Abstract
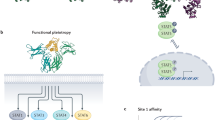
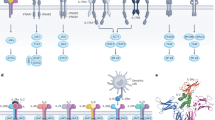
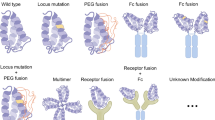
Cytokines can initiate and perpetuate human diseases, and are among the best-validated of therapeutic targets. Cytokines can be blocked by the use of soluble receptors; however, the use of this approach for cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1, IL-4, IL-6 and IL-13 that use multi-component receptor systems is limited because monomeric soluble receptors generally exhibit low affinity or function as agonists. We describe here a generally applicable method to create very high-affinity blockers called 'cytokine traps' consisting of fusions between the constant region of IgG and the extracellular domains of two distinct cytokine receptor components involved in binding the cytokine. Traps potently block cytokines in vitro and in vivo and represent a substantial advance in creating novel therapeutic candidates for cytokine-driven diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Deventer, S.J. Anti-TNF antibody treatment of Crohn's disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 58 (Suppl. 1), I114–1120 (1999).
Richard-Miceli, C. & Dougados, M. Tumour necrosis factor-α blockers in rheumatoid arthritis: Review of the clinical experience. Biodrugs 15, 251–259 (2001).
Elliott, M.J. et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with chimeric monoclonal antibodies to tumor necrosis factor α. Arthritis Rheum. 36, 1681–1690 (1993).
Goldenberg, M.M. Etanercept, a novel drug for the treatment of patients with severe, active rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Ther. 21, 75–87 (1999).
Mohler, K.M. et al. Soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors are effective therapeutic agents in lethal endotoxemia and function simultaneously as both TNF carriers and TNF antagonists. J. Immunol. 151, 1548–1561 (1993).
Bresnihan, B. et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Arthritis Rheum. 41, 2196–2204 (1998).
Cohen, S., Hurd, E. & Cush, J. Treatment of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in combination with methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 42, S273 (1999).
Nuki, G., Rozman, B. & Pavelka, K. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist continues to demonstrate clinical improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 40, S224 (1997).
Campion, G.V., Lebsack, M.E., Lookabaugh, J., Gordon, G. & Catalano, M. Dose-range and dose-frequency study of recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The IL-1Ra Arthritis Study Group. Arthritis Rheum. 39, 1092–1101 (1996).
Bresnihan, B. The prospect of treating rheumatoid arthritis with recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Biodrugs 15, 87–97 (2001).
Borish, L.C. et al. Interleukin-4 receptor in moderate atopic asthma. A phase I/II randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 160, 1816–1823 (1999).
Borish, L.C. et al. Efficacy of soluble IL-4 receptor for the treatment of adults with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 107, 963–970 (2001).
Bataille, R. et al. Biologic effects of anti-interleukin-6 murine monoclonal antibody in advanced multiple myeloma. Blood 86, 685–691 (1995).
Haddad, E. et al. Treatment of B-lymphoproliferative disorder with a monoclonal anti-interleukin-6 antibody in 12 patients: a multicenter phase 1-2 clinical trial. Blood 97, 1590–1597 (2001).
Beck, J.T. et al. Brief report: Alleviation of systemic manifestations of Castleman's disease by monoclonal anti-interleukin-6 antibody. N. Engl. J. Med. 330, 602–605 (1994).
Legouffe, E. et al. Human anti-mouse antibody response to the injection of murine monoclonal antibodies against IL-6. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 98, 323–329 (1994).
Carpenter, L.R., Yancopoulos, G.D. & Stahl, N. General mechanisms of cytokine receptor signaling. Adv. Protein Chem. 52, 109–140 (1999).
Davis, S. et al. LIFR β and gp130 as heterodimerizing signal transducers of the tripartite CNTF receptor. Science 260, 1805–1808 (1993).
Stahl, N. & Yancopoulos, G.D. The alphas, betas, and kinases of cytokine receptor complexes. Cell 74, 587–590 (1993).
Taga, T. et al. Interleukin-6 triggers the association of its receptor with a possible signal transducer, gp130. Cell 58, 573–581 (1989).
Dinarello, C.A. Biologic basis for interleukin-1 in disease. Blood 87, 2095–2147 (1996).
van den Berg, W.B., Joosten, L.A., Helsen, M. & van de Loo, F.A. Amelioration of established murine collagen-induced arthritis with anti-IL-1 treatment. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 95, 237–243 (1994).
Reimers, J. Interleukin-1b induced transient diabetes mellitus in rats. Danish Med. Bull. 45, 157–180 (1998).
van den Berg, W.B. Joint inflammation and cartilage destruction may occur uncoupled. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 20, 149–164 (1998).
Joosten, L.A., Helsen, M.M., van de Loo, F.A. & van den Berg, W.B. Anticytokine treatment of established type II collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice. A comparative study using anti-TNF α, anti- IL-1 α/β, and IL-1Ra. Arthritis Rheum. 39, 797–809 (1996).
Cieslewicz, G. et al. The late, but not early, asthmatic response is dependent on IL-5 and correlates with eosinophil infiltration. J. Clin. Invest. 104, 301–308 (1999).
Wills-Karp, M. Immunologic basis of antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17, 255–281 (1999).
Gundel, R. et al. IL-4 induced leucocyte trafficking in cynomolgus monkeys: correlation with expression of adhesion molecules and chemokine generation. Clin. Exp. Allergy 26, 719–729 (1996).
Foote, J. & Eisen, H.N. Kinetic and affinity limits on antibodies produced during immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 1254–1256 (1995).
Guler, H.-P. et al. A phase 1, single dose escalation study of IL-1 trap in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 44, S370 (2001).
Wills-Karp, M. et al. Interleukin-13: central mediator of allergic asthma. Science 282, 2258–2261 (1998).
Grunig, G. et al. Requirement for IL-13 independently of IL-4 in experimental asthma. Science 282, 2261–2263 (1998).
Coyle, A.J. et al. Interleukin-4 is required for the induction of lung Th2 mucosal immunity. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 13, 54–59 (1995).
Holash, J. et al. VEGF-trap: A VEGF blocker with potent antitumor effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 11393–11398 (2002).
Kim, E.S. et al. Potent VEGF blockade causes regression of coopted vessels in a model of neuroblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 11399–11404 (2002).
Joosten, L.A., Helsen, M.M. & van den Berg, W.B. Accelerated onset of collagen-induced arthritis by remote inflammation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 97, 204–211 (1994).
Wooley, P.H. et al. The effect of an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein on type II collagen-induced arthritis and antigen-induced arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 36, 1305–1314 (1993).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Schleifer and P.R. Vagelos for support; X. Wang, L. LaForge, A. Rafique, L. Kovac, H. Wang, E. Pasnikowski, W. Cheng, T. Sterlacci, A. Hijarunguru, A. Sweeney, E. Skop, M. Gunthart, A. Apedo, C. Sheng, S. Valluzzo, A. Coppi, W. Tu, K. Stafford, M. LaFond, K. Audo, M. Karow, P. Krueger, W. Mikulka, J. Martin and Y. Wei for their contributions; S. Staton and V. Lan for graphics; and the Regeneron scientific community and W.P. Jencks for his contribution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors are employees of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Economides, A., Carpenter, L., Rudge, J. et al. Cytokine traps: multi-component, high-affinity blockers of cytokine action. Nat Med 9, 47–52 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm811
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm811
This article is cited by
-
Involvement of inflammasomes in tumor microenvironment and tumor therapies
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2023)
-
An engineered ligand trap inhibits leukemia inhibitory factor as pancreatic cancer treatment strategy
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Functionally diverse heteromeric traps for ligands of the transforming growth factor-β superfamily
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
TSLP Inhibitors for Asthma: Current Status and Future Prospects
Drugs (2020)
-
The IL-1 family of cytokines and receptors in rheumatic diseases
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2019)