Abstract
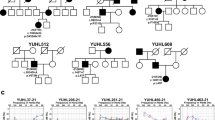
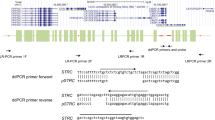
Abnormality in the P50 auditory-evoked potential gating is an endophenotype associated with schizophrenia. Biochemical and genetic studies have suggested that the alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) is involved in this sensory gating deficit. Two related alpha 7 genes (CHRNA7 and CHRNA7-like gene) resulting from a partial duplication (from exon 5 to exon 10) are present in the human genome. Two types of genetic variation, a large deletion and a −2 base-pair deletion in exon 6 resulting in a truncation of the open reading frame, affect specifically the CHRNA7-like gene. We developed a simple multiplex PCR assay on genomic DNA, allowing the quantification of the number of exons 6 and the distinction of all possible exon 6 genotypes. Genotyping of 70 schizophrenic patients and 77 controls showed that carrying at least one −2 bp deletion of exon 6 did not constitute a risk factor for schizophrenia. In contrast, the distribution of genotypes differed significantly between subjects with normal and abnormal P50 ratios, with an over-representation of genotypes carrying at least one −2 bp deletion of exon 6 among subjects exhibiting an abnormal P50 ratio. We thus conclude that the −2 bp deletion within the CHRNA7-like gene is a risk factor for P50 sensory gating deficit. Interestingly, most of the effect came from the non schizophrenic group, which may suggest that in schizophrenic patients other risk factors account for the large proportion of subjects exhibiting an abnormal P50 ratio.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Freedman R, Adler LE, Waldo M . Gating of the auditory evoked potential in children and adults Psychophysiology 1987 24: 223–227
Siegel C, Waldo M, Mizner G, Adler L, Freedman D . Deficit in sensory gating in schizophrenic patients and their relatives Arch Gen Psych 1984 41: 607–612
Myles-Worsley M, Coon H, Byerley W, Waldo M, Young D, Freedman R . Developmental and genetic influences on the P50 sensory gating phenotype Biol Psychiatry 1996 39: 289–295
Adler LE, Rose GM, Freedman R . Neurophysiologic studies of sensory gating in rats: effects of amphetamine, phencyclidine and haloperidol Biol Psychiatry 1986 21: 787–798
Luntz-Leybman V, Bickford PC, Freedman R . Cholinergic gating of response to auditory stimuli in rat hippocampus Brain Res 1992 587: 130–136
Freedman R, Hall M, Adler LE, Leonard S . Evidence in post-mortem brain tissue for decreased numbers of hippocampal nicotinic receptors in schizophrenia Biol Psychiatry 1995 38: 22–23
Freedman R, Coon H, Myles-Worsley M, Orr-Urtreger A, Olincy A, Davis A et al. Linkage of a neurophysiological deficit in schizophrenia to a chromosome 15 locus Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 94: 587–592
Gault J, Robinson M, Berger R, Drebing C, Logel J, Hopkins J et al. Genomic organization and partial duplication of the human alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene (CHRNA7) Genomics 1998 52: 173–185
Weiland S, Bertrand D, Leonard S . Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: from the gene to the disease Behav Brain Res 2000 113: 43–56
Riley BP, Makoff A, Mogudi-Carter M, Jenkins T, Williamson R et al. Haplotype transmission disequilibrium and evidence for the linkage of the CHRNA7 gene region to schizophrenia in Southern African Bantu families Am J Med Genet 2000 96: 196–201
Charbonnier F, Raux G, Wang Q, Drouot N, Cordier F, Limacher JM et al. Detection of exon deletions and duplications of the mismatch repair genes in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer families using multiplex polymerase chain reaction of short fluorescent fragments Cancer Res 2000 60: 2760–2763
Light GA, Geyer MA, Clementz BA, Cadenhead KS, Braff DL . Normal P50 suppression in schizophrenia patients treated with atypical antipsychotic medications Am J Psychiatry 2000 15: 767–771
Nagamoto HT, Adler LE, Waldo MC, Freedman R . Gating of auditory response in schizophrenics and normal controls: effects of recording site and stimulation interval on the P50 wave Schizophr Res 1991 4: 31–41
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr A Delacourte for brain samples. This study was supported by grants from MNERT projet cognitique, Pfizer, and Fondation de la Recherche Médicale (to EH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raux, G., Bonnet-Brilhault, F., Louchart, S. et al. The −2 bp deletion in exon 6 of the ‘alpha 7-like’ nicotinic receptor subunit gene is a risk factor for the P50 sensory gating deficit. Mol Psychiatry 7, 1006–1011 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001140
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001140
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Neurophysiology in psychosis: The quest for disease biomarkers
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
An acute dose, randomized trial of the effects of CDP-Choline on Mismatch Negativity (MMN) in healthy volunteers stratified by deviance detection level
Neuropsychiatric Electrophysiology (2015)
-
Disruption of sensory gating by moderate alcohol doses
Psychopharmacology (2014)
-
Association between the 2-bp deletion polymorphism in the duplicated version of the alpha7 nicotinic receptor gene and P50 sensory gating
European Journal of Human Genetics (2013)
-
Exploring the potential relevance of human-specific genes to complex disease
Human Genomics (2011)