Abstract
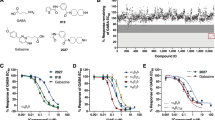
ALTHOUGH neurophysiological, behavioural and biochemical evidence suggests that benzodiazepines (BZ) may affect several neuronal systems within the central nervous system (CNS), recent studies indicate that some of these effects result from a specific interaction with GABAergic transmission1. The precise mechanism of this interaction remains in doubt, as facilitation of GABAergic transmission2, potentiation of GABAergic inhibition3,4, direct activation of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors5, and antagonism of GABA-mediated inhibition have all been attributed to the benzodiazepines6,7. In studies from this laboratory8, both the systemic and iontophoretic administration of BZs potentiated an inhibitory response produced by GABA in the dorsal raphe nucleus—suggesting that the potentiation was mediated through a change in the post-synaptic receptor. In addition, direct binding studies using 3H-diazepam have indicated a specific high affinity binding site which may be relevant to the pharmacological actions of BZ in brain9. In this study, we show that GABA can modulate the responsiveness of this BZ binding site since the addition of GABA to cortical membranes in vitro results in an increased affinity of the 3H-diazepam binding site for its ligand. This effect is mimicked by the GABA analogue, muscimol10, and antagonised by the GABA antagonist, (+)bicuculline.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Costa, E. & Greengard, P. (eds) Mechanism of Action of Benzodiazepines, Advances in Biochemical Psychopharmacology Vol. 14 (Raven, New York, 1975).
Curtis, D. R., Game, C. J. A. & Lodge, D. Expl Brain Res. 25, 413–428 (1976).
Kozhechkin, S. N. & Ostrovskaya, R. U. Nature 269, 72–73 (1977).
Choi, D. W., Farb, D. H. & Fischbach, G. D. Nature 269, 342–344 (1977).
Dray, A. & Straughan, D. W. J. Pharm. Pharmac. 28, 314–315 (1976).
Gähwiler, B. H. Brain Res. 107, 176–179 (1976).
Steiner, F. A. & Felix, D. Nature 260, 346–347 (1976).
Gallager, D. W. Eur. J. Pharmac. (in the press).
Squires, R. I. & Braestrap, C. Nature 266, 732–734 (1977).
Johnston, G. A. R., Curtis, D. R., DeGroat, W. C. & Duggan, A. W. Biochem. Pharmac. 17, 2488–2489 (1968).
Curtis, D. R., Duggan, A. W., Felix, D. & Johnston, G. A. R. Brain Res. 32, 69–96 (1971).
Olsen, R. W., Ban, M., Miller, T. & Johnston, G. A. R. Brain Res. 98, 383–387 (1975).
Collins, J. F. & Hill, R. G. Nature 249, 845–847 (1974).
Krnjević, K. Physiol. Rev. 54, 418–540 (1974).
Schechter, P. J. & Tranier, Y. Psychopharmacology 54, 145–148 (1977).
Gallager, D. W., Thomas, J. W. & Tallman, J. F. Biochem. Pharmac. (in the press).
Shank, R. P. & Aprison, M. H. J. Neurobiol. 2, 145–151 (1971).
Enna, S. J. & Snyder, S. H. Brain Res. 93, 168–174 (1975).
Krnjević, K. & Schwartz, S. in Structure and Functions of Inhibitory Neuronal Mechanisms (eds von Euler, C., Skoglund, S. & Söderberg, U.) 419–427 (Pergamon, Oxford, 1968).
Dray, A. Neuropharmacology 14, 887–891 (1975).
Mukherjee, C., Caron, M. G. & Lefkowitz, R. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72, 1945–1949 (1975).
Burt, D. R., Creese, I. & Snyder, S. H. Science 196, 326–328 (1977).
Tallman, J. F., Smith, C. C. & Henneberry, R. C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 873–877 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
TALLMAN, J., THOMAS, J. & GALLAGER, D. GABAergic modulation of benzodiazepine binding site sensitivity. Nature 274, 383–385 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/274383a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/274383a0
This article is cited by
-
Effect of flunitrazepam as an oral hypnotic on 24-hour blood pressure in healthy volunteers
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2018)
-
GABAA Receptors of Cerebellar Granule Cells in Culture: Interaction with Benzodiazepines
Neurochemical Research (2013)
-
Tiagabine Increases [11C]flumazenil Binding in Cortical Brain Regions in Healthy Control Subjects
Neuropsychopharmacology (2009)
-
Combined discriminative stimulus effects of midazolam with other positive GABAA modulators and GABAA receptor agonists in rhesus monkeys
Psychopharmacology (2005)
-
Evaluating molecular similarity using reduced representations of the electron density
Journal of Molecular Modeling (2005)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.