Abstract
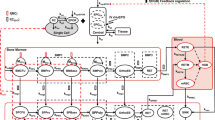
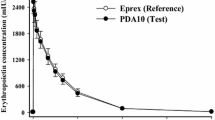
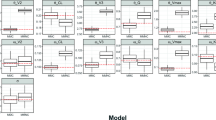
A mechanism-based pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) model was developed for recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEPO) to account for receptor-mediated endocytosis via erythropoietin receptor (EPOR) as a primary mechanism for nonlinear disposition of rHuEPO as well as activation of erythropoietic stimulation. Time profiles of rHuEPO concentrations following a wide range of intravenous (i.v.) doses in rats (10, 100, 450, 1,350, 4,050 IU/kg), monkeys (500, 2,000, 4,000 IU/kg), and man (10, 100, 150, 300, 500 IU/kg) were examined. The mean data of reticulocytes, red blood cells (RBC), and hemoglobin for five different doses in rats were analyzed. The PK model components included receptor binding, subsequent internalization and degradation, EPOR turnover, non-specific tissue distribution, and linear first-order elimination from plasma. The equilibrium dissociation constant (K D ) was similar between rats and monkeys (0.11 nM) and was 10-fold lower in humans (0.012 nM). The PD effects of rHuEPO were described by an indirect response model with lifespan cell loss and driven by the rHuEPO–EPOR complex. A generalized nonlinear PK model for rHuEPO taking into account EPOR binding of the drug in bone marrow was proposed and well described the PK profiles of rHuEPO following i.v. doses in rats, monkeys, and man. The present receptor-mediated PK/PD model for rHuEPO closely reflects underlying mechanisms of disposition and dynamics of rHuEPO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koury MJ, Sawyer ST and Brandt SJ (2002). New insights into erythropoiesis. Curr Opin Hematol 9: 93–100
Walrafen P, Verdier F, Kadri Z, Chretien S, Lacombe C and Mayeux P (2005). Both proteasomes and lysosomes degrade the activated erythropoietin receptor. Blood 105: 600–608
Chapel S, Veng-Pedersen P, Hohl RJ, Schmidt RL, McGuire EM and Widness JA (2001). Changes in erythropoietin pharmacokinetics following busulfan-induced bone marrow ablation in sheep: evidence for bone marrow as a major erythropoietin elimination pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298: 820–824
Kato M, Kamiyama H, Okazaki A, Kumaki K, Kato Y and Sugiyama Y (1997). Mechanism for the nonlinear pharmacokinetics of erythropoietin in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283: 520–527
Jin F and Krzyzanski W (2004). Pharmacokinetic model of target-mediated disposition of thrombopoietin. AAPS PharmSci 6: 1–8
Mager DE, Neuteboom B, Efthymiopoulos C, Munafo A and Jusko WJ (2003). Receptor-mediated pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of interferon-{beta}1a in monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306: 262–270
Segrave AM, Mager DE, Charman SA, Edwards GA and Porter CJH (2004). Pharmacokinetics of recombinant human leukemia inhibitory factor in sheep. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 309: 1085–1092
Stohlman F Jr and Brecher G (1959). Humoral regulation of erythropoiesis. V. Relationship of plasma erythropoietine level to bone marrow activity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 100: 40–3
Ramakrishnan R, Cheung WK, Farrell F, Joffee L and Jusko WJ (2003). Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of recombinant human erythropoietin after intravenous and subcutaneous dose administration in cynomolgus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306: 324–331
Ramakrishnan R, Cheung WK, Wacholtz MC, Minton N and Jusko WJ (2004). Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of recombinant human erythropoietin after single and multiple doses in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 44: 991–1002
Woo S, Krzyzanski W and Jusko WJ (2006). Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of recombinant human erythropoietin after intravenous and subcutaneous administration in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319: 1297–1306
Veng-Pedersen P, Chapel S, Al-Huniti NH, Schmidt RL, Sedars EM, Hohl RJ and Widness JA (2003). A differential pharmacokinetic analysis of the erythropoietin receptor population in newborn and adult sheep. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306: 532–537
Mager DE and Jusko WJ (2001). General pharmacokinetic model for drugs exhibiting target-mediated drug disposition. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 28: 507–532
Mager DE and Krzyzanski W (2005). Quasi-equilibrium pharmacokinetic model for drugs exhibiting target-mediated drug disposition. Pharm Res 22: 1589–1596
Cheung WK, Goon BL, Guilfoyle MC and Wacholtz MC (1998). Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of recombinant human erythropoietin after single and multiple subcutaneous doses to healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 64: 412–423
Fisher JW and Nakashima J (1992). The role of hypoxia in renal production of erythropoietin. Cancer 70: 928–939
Wintrobe MM (2003). Wintrobe’s clinical hematology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
D’Argenio DZ, Schumitzky A (1997) ADAPT II user’s guide: pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic system analysis software. Biomedical Simulations Resource, Los Angeles
Akahane K, Tojo A, Fukamachi H, Kitamura T, Saito T, Urabe A and Takaku F (1989). Binding of iodinated erythropoietin to rat bone marrow cells under normal and anemic conditions. Exp Hematol 17: 177–182
Veng-Pedersen P, Chapel S, Al-Huniti NH, Schmidt RL, Sedars EM, Hohl RJ and Widness JA (2004). Pharmacokinetic tracer kinetics analysis of changes in erythropoietin receptor population in phlebotomy-induced anemia and bone marrow ablation. Biopharm Drug Dispos 25: 149–156
Ng CM, Joshi A, Dedrick RL, Garovoy MR and Bauer RJ (2005). Pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic-efficacy analysis of efalizumab in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Pharm Res 22: 1088–1100
Eppler SM, Combs DL, Henry TD, Lopez JJ, Ellis SG, Yi J-H, Annex BH, McCluskey ER and Zioncheck TF (2002). A target-mediated model to describe the pharmacokinetics and hemodynamic effects of recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72: 20–32
Mager DE and Jusko WJ (2002). Receptor-mediated pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model of interferon-beta 1a in humans. Pharm Res 19: 1537–1543
Flaharty KK, Caro J, Erslev A, Whalen JJ, Morris EM, Bjornsson TD and Vlasses PH (1990). Pharmacokinetics and erythropoietic response to human recombinant erythropoietin in healthy men. Clin Pharmacol Ther 47: 557–564
Kinoshita H, Ohishi N, Kato M, Tokura S and Okazaki A (1992). Pharmacokinetics and distribution of recombinant erythropoietin in rats. Arzneimittelforschung 42: 174–178
Lappin TR, Maxwell AP and Johnston PG (2002). EPO’s alter ego: erythropoietin has multiple actions. Stem Cells 20: 485–492
Jelkmann W and Wagner K (2004). Beneficial and ominous aspects of the pleiotropic action of erythropoietin. Ann Hematol 83: 673–686
Masuda S, Nagao M, Takahata K, Konishi Y, Gallyas F Jr, Tabira T and Sasaki R (1993). Functional erythropoietin receptor of the cells with neural characteristics. Comparison with receptor properties of erythroid cells. J Biol Chem 268: 11208–11216
Egrie JC and Browne JK (2001). Development and characterization of novel erythropoiesis stimulating protein (NESP). Nephrol Dial Transplant 16(Suppl 3): 3–13
Macdougall IC (2005). CERA (Continuous Erythropoietin Receptor Activator): a new erythropoiesis-stimulating agent for the treatment of anemia. Curr Hematol Rep 4: 436–440
Wen D, Boissel JP, Tracy TE, Gruninger RH, Mulcahy LS, Czelusniak J, Goodman M and Bunn HF (1993). Erythropoietin structure-function relationships: high degree of sequence homology among mammals. Blood 82: 1507–1516
Jelkmann W (1992). Erythropoietin: structure, control of production and function. Physiol Rev 72: 449–489
Hoshino S, Teramura M, Takahashi M, Motoji T, Oshimi K, Ueda M and Mizoguchi H (1989). Expression and characterization of erythropoietin receptors on normal human bone marrow cells. Int J Cell Cloning 7: 156–167
Veng-Pedersen P, Widness JA, Wang J and Schmidt RL (1997). A tracer interaction method for nonlinear pharmacokinetics analysis: application to evaluation of nonlinear elimination. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 25: 569–593
Gross AW and Lodish HF (2006). Cellular trafficking and degradation of erythropoietin and novel erythropoiesis stimulating protein (NESP). J Biol Chem 281: 2024–2032
Dahlen DD, Broudy VC and Drachman JG (2003). Internalization of the thrombopoietin receptor is regulated by two cytoplasmic motifs. Blood 102: 102–108
Fandrey J (2004). Oxygen-dependent and tissue-specific regulation of erythropoietin gene expression. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 286: R977–R988
Wide L, Bengtsson C and Birgegard G (1989). Circadian rhythm of erythropoietin in human serum. Br J Haematol 72: 85–90
Klingmuller U (1997). The role of tyrosine phosphorylation in proliferation and maturation of erythroid progenitor cells - signals emanating from the erythropoietin receptor. Eur J Biochem 249: 637–647
Klingmuller U, Lorenz U, Cantley LC, Neel BG and Lodish HF (1995). Specific recruitment of SH-PTP1 to the erythropoietin receptor causes inactivation of JAK2 and termination of proliferative signals. Cell 80: 729–738
Supino-Rosin L, Yoshimura A, Altaratz H and Neumann D (1999). A cytosolic domain of the erythropoietin receptor contributes to endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. Eur J Biochem 263: 410–419
Birkhill FR, Maloney MA and Levenson SM (1951). Effect of transfusion polycythemia upon bone marrow activity and erythrocyte survival in man. Blood 6: 1021–1033
Al-Huniti NH, Widness JA, Schmidt RL and Veng-Pedersen P (2004). Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis of paradoxal regulation of erythropoietin production in acute anemia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310: 202–208
Krzyzanski W, Jusko WJ, Wacholtz MC, Minton N and Cheung WK (2005). Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of recombinant human erythropoietin after multiple subcutaneous doses in healthy subjects. Eur J Pharm Sci 26: 295–306
Trial J and Rice L (2004). Erythropoietin withdrawal leads to the destruction of young red cells at the endothelial-macrophage interface. Curr Pharm Des 10: 183–190
Woo S and Jusko WJ (2007). Interspecies comparisons of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of recombinant human erythropoietin. Drug Metab Dispos 35: 1672–1678
Mager DE, Neuteboom B and Jusko WJ (2005). Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of PEGylated IFN-beta 1a following subcutaneous administration in monkeys. Pharm Res 22: 58–61
Widness JA, Veng-Pedersen P, Peters C, Pereira LM, Schmidt RL and Lowe LS (1996). Erythropoietin pharmacokinetics in premature infants: developmental, nonlinearity, and treatment effects. J Appl Physiol 80: 140–148
Chapel SH, Veng-Pedersen P, Schmidt RL and Widness JA (2001). Receptor-based model accounts for phlebotomy-induced changes in erythropoietin pharmacokinetics. Exp Hematol 29: 425–431
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woo, S., Krzyzanski, W. & Jusko, W.J. Target-mediated pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic model of recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEPO). J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 34, 849–868 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-007-9074-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-007-9074-0