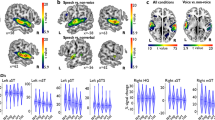
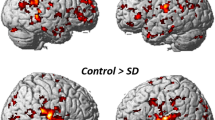
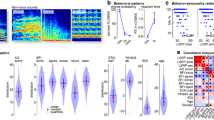
Abstract
Impairments in social interaction are a key feature of autism and are associated with atypical social information processing. Here we report functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) results showing that individuals with autism failed to activate superior temporal sulcus (STS) voice-selective regions in response to vocal sounds, whereas they showed a normal activation pattern in response to nonvocal sounds. These findings suggest abnormal cortical processing of socially relevant auditory information in autism.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual edn. 4 (American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC, USA, 2000).
Kanner, L. Nervous Child 2, 217–250 (1943).
Frith, U. & Happe, F. Cognition 50, 115–132 (1994).
Allison, T., Puce, A. & McCarthy, G. Trends Cogn. Sci. 4, 267–278 (2000).
Boucher, J. & Lewis, V. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 33, 843–859 (1992).
Critchley, H.D. et al. Brain 123, 2203–2212 (2000).
Pierce, K., Muller, R.A., Ambrose, J., Allen, G. & Courchesne, E. Brain 124, 2059–2073 (2001).
Schultz, R.T. et al. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 57, 331–340 (2000).
Belin, P., Zatorre, R.J., Lafaille, P., Ahad, P. & Pike, B. Nature 403, 309–312 (2000).
Klin, A. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 21, 29–42 (1991).
Rutherford, M.D., Baron-Cohen, S. & Wheelwright, S. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 32, 189–194 (2002).
Belin, P., Zatorre, R.J., Hoge, R., Evans, A.C. & Pike, B. Neuroimage. 10, 417–429 (1999).
Ceponiene, R. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 5567–5572 (2003).
Bonnel, A. et al. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 15, 226–235 (2003).
Castelli, F., Frith, C., Happe, F. & Frith, U. Brain 125, 1839–1849 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Pallier and J. B. Poline for support and advice and L. Mottron for useful comments on the manuscript. Supported by the National Science and Engineering Council of Canada; the Fonds de Recherche en Santé du Québec; the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, INSERM, France; the Commissariat à l'Energie Atomique, CEA, France; the France Foundation and the France-Télecom Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Voice versus non-voice - individual analysis. Coronal slices of each subject illustrate the activation peaks for the contrast voice minus non voice in individual analysis, P < 0.001. (PDF 225 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Individual data. (PDF 20 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Intra-group analysis. (PDF 17 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
Inter-group analysis. (PDF 17 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gervais, H., Belin, P., Boddaert, N. et al. Abnormal cortical voice processing in autism. Nat Neurosci 7, 801–802 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1291
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1291