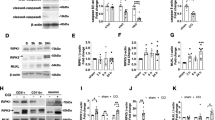
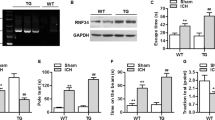
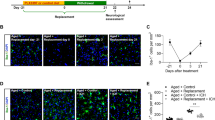
Abstract
Brain injury, as occurs in stroke or head trauma, induces a dramatic increase in levels of tumor necrosis factor–α (TNF), but its role in brain injury response is unknown. We generated mice genetically deficient in TNF receptors (TNFR–KO) to determine the role of TNF in brain cell injury responses. Damage to neurons caused by focal cerebral ischemia and epileptic seizures was exacerbated in TNFR–KO mice, indicating that TNF serves a neuroprotective function. Oxidative stress was Increased and levels of an antioxidant enzyme reduced in brain cells of TNFR–KO mice, indicating that TNF protects neurons by stimulating antioxidant pathways. Injury–induced microglial activation was suppressed in TNFR–KO mice, demonstrating a key role for TNF in injury–induced immune response. Drugs that target TNF signaling pathways may prove beneficial in treating stroke and traumatic brain injury.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taupin, V. et al. Increase in IL-6, IL-1 and TNF levells in rat brain following traumatic lesion. Influence of pre-and post-traumatic treatment with Ro5 4864, a peripheral-type (p site) benzodiazepine ligand. J. Neuroimmunol. 42, 177–185 (1993).
Minami, M., Kuraishi, Y. & Satoh, M. Effects of kainic acid on messenger RNA levels of IL-1 beta, IL-6, TNFα and LIF in the rat brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 176, 593–598 (1991).
Liu, T. et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α expression in ischemic neurons. Stroke 25, 1481–1488 (1994).
Tracey, K.J. & Cerami, A. Tumor necrosis factor: A pleiotropic cytokine and therapeutic target. Anna. Rev. Med. 5, 491–503 (1994).
van der Poll, T. & Lowry, S.F. Tumor necrosis factor in sepsis: Mediator of multiple organ failure or essential part of host defense? Shock 3, 1–12 (1995).
Selmaj, W., Farooq, M., Norton, W.T., Raine, C.S. & Brosnan, C.F. Proliferation of astrocytes in vitro in response to cytokines: A primary role for tumor necrosis factor. J. Immunol. 144, 129–135 (1990).
Merrill, J. Effects of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-α on astrocytes, microglia, oligodendrocytes, and glial precursors in vitro . Dev. Neurosci. 13, 130–137 (1991).
Lipton, S.A. HIV-related neuronal injury. Potential therapeutic intervention with calcium channel antagonists and NMDA antagonists. Mol. Neurobiol. 8, 181–196 (1994).
Louis, J.C., Magal, E., Takayama, S. & Varon, S. CNTF protection of oligodendrocytes against natural and tumor necrosis factor-induced death. Science 259, 689–692 (1993).
Chao, C.C. & Hu, S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha potentiates glutamate neurotoxicity in human fetal brain cell cultures. Dev. Neurosci. 16, 172–179 (1994).
Cheng, B., Christakos, S. & Mattson, M.P. Tumor necrosis factors protect neurons against excitotoxic/metabolic insults and promote maintenance of calcium homeostasis. Neuron 12, 139–153 (1994).
Gruss, H.J. & Dower, S.K. Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily: Involvement in the pathology of malignant lymphomas. Blood 85, 3378–3404 (1995).
Breder, C.D., Tsujimoto, M., Terano, Y., Scott, D.W. & Saper, C.B. Distribution and characterization of tumor necrosis factor-α-like immunoreactivity in the murine central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 337, 543–567 (1993).
Chung, I.Y. & Benveniste, E.N. Tumor necrosis factor alpha production by astrocytes. Induction by lipopolysaccharide, interferon gamma and interleukin-1 beta. J. Immunol. 144, 2999–3007 (1990).
Armitage, R.J. Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily members and their ligands. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 6, 407–413 (1994).
Beutler, B. & Van Huffel, C. An evolutionary and functional approach to the TNF receptor/ligand family. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 730, 118–133 (1994).
Kinouchi, K. et al. Identification and characterization of receptors for tumor necrosis factor-α in the brain. Biochem. Bivphys. Res. Commun. 181, 1532–1538 (1991).
Wolvers, D.A., Marquette, C., Berkenbosch, F. & Haour, F. Tumor necrosis factor α: Specific binding sites in the rodent brain and pituitary gland. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 4, 377–381 (1993).
Kolesnick, R. & Golde, D.W. The sphingomyelin pathway in tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 signaling. Cell 77, 325–328 (1994).
Rothe, M., Pan, M.-G., Henzel, W.J., Ayres, T.M. & Goeddel, D.V. The TNFR2-TRAF signaling complex contains two novel proteins related to baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. Cell 83, 1243–1252 (1995).
Rothe, J. et al. Mice lacking tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 are resistant to TNF-mediated toxicity but highly susceptible to infection by Listeria monocytogenes . Nature 364, 798–802 (1993).
Erickson, S.L. et al. Decreased sensitivity to tumour-necrosis factor but normal T-cell development in TNF receptor-2-deficient mice. Nature 372, 560–563 (1994).
Zheng, L. et al. Induction of apoptosis in mature T cells by tumour necrosis factor. Nature 377, 348–351 (1995).
Stein-Behrens, B., Mattson, M.P., Chang, I., Yeh, M. & Sapolsky, R.M. Stress excacerbates neuron loss and cytoskeletal pathology in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 14, 5373–5380 (1994).
Yang, G. et al. Human copper-zinc superoxide dismutase transgenic mice are highly resistant to reperfusion injury after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 25, 165–170 (1994).
Smith-Swintosky, V.L. et al. Metyrapone, an inhibitor of glucocorticoid production, reduces brain injury induced by focal and global ischemia and seizures. J. Cerebr. Blood Flow Metab. 16, 585–598 (1996).
Watson, B.D. & Ginsberg, M.D. Ischemic injury in the brain. Role of oxygen radical-mediated processes. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 559, 269–281 (1989).
Mattson, M.P., Lovell, M.A., Furukawa, K. & Markesbery, W.R. Neurotrophic factors attenuate glutamate-induced accumulation of peroxides, elevation of [Ca2+]i and neurotoxicity, and increase antioxidant enzyme activities in hippocampal neurons. J. Neurochem. 65, 1740–1751 (1995).
Wong, G.H. Protective roles of cytokines against radiation: Induction of mitochondrial MnSOD. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1271, 205–209 (1995).
Barger, S.W. et al. TNFα and TNFβ protect hippocampal neurons against amyloid β-peptide toxicity: Evidence for involvement of a kB-binding factor and attenuation of peroxide and Ca2+ accumulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 9328–9332 (1995).
Jorgensen, M.B. et al. Microglial and astroglial reactions to ischemic and kainic acid-induced lesions of the adult rat hippocampus. Exp. Neurol. 120, 70–88 (1993).
Mattson, M.P., Cheng, B. & Smith-Swintosky, V.L. Growth factor-mediated protection from excitotoxicity and disturbances in calcium and free radical metabolism. Semin. Neurosci. 5, 295–307 (1993).
Eddy, L.J., Goeddel, D.V. & Wong, G.H. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha pretreatment is protective in a rat model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 184, 1056–1059 (1992).
LaVail, M.M. et al. Multiple growth factors, cytokines, and neurotrophins rescue photoreceptors from the damaging effects of constant light. Natl. Proc. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 11249–11253 (1992).
Meda, L. et al. Activation of microglial cells by beta-amyloid protein and interferon-gamma. Nature 374, 647–650 (1995).
Peterson, P.K., Hu, S., Anderson, W.R. & Chao, C.C. Nitric oxide production and neurotoxicity mediated by activated microglia from human versus mouse brain. J. Infect. Dis. 170, 457–460 (1994).
Araujo, D.M. & Cotman, C.W. Basic FGF in astroglial, microglial, and neuronal cultures: Characterization of binding sites and modulation of release by lymphokines and trophic factors. J. Neurosci. 12, 1668–1678 (1992).
Wiessner, C., Gehrmann, J., Lindholm, D., Topper, R. & Kreutzberg, G.W. Hossmann, K.A. Expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and interleukin-1 beta mRNA in rat brain following transient forebrain ischemia. Acta Neuropathol. 86, 439–446 (1993).
Warner, B.B., Burhans, M.S., Clark, J.C. & Wispe, J.R. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases Mn-SOD expression: Protection against oxidant injury. Am. J. Physiol. 260, L296–301 (1991).
Barbara, J.A. et al. Dissociation of TNF-α cytotoxic and proinflammatory activities by p55 receptor-and p75 receptor-selective TNF-α mutants. EMBO J. 13, 843–850 (1994).
Aloisi, F. et al. Astrocyte cultures from human embryonic brain: Characterization and modulation of surface molecules by inflammatory cytokines. J. Neurosci. Res. 32, 494–506 (1992).
Panek, R.B. & Benveniste, E.N. Class II MHC gene expression in microglia. Regulation by the cytokines IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, and TGF-beta. J. Immunol. 154, 2846–2854 (1995).
Hopkins, S.J. & Rothwell, N.J. Cytokines and the nervous system. I: Expression and recognition. Trends Neurosci. 18, 83–88 (1995).
Feuerstein, G.Z., Liu, T. & Barone, F.C., Cytokines, inflammation, and brain injury: Role of tumor necrosis factor-α. Cerebrovasc. Brain Metab. Rev. 6, 341–360 (1994).
Lyden, P.D., Zivin, J.A., Chabolla, D.R., Jacobs, M.A. & Gage, F.H. Quantitative effects of cerebral infarction on spatial learning in rats. Exp. Neurol. 116, 122–132 (1992).
Gayoso, M.J. et al. Brain lesions and water-maze learning deficits after systemic administration of kainic acid to adult rats. Brain Res. 653, 92–100 (1994).
Bruce, A.J., Sakhi, S., Schreiber, S.S. & Baudry, M. Development of kainic acid and N-methyl-D-aspartic acid toxicity in organotypic hippocampal cultures. Exp. Neurol. 132, 209–219 (1995).
White, B.C. et al. Fluorescent histochemical localization of lipid peroxidation during brain reperfusion following cardiac arrest. Acta. Neuropathol. 86, 1–9 (1993).
Goodman, Y. & Mattson, M.P. Ceramide protects hippocampal neurons against excitotoxic and oxidative insults, and amyloid β-peptide toxicity. J. Neurochem. 66, 869–872 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruce, A., Boling, W., Kindy, M. et al. Altered neuronal and microglial responses to excitotoxic and ischemic brain injury in mice lacking TNF receptors. Nat Med 2, 788–794 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0796-788
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0796-788
This article is cited by
-
Neuroinflammation in Acute Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke
Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports (2023)
-
Inflammatory Cytokines Associated with Multiple Sclerosis Directly Induce Alterations of Neuronal Cytoarchitecture in Human Neurons
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2023)
-
Stress conditions induced circRNAs profile of extracellular vesicles in brain microvascular endothelial cells
Metabolic Brain Disease (2022)
-
Molecular and cellular pathways contributing to brain aging
Behavioral and Brain Functions (2021)
-
The protective role of proton-sensing TDAG8 in the brain injury in a mouse ischemia reperfusion model
Scientific Reports (2020)