channel antagonists. J Biol Chem 261:6230–6233
Fox AP, Nowycky MC, Tsien RW (1987a) Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 394:149–172
Fox AP, Nowycky MC, Tsien RW (1987b) Single-channel recordings of three types of calcium channels in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 394:173–200
Fedulova SA, Kostyuk PG, Veselovsky NS (1985) Two types of calcium channels in the somatic membrane of new born rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 359:431–446
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patch. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Kasai H, Aosaki T (1988) Divalent cation dependent inactivation of the high-voltage-activated Ca channel current in chick sensory neurons. Pflügers Arch 411:695–697
Kasai H, Aosaki T (1989) Modulation of Ca-channel current by an adenosine analog mediated by a GTP-binding protein in chick sensory neurons. Pflügers Arch 414:145–149
Kasai H, Aosaki T, Fukuda J (1987) Presynaptic Ca-antagonist ω-conotoxin irreversibly blocks N-type Ca-channels in chick sensory neurons. Neurosci Res 4:228–235
McCleskey EW, Fox AP, Feldman D, Tsien RW (1986) Different types of calcium channels. J Exp Biol 124:177–190
McCleskey EW, Fox AP, Feldman DJ, Cruz LJ, Olivera BM, Tsien RW, Yoshikami D (1987) ω-Conotoxin: Direct and persistent blockade of specific type of calcium channels in neurons but not muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:4327–4331
Nowycky MC, Fox AP, Tsien RW (1985) Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature 316:440–443
Swandulla D, Armstrong CM (1988) Fast-deactivating calcium channels in chick sensory neurons. J Gen Physiol 92:197–218
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aosaki, T., Kasai, H. Characterization of two kinds of high-voltage-activated Ca-channel currents in chick sensory neurons. Pflugers Arch. 414, 150–156 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00580957
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00580957