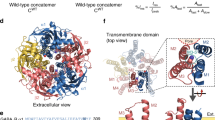
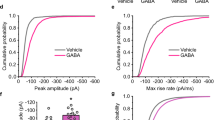
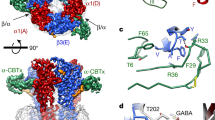
Abstract
γ-AMINOBUTYRIC acid type-A (GABAA) receptors are the major sites of fast synaptic inhibition in the brain. They are presumed to be pentameric heteroligomers assembled from four classes of subunits with multiple members: α (1-6), β (1-3), γ (1-3) and δ (1)1-5. Here, GABAA receptors consisting of α1, β1 and γ2L sub-units, coexpressed in mammalian cells with the tyrosine kinase vSRC (the transforming gene product of the Rous sarcoma virus), were phosphorylated on tyrosine residues within the γ2L and β1 subunits. Tyrosine phosphorylation enhanced the whole-cell current induced by GABA. Site-specific mutagenesis of two tyrosine residues within the predicted intracellular domain of the γ2L sub-unit abolished tyrosine phosphorylation of this subunit and eliminated receptor modulation. A similar modulation of GABAA receptor function was observed in primary neuronal cultures. As GABAA receptors are critical in mediating fast synaptic inhibition, such a regulation by tyrosine kinases may therefore have profound effects on the control of neuronal excitation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olsen, R. W. & Tobin, A. J. FASEB J. 4, 1469–1480 (1990).
Burt, D. R. & Kamatchi, G. L. FASEB J. 5, 2916–2923 (1991).
Schofield, P. R. et al. Nature 328, 221–227 (1987).
Nayeem, N. M., Green, T. P., Martin, I. L. & Barnard, E. A. J. Neurochem. 62, 815–818 (1994).
Pritchett, D. B. et al. Science 242, 1306–1310 (1988).
Pritchett, D. B. et al. Nature 338, 582–585 (1989).
Moss, S. J. et al. Neurosci. Lett. 123, 265–268 (1991).
Evans, G. I., Lewis, G. K., Ramsay, G. & Bishop, J. M. Molec. Cell Biol. 353, 769–772 (1985).
Moss, S. J., Smart, T. G., Blackstone, C. D. & Huganir, R. L. Science 257, 661–665 (1992).
Krishek, B. J. et al. Neuron 12, 1081–1095 (1994).
Wagner, K. R., Mei, L. & Huganir, R. L. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1, 65–73 (1991).
Swope, S. L., Moss, S. J., Blackstone, C. D. & Huganir, R. L. FASEB J. 6, 2514–2523 (1992).
Moss, S. J., Blackstone C. D. & Huganir R. L. Neurochem. Res. 18, 105–110 (1993).
Herbst, R., Lammers, R., Schlessinger, J. & Ullrich, A. J. J. biol. Chem 266, 19908–19916 (1991).
Songyang, Z. et al. Nature 373, 536–539 (1994).
Herb, A. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 1433–1437 (1992).
Pritchett, D. B., Luddens, H. & Seeburg, P. H. Science 245, 1389–1392 (1989).
Smart, T. G. J. Physiol. Lond. 447, 587–625 (1992).
Stelzer, A., Kay, A. R. & Wong, R. K. S. Science 241, 339–341 (1988).
Kano, M., Rexhauser, U., Dresser, J. & Konnerth, A. Nature 356, 601–604 (1992).
Moss, S. J., Doherty, C. A. & Huganir, R. L. J. biol. Chem. 267, 14470–14476 (1992).
McDonald, B. M. & Moss, S. J. J. biol Chem. 269, 18111–18117 (1994).
Valenzuela, C. F. et al. Molec. Brain. Res. 31, 165–172 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moss, S., Gorrie, G., Amato, A. et al. Modulation of GABAA receptors by tyrosine phosphorylation . Nature 377, 344–348 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/377344a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/377344a0
This article is cited by
-
Interaction of Glutamate Receptors and GABA Neurons in the Central Nervous System
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2017)
-
GABAA receptor trafficking and its role in the dynamic modulation of neuronal inhibition
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2008)
-
Effect of Chronic Administration of Ethanol on the Regulation of Tyrosine Kinase Phosphorylation of the GABAA Receptor Subunits in the Rat Brain
Neurochemical Research (2007)
-
Two isoforms of GABAA receptor β2 subunit with different electrophysiological properties: differential expression and genotypical correlations in schizophrenia
Molecular Psychiatry (2006)
-
Tyrosine Kinase Phosphorylation of GABAA Receptor α1, β2 and γ2 Subunits Following Chronic Intermittent Ethanol (CIE) Exposure of Cultured Cortical Neurons of Mice
Neurochemical Research (2006)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.