Abstract
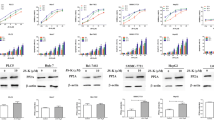
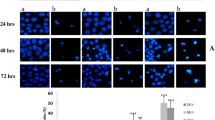
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play an important role in cell death induced by many different stimuli. Direct exposure of human hepatoma cell line SMMC-7221 to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) can induce apoptosis characterized by morphological evidence and fragmentation of DNA assayed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase assay (TUNEL assay). Analysis of flow cytometry indicated that H2O2 can decrease the level of CD95(APO-1/Fas), and it is confirmed that H2O2 can also activate the differential expression of some specific gene such as p53 by means of RT-PCR technique. The results indicated that CD95 signal transduction system may be involved in the H2O2-induced apoptosis, and can regulate some specific genes associated with apoptosis in transcription and translation levels such as p53.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Halliwell B & Gutteridge JMC (1990) Methods Enzymol. 186: 1–85
Sakagami H, Kuribayashi N, Iida M, Hagiwara T, Takahashi H, Yoshida H, Shiota F, Ohata H, Momose K & Takeda M (1996) Life Sci. 58: 1131–1138
Fisher DE (1994) Cell 78: 539–542
Lowe SW, Ruley HE, Jacks T & Housman DE (1993) Cell 74: 957–967
Kastan MB, Zhan Q, El-Deiry WS, Carrier F, Jacks T, Walsh WV, Plunkett BS & Vogelstein B (1992) Cell 71: 587–597
Lowe SW, Schmitt EM, Smith SW, Osborne BA & Jacks T (1993) Nature 362: 847–849
Bates S & Vousden KH (1996) Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 6: 12–19
Barak Y, Juven T, Haffner R & Oren M (1993) EMBO J. 12: 461–468
Chen CY, Oliner JD, Zhan Q, Fornace AJ, Vogelstein B & Kastan MB (1994) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 2684–2688
El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW & Vogelstein B (1993) Cell 75: 817–825
Owen-Schaub LB, Zhang W, Cusack JC, Angelo LS, Santee SM, Fujiwara T, Roth JA, Deisseroth AB, Zhang WW, Kruzel E & Radinsk R (1995) Mol. Cell Biol. 15: 3032–3040
Itoh N, Yonehara S, Ishii A, Yonehara M, Mizuchima SI, Sameshima M, Hase A, Seto Y & Nagata S (1991) Cell 66: 233–243
Smith CA, Farrah T & Goodwin RG (1994) Cell 76: 959–962
Lowin B, Hahne M, Mattmann C & Tschopp J (1994) Nature 370: 650–652
Galle PR, Hofmann WJ, Walczak H, Schaller H, Otto G, Stremmel W, Krammer PH & Runkel L (1995) J. Exp. Med. 182: 1123–1230
Ogasawara J, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Adachi M, Matsuzawa A, Kasugai T, Kitamura Y, Itoh N, Suda T & Nagata S (1993) Nature 364: 806–809
Dong SC, Ren JX, Yang XP, Gu JX & Chen HL (1994) Acta Biochem. Biophys. Sin. 26: 535–540
Li J, Zheng Y, Zheng RL, Liu ZM & Jia ZJ (1995) Chinese Pharmac. J. 30: 269–271
Hebert L, Pandey S & Wang E (1994) Exp. Cell Res. 210: 10–18
Schulz JB, Weller M &Klockgether T 1996 J.Neurosci. 16: 4696–470
Cesarone CF, Bolognesi C & Santi L (1979) Anal. Biochem. 100: 188–191
Negoescu A, Lorimier P, Labat-Moleur F, Droutet C, Robert C, Guillermet C, Brambilla C & Brambilla E (1996). J. Histochem. Cytochem. 44: 959–968
Muller M, Strand S, Hug H, Heinemann EM, Walczak H, Hofmann WJ, Stremmel W, Krammer PH & Galle PR (1997) J. Clin. Invest. 99: 403–413
Bouillet P, Oulad-Abdelghani M, Vicaire S, Garnier J-M, Schuhbaur B, Dolle P & Chambon P (1995) Dev. Biol. 170: 420–433
Lafon C, Mazars P, Guerrin M, Barboule N, Charcosset JY & Valette A (1995) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1266: 288–295
Gansauge S, Gansauge F, Nussler AK, Rau B, Poch B, Schoenberg MH & Beger HG (1997) FEBS Lett. 410: 160–164
Krapp A, Knofler M, Fruitiger S, Hughes GJ, Hagenbuchle O & Wellauer PK (1996) EMBO J. 15: 4317–4329
Liang P & Pardee AB (1992) Science 257: 967–971
Sokolov BP & Prockop DJ (1994) Nucleic Acid Res. 22: 4009–4015
Liang P, Averboukh L & Pardee AB (1993) Nucleic Acid Res. 21: 3269–3275
Gardner AM, Xu FH, Fady C, Jacoby FJ, Duffey DC, Tu YP & Lichtenstein A (1997) Free Rad. Biol. Med. 22: 73–83
Evans CA, Owen-Lynch JP, Whetton AD & Dive C (1993) Cancer Res. 53: 1735–1738
Landowski TH, Gleason-Guzman MC & Daton WS (1997) Blood 89: 1854–1861
Chomczynski P & Sacchi N (1987) Anal. Biochem. 162: 156–159
Lowe SW, Schmitt EM, Smith SW, Osborne BA & Jacks T (1993) Nature 362: 847–849
Friesen C, Herr I, Krammer PH & Debatin KM (1996) Nat. Med. 2: 574–580
Inazawa J, Itoh H, Abe T & Nagata S (1992) Genomics 14: 821–822
Krammer PH, Behrmann I, Daniel P, Dhein J & Debatin KM (1994) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 6: 279–289
William GT & Smith CA (1993) Cell 74: 777–779
Basset P, Bellocq JP, Wolf C, Stoll I, Hutin P, Limacher JM, Podhajcer OP, Chenard MP, Rio MC & Chambon P (1990) Nature 348: 699–704
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B & Harris CC (1991) Science 253: 49–53
Kern SE, Pietenpol JA, Thiagalingam S, Seymour A, Kinzler KW & Volgelstein B (1992) Nature 256: 827–830
Shaw P, Bovey R, Tardy S, Sahli R, Sordat B & Costa J (1992) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 4495–4499
Clarke AR, Purdie CA, Harrison DJ, Morris RG, Bird CC, Hooper ML & Wyllie AH (1993) Nature 362: 849–852
Wang XW, Yeh H, Schaeffer L, Roy R, Moncollin V, Egly JM, Wang Z, Friedberg EC, Friedberg EC, Evans MK, Taffe BG, Bohr VA, Weeda G, Hoeijmakers JHJ, Forrecter K & Harris CC (1995) Nature Genet. 10: 188–195
Lane DP (1992) Nature 358: 15–16
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, C., Li, J., Zheng, R. et al. Hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma cells is mediated by CD95(APO-1/Fas) receptor/ligand system and may involve activation of wild-type p53. Mol Biol Rep 27, 1–11 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007003229171
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007003229171