Abstract
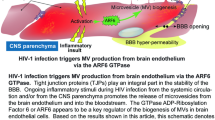
Breakdown of the blood-brain barrier has been shown to contribute to neurological disorders that are prevalent in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected individuals, but the mechanisms involved in HIV-1-associated blood-brain barrier dysfunction remain incompletely understood. Using human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs) that constitute the blood-brain barrier, the authors determined the cytotoxic effects of gp120 on HBMECs. The authors showed that gp120 induced cytotoxicity of HBMECs derived from children, which required cotreatment with interferon (IFN)-γ. IFN-γ treatment exhibited up-regulation of the chemokine receptors CCR3 and CCR5 in children’s HBMECs. In contrast, HBMECs isolated from adults were not responsive to gp120-mediated cytotoxicity. Peptides of gp120 representing binding regions for CD4 and chemokine receptors as well as CD4 antibody inhibited gp120-mediated cytotoxicity of HBMECs. RANTES, as expected, inhibited M-tropic gp120-mediated HBMEC cytotoxicity, whereas stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)-1α failed to inhibit T-tropic gp120-mediated cytotoxicity. Of interest, gp120 peptides representing non-CD4/non-chemokine receptor binding regions inhibited gp120-mediated HBMEC cytotoxicity. In addition, the authors showed that gp120-mediated HBMEC cytotoxicity involved p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Taken together, these findings showed that gp120, in the presence of IFN-γ, can cause dysfunction of the blood-brain barrier endothelium via MAPK pathways involving several gp120-HBMEC interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annunziata P, Cioni C, Santonini R, Paccagnini E (2002). Substance P antagonist blocks leakage and reduces activation of cytokine-stimulated rat brain endothelium. J Neuroimmunol 131: 41–49.
Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Akerstrom V (1997). HIV-1 protein gp120 crosses the blood-brain barrier: role of adsorptive endocytosis. Life Sci 61: 119–125.
Berger EA, Murphy PM, Farber JM (1999). Chemokines receptors as HIV-1 coreceptors: roles in viral entry, tropism and disease. Ann Rev Immunol 17: 657–700.
Cheng-Mayer C, Quiroga M, Tung J, Dina D, Levy JA (1990). Viral determinants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 T-cell or macrophage tropism, cytopathogenicity, and CD4 antigen modulation. J Virol 64: 4390–4398.
Dallasta LM, Pisarov LA, Esplen JE, Werley JV, Moses AV, Nelson JA, Achim CL (1999). Blood-brain barrier tight junction disruption in human immunodeficiency virus-1 encephalitis. Am J Pathol 155: 1915–1927.
Del Corno M, Liu QH, Schols D, Clercq E, Gessani S, Freedman BD, Collman RG (2001). HIV-1 gp120 and chemokine activation of pyk2 and mitogenactivated protein kinases in primary macrophages mediated by calcium-dependent, pertussis toxin-insensitive chemokine receptor signaling. Blood 98: 2909–2916.
Epstein LG, Sharer LR, Cho ES, Myenhofer M, Navia BA, Price RW (1984–1985). HTLV-III/LAV-like retrovirus particles in the brains of patients with AIDS encephalopathy. AIDS Res 1: 447–454.
Helseth E, Kowalski M, Gabuzda D, Olhevsky U, Haseltine W, Sodroski J (1990). Rapid complementation assays measuring replicative potential of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein mutants. J Virol 64: 2416–2420.
Hurwitz AA, Berman JW, Lyman WD (1994). The role of the blood-brain barrier in HIV infection of the central nervous system. Adv Neuroimmunol 4: 249–256.
Kanmogne GD, Primeaux C, Grammas P (2005). HIV-1 gp120 proteins alter tight junction protein expression and brain endothelial cell permeability: implications for the pathogenesis of HIV-associated dementia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64: 498–505.
Kanmogne GD, Kennedy RC, Grammas P (2002). HIV-1 gp120 proteins and gp160 peptides are toxic to brain endothelial cells and neurons: possible pathway for HIV entry into the brain and HIV-associated dementia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61: 992–1000.
McDougal JS, Kennedy M, Sligh J, Cort S, Mowie A, Nicholson J (1986). Binding of HTLV-III/LAV to T4+ T cells by a complex of the 110K viral protein and the T4 molecule. Science 231: 382–385.
Meyenhofer MF, Epstein LG, Cho ES, Sharer LR (1987). Ultrastructural morphology and intracellular production of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 46: 474–484.
Mirra SS, Del Rio C (1989). The fine structure of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome encephalopathy. Arch Pathol Lab Med 113: 858–865.
Mizukami Y, Okamura T, Miura T, Kimura M, Mogami K, Todoroki-Ikeda N, Kobayashi S, Matsuzaki M (2001). Phosphorylation of proteins and apoptosis induced by c-Jun N-terminal kinase1 activation in rat cardiomyocytes by H(2)O(2) stimulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1540: 213–220.
Moses AV, Nelson JA (1994). HIV infection of human brain capillary endothelial cells-implications for AIDS dementia. Adv Neuroimmunol 4: 239–247.
Moses AV, Bloom FE, Pauza CD, Nelson JA (1993). Human immunodeficiency virus infection of human brain capillary endothelial cells occurs via a CD4/galactosylceramide-independent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90: 10474–10478.
Mutoh T, Kumano T, Nakagawa H, Kuriyama M (1999). Involvement of tyrosine phosphorylation in HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor-induced cell death in L6 myoblasts. FEBS Lett 444: 85–89.
O’Brian W, Koyanagi Y, Namazie A, Zho JQ, Diagne A, Idler K, Zack J, Chen ISY (1990): HIV-1 tropism for mononuclear phagocytes can be determined by regions of gp120 outside the CD4-binding domain. Nature 348: 69–73.
Popik W, Pitha PM (2000). Exploitation of cellular signaling by HIV-1: unwelcome guests with master keys that signal their entry. Virol 276: 1–6.
Sharer LR, Epstein LG, Cho ES, Joshi VY, Meyenhofer MF, Rankin LF, Petito CK (1986). Pathologic features of AIDS encephalopathy in children: evidence for LAV/HTLV-III infection of brain. Hum Pathol 17: 271–284.
Sissons J, Kim KS, Stins M, Jayasekera S, Alsam S, Khan NA (2005). Acanthamoeba induces host cell death via a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-dependent mechanism. Infect Immun 73: 2704–2708.
Stins MF, Gilles F, Kim KS (1997). Selective expression of adhesion molecules on human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Neuroimmunol 76: 81–90.
Stins MF, Pearce D, Choi HJ, DiCello F, Pardo CA, Kim KS (2004). CD4 and chemokine recptors on human brain microvascular endopthelial cells, implications for human immodeficiency virus type 1 pathogenesis. Endothelium 11: 1–10.
Stins MF, Pearce D, Di Cello F, Erdreich-Epstein A, Pardo CA, Kim KS (2003). Induction of intercellular adhesion molecule on human brain endothelial cells by HIV-1 gp 120: Role of CD4 and chemokine corecptors. Lab Invest 83: 1787–1798.
Stins MF, Shen Y, Huang SH, Gilles F, Kalra VK, Kim KS (2001). Gp120 activates children’s brain endothelial cells via CD4. J NeuroVirol 7: 125–134.
Toborek M, Lee YW, Flora G, Pu H, Andras IE, Wylegala E, Hennig B, Nath A (2005). Mechanisms of the blood-brain barrier disruption in HIV-1 infection. Cell Mol Neurobiol 25: 181–199.
Weiser B, Peress N, La Neve D, Eilbott DJ, Seidman R, Burger H (1990). Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 expression in the central nervous system correlates directly with extent of disease. Proc Nati Acad Sci U S A 87: 3997–4001.
Zella D, Barabitskaja O, Burns JM, Romerio F, Dunn DE, Revello MG, Gerna G, Reitz MS Jr, Gallo RC, Weichold FF (1998). Interferon-gamma increases expression of chemokine receptors CCR1, CCR3, and CCR5, but not CXCR4 in monocytoid U937 cells. Blood 91: 4444–4450.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by NIH grants.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, N.A., Di Cello, F., Stins, M. et al. Gp120-mediated cytotoxicity of human brain microvascular endothelial cells is dependent on p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. Journal of NeuroVirology 13, 242–251 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280701286531
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280701286531