Abstract
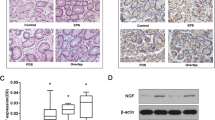
Many studies have indicated changes in neuropeptides in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), but with contradictory results. Nerve growth factor also has a potential role in the maintenance of enteric nerves and may be associated with IBD. A quantitative immunohistochemical method was used to measure area density of immunoreactive nerves in the colonic mucosa of surgical specimens. No significant differences in immunoreactivity for substance P, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, growth associated protein 43, and the neurotrophin receptor p75 were seen in the control, Crohn's, and ulcerative colitis groups. Compared to age-matched normal colon (N = 18), there was an increase in neutrophil number in Crohn's (P < 0.05) and ulcerative colitis (P < 0.01) (both N = 9). There were positive correlations (P < 0.05) between neutrophil number and growth associated protein, between p75 and substance P immunoreactive nerves in ulcerative colitis, and between p75 and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in Crohn's specimens. These data indicate a link between the immunologic and nervous systems in IBD.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Collins SM: The immunomodulation of enteric neuromuscular function: implications for motility and inflammatory disorders. Gastroenterology 111:1683–1699, 1996
Keranen U, Kiviluoto T, Jarvinen H, Back N, Kivilaakso E, Soinila S: Changes in substance P-immunoreactive innervation of human colon associated with ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci 40:2250–2258, 1995
Holzer P: Implications of tachykinins and calcitonin generelated peptide in inflammatory bowel disease. Digestion 59:269–283, 1998
Fairclouge PD, Bloom SR, Mitchell SJ: Plasma-VIP in ulcerative colitis. Lancet 1:964, 1976
Bishop AE, Polak JM, Bryant MG, Bloom SR, Hamilton S: Abnormalities of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-containing nerves in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 79:853–860, 1980
Sjolund K, Schaffalitzky OB, Muckadell DE, Fahrenkrug J, Hakanson R, Peterson BG, Sundler F: Peptide-containing nerve fibres in the gut wall in Crohn's disease. Gut 24:724–733, 1983
O'Morain C, Bishop AE, McGregor GP, Levi AJ, Bloom SR, Polak JM, Peters TJ: Vasoactive intestinal peptide concentrations and immunocytochemical studies in rectal biopsies from patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 25:57–61, 1984
Koch TR, Carney JA, Go VL: Distribution and quantitation of gut neuropeptides in normal intestine and inflammatory bowel diseases. Dig Dis Sci 32:369–376, 1987
Duffy LC, Zielezny MA, Riepenhoff-Talty M, Byers TE, Marshall J, Weiser MM, Graham S, Ogra PL: Vasoactive intestinal peptide as a laboratory supplement to clinical activity index in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci 34:1528–1535, 1989
Goldin E, Karmeli F, Selinger Z, Rachmilewitz D: Colonic substance P levels are increased in ulcerative colitis and decreased in chronic severe constipation. Dig Dis Sci 34:754–757, 1989
Koch TR, Michener SR, Go VL: Plasma vasoactive intestinal polypeptide concentration determination in patients with diarrhea. Gastroenterology 100:99–106, 1991
Mazumdar S, Das KM: Immunocytochemical localization of vasoactive intestinal peptide and substance P in the colon from normal subjects and patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol 87:176–181, 1992
Bernstein CN, Robert ME, Eysselein VK: Rectal substance P concentrations are increased in ulcerative colitis but not in Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol 88:908–913, 1993
Besterman HS, Mallinson CN, Modigliani R, Christofides ND, Pera CA, Ponti V, Sarson DL, Bloom SR: Gut hormones in inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 18:845–852, 1993
Surrenti C, Renzi D, Garcea MR, Surreni E, Salvadori G: Colonic vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in ulcerative colitis. J Physiol (London) 87:307–311, 1993
Todorovic V, Janic B, Koko V, Micev M, Nikolic JA, Ratkovic M, Leposavic G, Jankovic T, Knezevic-Usaj S, Milicevic Z: Colonic vasoactive intestinal polypeptide(VIP) in ulcerative colitis—a radioimmunoassay and immunohistochemical study. Hepatogastroenterology 43:483–488, 1996
Yamamoto H, Morise K, Kusugami K, Furusawa A, Konagaya T, Nishio Y, Kaneko H, Uchida K, Nagai H, Mitsuma T, Nagura H: Abnormal neuropeptide concentration in rectal mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol 31:525–532, 1996
Watanabe T, Kubota Y, Muto T: Substance P containing nerve fibers in rectal mucosa of ulcerative colitis. Dis Colon Rectum 40:718–725, 1997
Renzi D, Mantellini P, Calabro A, Panerai C, Amorosi A, Paladini E, Salvadori G, Garcea MR, Surrenti C: Substance P and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide but not calcitonin generelated peptide concentrations are reduced in patients with moderate and severe ulcerative colitis. Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol 30:62–70, 1998
Watanabe T, Kubota Y, Muto T: Substance P containing nerve fibers in ulcerative colitis. Int J Colorectal Dis 13:61–67, 1998
Heuss D, Schlotzer-Schrehardt U: Subcellular localization of phosphoprotein B-50 in regenerating muscle. An immunoelectron microscopic study. Neurol Res 20:360–364, 1988
Li Y, Jiang N, Power C, Chopp M: Neuronal damage and plasticity identified by microtubule-associate protein 2, growth-associated protein 43, and cyclin D1 immunoreactivity after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 29:1972–1981, 1998
Di Sebastiano P, Fink T, Di Mola FF, Weihe E, Innocenti P, Friess H, Buchler MW: Neuroimmune appendicitis. Lancet 354:462–466, 1999
Kobayashi H, Yamataka A, Fujimoto T, Lane GJ, Miyano T: Mast cells and gut nerve development: Implications for Hirschsprung's disease and intestinal neuronal dysplasia. J Pediatr Surg 34:543–548, 1999
Chao MV, Hempstead BL: p75 and Trk: A two-receptor system. Trends Neurosci 18:321–326, 1995
Woolf CJ, Ma Q, Allchorne A, Poole S: Peripheral cell types contributing to the hyperalgesic action of nerve growth factor in inflammation. J Neurosci 16:2716–2723, 1996
Di Mola FF, Friess H, Zhu ZW, Koliopanos A, Bley T, Di Sebastiano P, Innocenti P, Zimmermann A, Buchler MW: Nerve growth factor and Trk high affinity receptor (TrkA) gene expression in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 46:670–679, 2000
Mantyh CR, Gates TS, Zimmerman RP, Welton ML, Edward PP, Vigna SR, Maggio JE, Kruger L, Mantyh PW: Receptor binding sites for substance P, but not substance K or neuromedin K, are expressed in high concentrations by arterioles, venules, and lynph nodules in surgical specimens obtained from patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:3235–3239, 1988
Mantyh PW, Catton MD, Boehmer CG, Welton ML, Passaro EP, Maggio JE, Vigna R: Receptors for sensory neuropeptides in human inflammatory diseases: Implications for the effector role of sensory neurons. Peptides 10:627–645, 1989
Mantyh CR, Vigna SR, Bollinger RR, Manth PW, Maggio JE, Pappas TN: Differential expression of substance P receptors in patients with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 109:850–860, 1995
Lindsay RM, Lockett C, Sternberg J, Winter J: Neuropeptide expression in cultures of adult sensory neurons: Modulation of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide levels by nerve growth factor. Neuroscience 33:53–65, 1989
Saldanha G, Hongo J, Plant G, Acheson J, Levy I, Anand P: Decreased CGRP, but preserved TrkA immunoreactivity in nerve fibres in inflamed human superficial temporal arteries. J Neurol Neurosurg 66:390–392, 1999
Gershon MD: V. Genes, lineages, and tissue interactions in the development of the enteric nervous system. Am J Physiol 275:G869–G873, 1998
Porter AJ, Wattchow DA, Brookes SJH, Costa M: Projections of nitric oxide synthase and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-reactive submucosal neurons in the human colon. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14:1180–1187, 1999
Horsch D, Kirsch JJ, Weihe E: Elevated density and plasticity of nerve fibres in anal fissures. Int J Colorectal Dis 13:134–140, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, C., Kumar, R., Lubowski, D. et al. Neuropeptides and Nerve Growth in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Quantitative Immunohistochemical Study. Dig Dis Sci 47, 495–502 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017943430627
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017943430627