Abstract
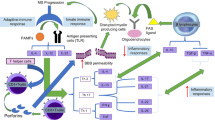
This review discusses clinical and preclinical evidence that supports the use of cannabinoid receptor agonists for the management of multiple sclerosis. In addition, it considers preclinical findings that suggest that as well as ameliorating signs and symptoms of multiple sclerosis, cannabinoid CB1 and/or CB2 receptor activation may suppress some of the pathological changes that give rise to these signs and symptoms. Evidence that the endocannabinoid system plays a protective role in multiple sclerosis is also discussed as are potential pharmacological strategies for enhancing such protection in the clinic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Howlett AC, Barth F, Bonner TI, Cabral G, Casellas P, Devane WA, Felder CC, Herkenham M, Mackie K, Martin BR, Mechoulam R, Pertwee RG (2002) International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol Rev 54:161–202
Ashton JC, Friberg D, Darlington CL, Smith PF (2006) Expression of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor in the rat cerebellum: an immunohistochemical study. Neurosci Lett 396:113–116
Gong JP, Onaivi ES, Ishiguro H, Liu QR, Tagliaferro PA, Brusco A, Uhl GR (2006) Cannabinoid CB2 receptors: immunohistochemical localization in rat brain. Brain Res 1071:10–23
Van Sickle MD, Duncan M, Kingsley PJ, Mouihate A, Urbani P, Mackie K, Stella N, Makriyannis A, Piomelli D, Davison JS, Marnett LJ, Di Marzo V, Pittman QJ, Patel KD, Sharkey KA (2005) Identification and functional characterization of brainstem cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Science 310:329–332
Di Marzo V, De Petrocellis L, Bisogno T (2005) The biosynthesis, fate and pharmacological properties of endocannabinoids. In: Pertwee RG (ed) Cannabinoids. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology Vol. 168, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 147–185
Hillard CJ, Jarrahian A (2003) Cellular accumulation of anandamide: consensus and controversy. Br J Pharmacol 140:802–808
Pertwee RG (2005a) Pharmacological actions of cannabinoids. In: Pertwee RG (ed) Cannabinoids. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology Vol. 168, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 1–51
Pertwee RG (2005b) The therapeutic potential of drugs that target cannabinoid receptors or modulate the tissue levels or actions of endocannabinoids. AAPS J 7:E625–E654
Vaughan CW, Christie MJ (2005) Retrograde signalling by endocannabinoids. In: Pertwee RG (ed) Cannabinoids. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology Vol. 168, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 367–383
Pertwee RG (2005c) Inverse agonism and neutral antagonism at cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Life Sci 76:1307–1324
Price MR, Baillie GL, Thomas A, Stevenson LA, Easson M, Goodwin R, McLean A, McIntosh L, Goodwin G, Walker G, Westwood P, Marrs J, Thomson F, Cowley P, Christopoulos A, Pertwee RG, Ross RA (2005) Allosteric modulation of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Mol Pharmacol 68:1484–1495
Alexander JP, Cravatt BF (2006) The putative endocannabinoid transport blocker LY2183240 is a potent inhibitor of FAAH and several other brain serine hydrolases. J Am Chem Soc 128:9699–9704
Kaczocha M, Hermann A, Glaser ST, Bojesen IN, Deutsch DG (2006) Anandamide uptake is consistent with rate-limited diffusion and is regulated by the degree of its hydrolysis by fatty acid amide hydrolase. J Biol Chem 281:9066–9075
Ungerleider JT, Andyrsiak T, Fairbanks L, Ellison GW, Myers LW (1987) Delta-9-THC in the treatment of spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis. Adv Alcohol Subst Abuse 7:39–50
Petro DJ, Ellenberger C (1981) Treatment of human spasticity with Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. J Clin Pharmacol 21:413S–416S
Meinck HM, Schönle PW, Conrad B (1989) Effect of cannabinoids on spasticity and ataxia in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 236:120–122
Killestein J, Hoogervorst ELJ, Reif M, Kalkers NF, van Loenen AC, Staats PGM, Gorter RW, Uitdehaag BMJ, Polman CH (2002) Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of orally administered cannabinoids in MS. Neurology 58:1404–1407
Vaney C, Heinzel-Gutenbrunner M, Jobin P, Tschopp F, Gattlen B, Hagen U, Schnelle M, Reif M (2004) Efficacy, safety and tolerability of an orally administered cannabis extract in the treatment of spasticity in patients with multiple sclerosis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Mult Scler 10:417–424
Brenneisen R, Egli A, ElSohly MA, Henn V, Spiess Y (1996) The effect of orally and rectally administered Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol on spasticity: a pilot study with 2 patients. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 34:446–452
Zajicek J, Fox P, Sanders H, Wright D, Vickery J, Nunn A, Thompson A (2003) Cannabinoids for treatment of spasticity and other symptoms related to multiple sclerosis (CAMS study): multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 362:1517–1526
Wade DT, Robson P, House H, Makela P, Aram J (2003) A preliminary controlled study to determine whether whole-plant cannabis extracts can improve intractable neurogenic symptoms. Clin Rehabil 17:21–29
Wade DT, Makela P, Robson P, House H, Bateman C (2004) Do cannabis-based medicinal extracts have general or specific effects on symptoms in multiple sclerosis? A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study on 160 patients. Mult Scler 10:434–441
Brady CM, DasGupta R, Dalton C, Wiseman OJ, Berkley KJ, Fowler CJ (2004) An open-label pilot study of cannabis-based extracts for bladder dysfunction in advanced multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 10:425–433
Hamann W, di Vadi PP (1999) Analgesic effect of the cannabinoid analogue nabilone is not mediated by opioid receptors. Lancet 353:560
Svendsen KB, Jensen TS, Bach FW (2004) Does the cannabinoid dronabinol reduce central pain in multiple sclerosis? Randomised double blind placebo controlled crossover trial. Br Med J 329:253–257
Rog DJ, Nurmikko TJ, Friede T, Young CA (2005) Randomized, controlled trial of cannabis-based medicine in central pain in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 65:812–819
Clifford DB (1983) Tetrahydrocannabinol for tremor in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 13:669–671
Martyn CN, Illis LS, Thom J (1995) Nabilone in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Lancet 345:579
Greenberg HS, Werness SAS, Pugh JE, Andrus RO, Anderson DJ, Domino EF (1994) Short-term effects of smoking marijuana on balance in patients with multiple sclerosis and normal volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther 55:324–328
Schon F, Hart PE, Hodgson TL, Pambakian ALM, Ruprah M, Williamson EM, Kennard C (1999) Suppression of pendular nystagmus by smoking cannabis in a patient with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 53:2209–2210
Zajicek JP, Sanders HP, Wright DE, Vickery PJ, Ingram WM, Reilly SM, Nunn AJ, Teare LJ, Fox PJ, Thompson AJ (2005) Cannabinoids in multiple sclerosis (CAMS) study: safety and efficacy data for 12 months follow up. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:1664–1669
Freeman RM, Adekanmi O, Waterfield MR, Waterfield AE, Wright D, Zajicek J (2006) The effect of cannabis on urge incontinence in patients with multiple sclerosis: a multicentre, randomised placebo-controlled trial (CAMS-LUTS). Int Urogynecol J 17:636–641
Pertwee RG (2004) The pharmacology and therapeutic potential of cannabidiol. In: Di Marzo V (ed) Cannabinoids. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, pp 32–83
Consroe P, Musty R, Rein J, Tillery W, Pertwee R (1997) The perceived effects of smoked cannabis on patients with multiple sclerosis. Eur Neurol 38:44–48
Clark AJ, Ware MA, Yazer E, Murray TJ, Lynch ME (2004) Patterns of cannabis use among patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 62:2098–2100
Page SA, Verhoef MJ, Stebbins RA, Metz LM, Levy JC (2003) Cannabis use as described by people with multiple sclerosis. Can J Neurol Sci 30:201–205
Schnelle M, Grotenhermen F, Reif M, Gorter RW (1999) Results of a standardized survey on the medical use of cannabis products in the German-speaking area. Forsch Komplementärmed 6(3):28–36
Ware MA, Adams H, Guy GW (2005) The medicinal use of cannabis in the UK: results of a nationwide survey. Int J Clin Pract 59:291–295
Chong MS, Wolff K, Wise K, Tanton C, Winstock A, Silber E (2006) Cannabis use in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 12:646–651
Wade DT, Makela PM, House H, Bateman C, Robson P (2006) Long-term use of a cannabis-based medicine in the treatment of spasticity and other symptoms in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 12:639–645
De Vry J, Jentzsch KR, Kuhl E, Eckel G (2004) Behavioral effects of cannabinoids show differential sensitivity to cannabinoid receptor blockade and tolerance development. Behav Pharmacol 15:1–12
Lyman WD, Sonett JR, Brosnan CF, Elkin R, Bornstein MB (1989) Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol: a novel treatment for experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 23:73–81
Wirguin I, Mechoulam R, Breuer A, Schezen E, Weidenfeld J, Brenner T (1994) Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by cannabinoids. Immunopharmacology 28:209–214
Sánchez AJ, González-Pérez P, Galve-Roperh I, García-Merino A (2006) R-(+)-[2,3-Dihydro-5-methyl-3-(4-morpholinylmethyl)-pyrrolo-[1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazin-6-yl]-1-naphtalenylmethanone (WIN-2) ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and induces encephalitogenic T cell apoptosis: partial involvement of the CB2 receptor. Biochem Pharmacol 72:1697–1706
Ni X, Geller EB, Eppihimer MJ, Eisenstein TK, Adler MW, Tuma RF (2004) Win 55212-2, a cannabinoid receptor agonist, attenuates leukocyte/endothelial interactions in an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model. Mult Scler 10:158–164
Croxford JL, Miller SD (2003) Immunoregulation of a viral model of multiple sclerosis using the synthetic cannabinoid R(+)WIN55,212. J Clin Invest 111:1231–1240
Arévalo-Martín A, Vela JM, Molina-Holgado E, Borrell J, Guaza C (2003) Therapeutic action of cannabinoids in a murine model of multiple sclerosis. J Neurosci 23:2511–2516
Ortega-Gutiérrez S, Molina-Holgado E, Arévalo-Martín A, Correa F, Viso A, López-Rodríguez ML, Di Marzo V, Guaza C (2005) Activation of the endocannabinoid system as a therapeutic approach in a murine model of multiple sclerosis. FASEB J 19:1338–1340
Baker D, Pryce G, Croxford JL, Brown P, Pertwee RG, Huffman JW, Layward L (2000) Cannabinoids control spasticity and tremor in a multiple sclerosis model. Nature 404:84–87
Wilkinson JD, Whalley BJ, Baker D, Pryce G, Constanti A, Gibbons S, Williamson EM (2003) Medicinal cannabis: is Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol necessary for all its effects? J Pharm Pharmacol 55:1687–1694
Brooks JW, Pryce G, Bisogno T, Jaggar SI, Hankey DJR, Brown P, Bridges D, Ledent C, Bifulco M, Rice ASC, Di Marzo V, Baker D (2002) Arvanil-induced inhibition of spasticity and persistent pain: evidence for therapeutic sites of action different from the vanilloid VR1 receptor and cannabinoid CB1/CB2 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 439:83–92
Pryce G, Baker D (2007) Control of spasticity in a multiple sclerosis model is mediated by CB1, not CB2, cannabinoid receptors. Br J Pharmacol advance online publication; DOI 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707003
Baker D, Pryce G, Croxford JL, Brown P, Pertwee RG, Makriyannis A, Khanolkar A, Layward L, Fezza F, Bisogno T, Di Marzo V (2001) Endocannabinoids control spasticity in a multiple sclerosis model. FASEB J 15:300–302
Malfitano AM, Matarese G, Pisanti S, Grimaldi C, Laezza C, Bisogno T, Di Marzo V, Lechler RI, Bifulco M (2006) Arvanil inhibits T lymphocyte activation and ameliorates autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 171:110–119
Mestre L, Correa F, Arévalo-Martín A, Molina-Holgado E, Valenti M, Ortar G, Di Marzo V, Guaza C (2005) Pharmacological modulation of the endocannabinoid system in a viral model of multiple sclerosis. J Neurochem 92:1327–1339
Sospedra M, Martin R (2005) Immunology of multiple sclerosis. Annu Rev Immunol 23:683–747
Katona S, Kaminski E, Sanders H, Zajicek J (2005) Cannabinoid influence on cytokine profile in multiple sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol 140:580–585
Killestein J, Hoogervorst ELJ, Reif M, Blauw B, Smits M, Uitdehaag BMJ, Nagelkerlen L, Polman CH (2003) Immunomodulatory effects of orally administered cannabinoids in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 137:140–143
Cabranes A, Venderova K, de Lago E, Fezza F, Sánchez A, Mestre L, Valenti M, García-Merino A, Ramos JA, Di Marzo V, Fernández-Ruiz J (2005) Decreased endocannabinoid levels in the brain and beneficial effects of agents activating cannabinoid and/or vanilloid receptors in a rat model of multiple sclerosis. Neurobiol Dis 20:207–217
Cabranes A, Pryce G, Baker D, Fernández-Ruiz J (2006) Changes in CB1 receptors in motor-related brain structures of chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis mice. Brain Res 1107:199–205
Savinainen JR, Kokkola T, Salo OMH, Poso A, Järvinen T, Laitinen JT (2005) Identification of WIN55212-3 as a competitive neutral antagonist of the human cannabinoid CB2 receptor. Br J Pharmacol 145:636–645
Jackson SJ, Pryce G, Diemel LT, Cuzner ML, Baker D (2005) Cannabinoid-receptor 1 null mice are susceptible to neurofilament damage and caspase 3 activation. Neuroscience 134:261–268
Pryce G, Ahmed Z, Hankey DJR, Jackson SJ, Croxford JL, Pocock JM, Ledent C, Petzold A, Thompson AJ, Giovannoni G, Cuzner ML, Baker D (2003) Cannabinoids inhibit neurodegeneration in models of multiple sclerosis. Brain 126:2191–2202
Jackson SJ, Baker D, Cuzner ML, Diemel LT (2004) Cannabinoid-mediated neuroprotection following interferon-gamma treatment in a three-dimensional mouse brain aggregate cell culture. Eur J Neurosci 20:2267–2275
Cabral GA, Staab A (2005) Effects on the immune system. In: Pertwee RG (ed) Cannabinoids. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, Vol. 168, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 385–423
Marsicano G, Goodenough S, Monory K, Hermann H, Eder M, Cannich A, Azad SC, Cascio MG, Gutiérrez SO, van der Stelt M, López-Rodríguez ML, Casanova E, Schütz G, Zieglgänsberger W, Di Marzo V, Behl C, Lutz B (2003) CB1 cannabinoid receptors and on-demand defense against excitotoxicity. Science 302:84–88
Eljaschewitsch E, Witting A, Mawrin C, Lee T, Schmidt PM, Wolf S, Hoertnagl H, Raine CS, Schneider-Stock R, Nitsch R, Ullrich O (2006) The endocannabinoid anandamide protects neurons during CNS inflammation by induction of MKP-1 in microglial cells. Neuron 49:67–79
de Lago E, Fernández-Ruiz J, Ortega-Gutiérrez S, Cabranes A, Pryce G, Baker D, López-Rodríguez M, Ramos JA (2006) UCM707, an inhibitor of the anandamide uptake, behaves as a symptom control agent in models of Huntington’s disease and multiple sclerosis, but fails to delay/arrest the progression of different motor-related disorders. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 16:7–18
de Lago E, Ligresti A, Ortar G, Morera E, Cabranes A, Pryce G, Bifulco M, Baker D, Fernández-Ruiz J, Di Marzo V (2004) In vivo pharmacological actions of two novel inhibitors of anandamide cellular uptake. Eur J Pharmacol 484:249–257
Ligresti A, Cascio MG, Pryce G, Kulasegram S, Beletskaya I, De Petrocellis L, Saha B, Mahadevan A, Visintin C, Wiley JL, Baker D, Martin BR, Razdan RK, Di Marzo V (2006) New potent and selective inhibitors of anandamide reuptake with antispastic activity in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Br J Pharmacol 147:83–91
Deutsch DG, Lin S, Hill WAG, Morse KL, Salehani D, Arreaza G, Omeir RL, Makriyannis A (1997) Fatty acid sulfonyl fluorides inhibit anandamide metabolism and bind to the cannabinoid receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 231:217–221
Lang W, Qin C, Hill WAG, Lin S, Khanolkar AD, Makriyannis A (1996) High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of anandamide amidase activity in rat brain microsomes. Anal Biochem 238:40–45
Khanolkar AD, Abadji V, Lin S, Hill WAG, Taha G, Abouzid K, Meng Z, Fan P, Makriyannis A (1996) Head group analogs of arachidonylethanolamide, the endogenous cannabinoid ligand. J Med Chem 39:4515–4519
Beltramo M, Stella N, Calignano A, Lin SY, Makriyannis A, Piomelli D (1997) Functional role of high-affinity anandamide transport, as revealed by selective inhibition. Science 277:1094–1097
Jarrahian A, Manna S, Edgemond WS, Campbell WB, Hillard CJ (2000) Structure–activity relationships among N-arachidonylethanolamine (anandamide) head group analogues for the anandamide transporter. J Neurochem 74:2597–2606
De Petrocellis L, Bisogno T, Davis JB, Pertwee RG, Di Marzo V (2000) Overlap between the ligand recognition properties of the anandamide transporter and the VR1 vanilloid receptor: inhibitors of anandamide uptake with negligible capsaicin-like activity. FEBS Lett 483:52–56
López-Rodríguez ML, Viso A, Ortega-Gutiérrez S, Fowler CJ, Tiger G, de Lago E, Fernández-Ruiz J, Ramos JA (2003) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of new endocannabinoid transporter inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 38:403–412
Fowler CJ, Tiger G, Ligresti A, López-Rodríguez ML, Di Marzo V (2004) Selective inhibition of anandamide cellular uptake versus enzymatic hydrolysis—a difficult issue to handle. Eur J Pharmacol 492:1–11
Ruiz-Llorente L, Ortega-Gutiérrez S, Viso A, Sánchez MG, Sánchez AM, Fernández C, Ramos JA, Hillard C, Lasunción MA, López-Rodríguez ML, Díaz-Laviada I (2004) Characterization of an anandamide degradation system in prostate epithelial PC-3 cells: synthesis of new transporter inhibitors as tools for this study. Br J Pharmacol 141:457–467
Melck D, Bisogno T, De Petrocellis L, Chuang H, Julius D, Bifulco M, Di Marzo V (1999) Unsaturated long-chain N-acyl-vanillyl-amides (N-AVAMs): vanilloid receptor ligands that inhibit anandamide-facilitated transport and bind to CB1 cannabinoid receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 262:275–284
Di Marzo V, Breivogel C, Bisogno T, Melck D, Patrick G, Tao Q, Szallasi A, Razdan RK, Martin BR (2000) Neurobehavioral activity in mice of N-vanillyl-arachidonyl-amide. Eur J Pharmacol 406:363–374
Ortar G, Ligresti A, De Petrocellis L, Morera E, Di Marzo V (2003) Novel selective and metabolically stable inhibitors of anandamide cellular uptake. Biochem Pharmacol 65:1473–1481
Berrendero F, Sánchez A, Cabranes A, Puerta C, Ramos JA, García-Merino A, Fernández-Ruiz J (2001) Changes in cannabinoid CB1 receptors in striatal and cortical regions of rats with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis, an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Synapse 41:195–202
Yiangou Y, Facer P, Durrenberger P, Chessell IP, Naylor A, Bountra C, Banati RR, Anand P (2006) COX-2, CB2 and P2X7-immunoreactivities are increased in activated microglial cells/macrophages of multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord. BMC Neurol 6, DOI 10.1186/1471-2377-6-12
Maresz K, Carrier EJ, Ponomarev ED, Hillard CJ, Dittel BN (2005) Modulation of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor in microglial cells in response to inflammatory stimuli. J Neurochem 95:437–445
Witting A, Chen L, Cudaback E, Straiker A, Walter L, Rickman B, Möller T, Brosnan C, Stella N (2006) Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis disrupts endocannabinoid-mediated neuroprotection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:6362–6367
La Rana G, Russo R, Campolongo P, Bortolato M, Mangieri RA, Cuomo V, Iacono A, Raso GM, Meli R, Piomelli D, Calignano A (2006) Modulation of neuropathic and inflammatory pain by the endocannabinoid transport inhibitor AM404 [N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-eicosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenamide]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317:1365–1371
Costa B, Siniscalco D, Trovato AE, Comelli F, Sotgiu ML, Colleoni M, Maione S, Rossi F, Giagnoni G (2006) AM404, an inhibitor of anandamide uptake, prevents pain behaviour and modulates cytokine and apoptotic pathways in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Br J Pharmacol 148:1022–1032
Palazzo E, de Novellis V, Petrosino S, Marabese I, Vita D, Giordano C, Di Marzo V, Mangoni GS, Rossi F, Maione S (2006) Neuropathic pain and the endocannabinoid system in the dorsal raphe: pharmacological treatment and interactions with the serotonergic system. Eur J Neurosci 24:2011–2020
Petrosino S, Palazzo E, de Novellis V, Bisogno T, Rossi F, Maione S, Di Marzo V (2007) Changes in spinal and supraspinal endocannabinoid levels in neuropathic rats. Neuropharmacology 52:415–422
Chang L, Luo L, Palmer JA, Sutton S, Wilson SJ, Barbier AJ, Breitenbucher JG, Chaplan SR, Webb M (2006) Inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase produces analgesia by multiple mechanisms. Br J Pharmacol 148:102–113
Jayamanne A, Greenwood R, Mitchell VA, Aslan S, Piomelli D, and Vaughan CW (2006) Actions of the FAAH inhibitor URB597 in neuropathic and inflammatory chronic pain models. Br J Pharmacol 147:281–288
Lichtman AH, Shelton CC, Advani T, Cravatt BF (2004) Mice lacking fatty acid amide hydrolase exhibit a cannabinoid receptor-mediated phenotypic hypoalgesia. Pain 109:319–327
Siegling A, Hofmann HA, Denzer D, Mauler F, De Vry J (2001) Cannabinoid CB1 receptor upregulation in a rat model of chronic neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 415:R5–R7
Lim G, Sung B, Ji RR, Mao J (2003) Upregulation of spinal cannabinoid-1-receptors following nerve injury enhances the effects of Win 55,212-2 on neuropathic pain behaviors in rats. Pain 105:275–283
Zhang J, Hoffert C, Vu HK, Groblewski T, Ahmad S, O’Donnell D (2003) Induction of CB2 receptor expression in the rat spinal cord of neuropathic but not inflammatory chronic pain models. Eur J Neurosci 17:2750–2754
Mitrirattanakul S, Ramakul N, Guerrero AV, Matsuka Y, Ono T, Iwase H, Mackie K, Faull KF, Spigelman I (2006) Site-specific increases in peripheral cannabinoid receptors and their endogenous ligands in a model of neuropathic pain. Pain 126:102–114
Amaya F, Shimosato G, Kawasaki Y, Hashimoto S, Tanaka Y, Ji RR, Tanaka M (2006) Induction of CB1 cannabinoid receptor by inflammation in primary afferent neurons facilitates antihyperalgesic effect of peripheral CB1 agonist. Pain 124:175–183
Mestre L, Correa F, Docagne F, Clemente D, Guaza C (2006) The synthetic cannabinoid WIN 55,212-2 increases COX-2 expression and PGE2 release in murine brain-derived endothelial cells following Theiler’s virus infection. Biochem Pharmacol 72:869–880
Maresz K, Pryce G, Ponomarev ED, Marsicano G, Croxford JL, Shriver LP, Ledent C, Cheng X, Carrier EJ, Mann MK, Giovannoni G, Pertwee RG, Yamamura T, Buckley NE, Hillard CJ, Lutz B, Baker D, Dittel BN (2007) Direct suppression of CNS autoimmune inflammation via the cannabinoid receptor CB1 on neurons and CB2 on autoreactive T cells. Nat Med 13:492–497
Xu H, Cheng B, Manivannan A, Cabay L, Pertwee RG, Coutts A, Forrester JV (2007) Antiinflammatory property of the cannabinoid receptor-2 selective agonist JWH-133 in a rodent model of autoimmune uveoretinitis. J Leukoc Biol. Published on-line; jlb.0307159v1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pertwee, R.G. Cannabinoids and Multiple Sclerosis. Mol Neurobiol 36, 45–59 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-007-0005-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-007-0005-2