Abstract
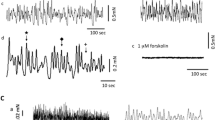
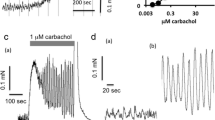
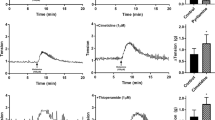
Gallbladder motility is modulated by intrinsicnerves, the identities of which are not wellestablished. The aim of this study was to determine theeffect of nicotinic receptor stimulation of intrinsic nerves on gallbladder muscle contractility.Guinea pig gallbladder muscle strips were studied invitro . Histamine 1 μM was used to increase baselinetone. The nicotinic receptor agonist,1,1-dimethyl-4-phenylpiperazinium (DMPP), produced a biphasic responsecharacterized by an initial transient contractionfollowed by a sustained relaxation. The initialcontraction was inhibited by the neural blockertetrodotoxin, the nicotinic antagonist hexamethonium, and the muscarinicantagonist atropine, but not by a substance P receptorantagonist or a bombesin receptor antagonist. Therelaxation response to DMPP was not affected bytetrodotoxin, but was reduced by hexamethonium andomega-conotoxin GVIA, an inhibitor of neurotransmitterrelease. The relaxation response was reduced by thenitric oxide synthase inhibitor L-NAME, but not by avasoactive intestinal peptide antagonist or propranolol.DMPP produces a biphasic response in the guinea piggallbladder. The initial contractile response ismediated by nicotinic receptors on the cell body or axon of cholinergic nerves. The relaxation responseappears to result, in part, from activation of nicotinicreceptors on nerve terminals of nitric oxide-releasingnerves. These results suggest nicotinic receptors have heterogeneity in location depending onexcitatory or inhibitory neuronal function.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Yau WM, Youther ML: Modulation of gallbladder motility by intrinsic cholinergic neurons. Am J Physiol 247:G662-G666, 1984
Brotschi EZ, Pattavino J, Williams LF: Intrinsic nerves affect gallbladder contraction in the guinea pig. Gastroenterology 99:826-830, 1990
Fisher RS, Rock E, Malmud LS: Cholinergic effects on gallbladder emptying in humans. Gastroenterology 89:716-722, 1985
Hanyu N, Dodds WJ, Layman RD, Hogan WJ, Chey WJ, Takahashi I: Mechanism of cholecystokinin-induced contraction of the opossum gallbladder. Gastroenterology 98:1299- 1306, 1990
Takahashi T, May D, Owyang C: Cholinergic dependence of gallbladder response to cholecystokinin in the guinea pig in vivo. Am J Physiol 261:G565-G569, 1991
Mawe GM: Tachykinins as mediators of slow EPSPs in guineapig gall-bladder ganglia: Involvement of neurokinin-3 receptors. J Physiol 485:513-524, 1995
Schjoldager B, Poulsen SS, Schmidt P, Coy DH, Holst JJ: Gastrin-releasing peptide is a transmitter mediating porcine gallbladder contraction: Am J Physiol 260:G577-G585, 1991
Mourelle M, Guarner F, Moncada S, Malagelada J-R: The L-arginine:nitric oxide pathway regulates gallbladder motility in the guinea pig. Gut 34:911-915, 1993
Sundler F, Alumets J, Hakanson R, Ingemansson S, Fahrenkrug J, de Muckadell OS: VIP innervation of the gallbladder. Gastroenterology 72:1375-1377, 1977
Chen O, Lee KY, Biancani P, Behar J: Mechanisms of gallbladder relaxation in the cat. Dig Dis Sci 41:1882, 1996 (abstract)
Davison JS, Al-Hassani M, Crowe R, Burnstock G: The nonadrenergic, inhibitory innervation of the guinea-pig gallbladder. Pfluegers Arch 377:43-49, 1978
Parkman HP, Pagano AP, Martin JS, Ryan JP: Electric field stimulation (EFS) induced guinea pig gallbladder contractions: Role of calcium channels in acetylcholine release. Dig Dis Sci 41:1881, 1996 (abstract)
Mourelle M, Guarner F, Moncada S, Malagelada J-R: The arginine/nitric oxide pathway modulates sphincter of Oddi motor activity in guinea pigs and rabbits. Gastroenterology 105:1299-1305, 1993
Takahashi T, Tsunoda Y, Lu Y, Wiley J, Owyang C: Nicotinic receptor-evoked re lease of acetylcholine and somatostatin in the mye nteric plexus is coupled to calcium influx via N-type calcium channels. J Pharm Exp Ther 263:1-5, 1992
Chakder S, Rattan S: Release of nitric oxide by activation of nonadrenergic noncholinergic neurons of internal anal sphincter. Am J Physiol 264:G7-G12, 1993
Parkman HP, Pagano AP, Ryan JP: Dual effects of PACAP on guinea pig gallbladder muscle via PACAP-preferring and VIP/ PACAP-preferring receptors. Am J Physiol 272:G1433-G1438, 1997
Cai W-Q, Gabella G: Innervation of the gallbladder and biliary pathways in the guinea pig. J Anat 136:97-109, 1983
Talmage EK, Pouliot WA, Schemann M, Mawe GM: Structure and chemical coding of human, canine and opossum gallbladder ganglia. Cell Tissue Res 284:289-302, 1996
Talmage EK, Mawe GM: NADPH-diaphorase and VIP are co-localized in neurons of gallbladder ganglia. J Auton Nerv Sys 43:83-90, 1993
Murthy KS, Zhang KM, Jin JG, Grider JR, Makhlouf GM: VIP-mediated G protein-coupled Ca21 influx activates a constitive NOS in dispersed gastric muscle cells. Am J Physiol 265:G660-G671, 1993
Salomons H, Keaveny AP, Henihan R, Offner G, Sengupta A, LaMorte WW, Afdhal NH: Nitric oxide and gallbladder motility in prairie dogs. Am J Physiol 272:G770-G778, 1997
Grider JR, Jin J-G: Vasoactive intestinal peptide release and l-citrulline production from isolated ganglia of the myenteric plexus: Evidence for regulation of vasoactive intestinal peptide release by nitric oxide. Neuroscience 54:521-526, 1993
Shuttleworth CWR, Weinert JS, Sanders KM, Buxton ILO: Detection of nitric oxide from canine enteric neurons. J Autonom Nerv Syst 56:61-68, 1995
Dolezal V, Schobert A, Hertting G: Presynaptic nicotinic receptors stimulate increases in intraterminal calcium of chick sympathetic neurons in culture. J Neurochem 65:1874-1879, 1995
McCleskey EW, Fox AP, Feldman DH, Cruz LJ, Olivera BM, Tsien RW, Yoshikami D: Omega-conotoxin: Direct and persistent blockade of specific type s of calcium channels in neurons but not muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:4327-4331, 1987
Lukas RJ: Nicotinic ace tylcholine receptor diversity: Agonist binding and functional potency. Prog Brain Res 79:117-127, 1989
Sargent PB: The diversity of neuronal nicotinic ace tylcholine receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 16:403-443, 1993
Varanda WA, Aracava Y, Sherry SM, VanMeter WG, Eldefrawi ME, Albuquerque EX: The ace tylcholine receptor of the neuromuscular junction recognize s mecamylamine as a noncompetitive antagonist. Mol Pharmacol 28:128-137, 1985
Lukas RJ, Bencherif M: Heterogeneity and regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Int Rev Neurobiol 34:25-115, 1992
Talmage EK, Pouliot WA, Cornbrooks EB, Mawe GM: Transmitter diversity in ganglion cells of the guinea pig gallbladder: An immunohistochemistry study. J Comp Neurol 317:45-56, 1992
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parkman, H.P., Pagano, A.P. & Ryan, J.P. Investigation of Endogenous of Guinea Pig Gallbladder Using Nicotinic Agonist Stimulation. Dig Dis Sci 43, 2237–2243 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026662521485
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026662521485