Abstract
Purpose. The purpose of the present study was to examine the pharmacokinetic features and tissue distribution of N-[2-(2-fluorophenethyl)]-N′-[2-(5-bromopyridyl)]-thiourea (HI-240), a novel non-nucleoside inhibitor of HIV reverse transcriptase with potent anti-viral activity against AZT-sensitive as well as multidrug-resistant HIV-1 strains.
Methods. A sensitive and accurate high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-based quantitative detection method was established to measure concentrations of HI-240 in pharmacokinetic studies. The plasma concentration-time data were modeled by using the WinNonlin program to estimate the pharmacokinetic parameter values.
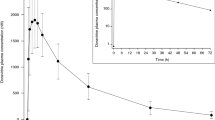
Results. HI-240 had an elimination half-life of 78.3 ± 2.0 min after i.v. administration and 196.8 ± 3.1 min after i.p. administration. The systemic clearance of HI-240 was 2194 ± 61 ml/h/kg after i.v. administration and 9339 ± 1160 ml/h/kg after i.p. administration. Following i.v. injection, HI-240 rapidly distributed to and accumulated in multiple tissues with particularly high accumulation in adipose tissue, adrenal gland, and uterus+ovary. The concentration of HI-240 in brain tissue was comparable to that in the plasma, indicating that HI-240 easily crosses the blood-brain-barrier. Following i.p. injection, HI-240 was rapidly absorbed with a t1/2ka and a tmax values of less than 10 min. Following oral administration, HI-240 was absorbed with a t1/2ka of 4.2 ±1.1 min and a tmax of 95.1 ± 25.1 min. The intraperitoneal bioavailability was estimated at 23.5%, while the oral bioavailability was only 1%.
Conclusions. The HPLC-based accurate and precise analytical detection method and pilot pharmacokinetic studies described herein provide the basis for advanced preclinical pharmacodynamic studies of HI-240. The ability of HI-240 to distribute rapidly and extensively into extravascular compartments and easily cross the blood-brain barrier represent significant pharmacokinetic advantages over AZT.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. D. Young. Non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Perspectives in Drug Discovery Design 1:181-192, 1993.
E. De Clercq. The role of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRIs) in the therapy of HIV-1 infection. Antiviral Res. 38:153-179, 1998.
R. Vig, C. Mao, T. K. Venkatachalam, L. T. Ahlgren, E. A. Sudbeck, and F. M. Uckun. Rational design and synthesis of phenethyl-5-bromopyridyl thiourea derivatives as potent non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV reverse transcriptase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 6:1789-1797 (1998).
C. Mao, E. A. Sudbeck, T. K. Venkatachalam, and F. M. Uckun. Rational design of N-[2-(2,5-dimethoxyphenylethyl)]-N′-[2-(5-dibromopyridyl)-thiourea] (H1-236) as a potent nonnucleoside inhibitor of drug-resistant human immunodeficiency virus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 9:1593-1598 (1999).
C. Mao, R. Vig, T. K. Venkatachalam, E. Sudbeck, and F. M. Uckun. Structure-based design of N-[2-(1-piperidinylethyl)]-N′-[2[(5-bromopyridyl)]-thiourea and N-[2-(1-piperazinylethyl)-N′-[2-(5-bromopyridyl)]-thiourea as potent non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 8(1):2213-2218 (1998).
C. L. Chen, R. Malaviya, C. Navara, H. Chen, B. Bechard, G. Mitcheltree, X. P. Liu, and F. M. Uckun. Pharmacokinetics and biological activity of the novel mast cell inhibitor, 4-(3′-hydroxyphenyl)-amino-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline in mice. Pharm. Res. 16:117-122 (1999).
C. L. Chen, H. Chen, D. M. Zhu, and F. M. Uckun. Quantitative high-performance liquid chromatography based detection method for calphostin C, a naturally occurring perylenequinone with potent antileukemic activity. J. Chromatogr. B. 724:157-162 (1999).
H. Rosenkrantz, Z. Hadidian, H. Seay, and M. M. Masson. Dimethyl sulfoxide: its stroid solubility and endocrinologic and pharmacologic-toxicologic characteristics. Cancer Chemother. Rep. 31:7-24 (1963).
J. E. Wilson, D. E. Brown, and E. K. Timmens. A toxicological study of dimethyl sulfoxide. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 7:104-112 (1965).
M. Gibaldi and D. Perrier. Pharmacokinetics. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York and Basel, 1982. 13.
B. Davies and T. Morris. Physiological parameters in laboratory animals and humans. Pharm. Res. 10:1093-1095 (1993).
C. Ahgren, K. Backro, F. W. Bell, A. S. Cantrell, M. Clemens, J. M. Colacino, J. B. Deeter, J. A. Engelhardt, M. Hogberg, S. R. Jaskunas, N. G. Johansson, C. L. Jordan, J. S. Kasher, M. D. Kinnick, P. Lind, C. Lopez, J. M. Jr. Morin, M. A. Muesing, R. Noreen, B. Oberg, C. J. Paget, J. A. Palkowitz, C. A. Parrish, P. Pranc, M. K. Rippy, C. Rydergard, C. Sahlberg, S. Swanson, R. J. Ternansky, T. Unge, R. T. Vasileff, L. Vrang, S. J. West, H. Zhang, and X. X. Zhou. The PETT series, a new class of potent nonnucleoside inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 39:1329-1335 (1995).
P. de Miranda, T. C. Burnette, and S.S. Good. Tissue distribution amd metabolic disposition of zidovudine in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 18:315-320 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CL., Uckun, F.M. Evaluation of the Pharmacokinetic Features and Tissue Distribution of the Potent Nonnucleoside Inhibitor of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase, N-[2-(2-fluorophenethyl)]-N′-[2-(5-bromopyridyl)]-thiourea (HI-240) with an Analytical HPLC Method. Pharm Res 16, 1226–1232 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014814313681
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014814313681