Abstract
Background
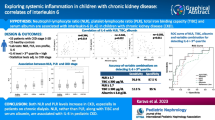
Many studies have indicated a role for cytokines in chronic kidney disease (CKD). The aim of this study was to evaluate plasma and urinary levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1/CCL2), transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1), and interleukin-8 (IL-8/CXCL8) in pediatric patients with CKD stages 2–4.
Methods
Cytokines were measured in 37 healthy controls and in 42 CKD patients by enzyme-linked immunoassay. Patients were divided into groups according to CKD etiology: glomerular disease (group 1, n = 11) and congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract (group 2, n = 31). Urinary cytokine measurements were standardized for creatinine.
Results
Plasma and urinary levels of MCP-1/CCL2 were significantly higher in both CKD groups compared to the control group. Between the two CKD groups, only urinary MCP-1/CCL2 levels were significantly different, with MCP-1/CCL2 levels higher in group 1 patients. Plasma and urinary levels of IL-8/CXCL8 and TGF-β1 were undetectable in the control group but comparable between the two CKD groups. In group 1 patients, urinary MCP-1/CCL2 levels were negatively correlated to serum albumin levels and positively correlated to the levels of total cholesterol and triglycerides. In group 2 patients, urinary levels of IL-8/CXCL8 were negatively correlated with the estimated glomerular filtration rate and positively correlated with body mass index.
Conclusions
Differences in cytokine profiles may be related to CKD etiology and other disease-associated alterations.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warady BA, Chadha V (2007) Chronic kidney disease in children: the global perspective. Pediatr Nephrol 22:1999–2009
Mak RH (2007) Chronic kidney disease in children: state of the art. Pediatr Nephrol 22:1687–1688
Chesney RW, Brewer E, Moxey-Mims M, Watkins S, Furth SL, Harmon WE, Fine RN, Portman RJ, Warady BA, Salusky IB, Langman CB, Gipson D, Scheidt P, Feldman H, Kaskel FJ, Siegel NJ (2006) Report of an NIH task force on research priorities in chronic kidney disease in children. Pediatr Nephrol 21:14–25
Nascimento MM, Pecoits-Filho R, Lindholm B, Riella MC, Stenvinkel P (2002) Inflammation, malnutrition and atherosclerosis in end-stage renal disease: a global perspective. Blood Purif 20:454–458
Pecoits-Filho R, Lindholm B, Stenvinkel P (2002) The malnutrition, inflammation, and atherosclerosis (MIA) syndrome - the heart of the matter. Nephrol Dial Transplant 17[Suppl 11]:28–31
Silverstein DM (2009) Inflammation in chronic kidney disease: role in the progression of renal and cardiovascular disease. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1445–1452
Cheung WW, Paik KH, Mak RH (2010) Inflammation and cachexia in chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 25:711–724
Eardley KS, Kubal C, Zehnder D, Quinkler M, Lepenies J, Savage CO, Howie AJ, Kaur K, Cooper MS, Adu D, Cockwell P (2008) The role of capillary density, macrophage infiltration and interstitial scarring in the pathogenesis of human chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 74:495–504
Vianna HR, Soares CB, Tavares MS, Teixeira MM, Simões e Silva AC (2011) Inflammation in chronic kidney diseases: the role of cytokines. Braz J Nephrol 33:351–364
Gerard C, Rollins BJ (2001) Chemokines and disease. Nat Immunol 2:108–115
Mackay CR (2001) Chemokines: immunology’s high impact factors. Nat Immunol 2:95–101
Segerer S (2003) The role of chemokines and chemokine receptors in progressive renal diseases. Am J Kidney Dis 41:S15–S18
Liu Y (2006) Renal fibrosis: new insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int 69:213–217
Qi W, Chen X, Polhill TS, Sumual S, Twigg S, Gilbert RE, Pollock CA (2006) TGF-beta1 induces IL-8 and MCP-1 through a connective tissue growth factor-independent pathway. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F703–F709
Vasconcelos MA, Bouzada MC, Silveira KD, Moura LR, Santos FF, Oliveira JM, Carvalho FF, Teixeira MM, Simões e Silva AC, Oliveira EA (2011) Urinary levels of TGF β-1 and of cytokines in patients with prenatally detected nephrouropathies. Pediatr Nephrol 26:739–747
Marks SD, Shah V, Pilkington C, Tullus K (2010) Urinary monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 correlates with disease activity in lupus nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 25:2283–2288
Mukaida N, Harada A, Matsushima K (1998) Interleukin-8 (IL-8) and monocyte chemotactic and activating factor (MCAF/MCP-1), chemokines essentially involved in inflammatory and immune reactions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 9:9–23
Pereira AB, Teixeira AL, Rezende NA, Pereira RM, Miranda DM, Oliveira EA, Teixeira MM, Simões e Silva AC (2012) Urinary chemokines and anti-inflammatory molecules in renal transplanted patients as potential biomarkers of graft function: a prospective study. Int Urol Nephrol 44:1539–1548
Souto MF, Teixeira AL, Russo RC, Penido MG, Silveira KD, Teixeira MM, Simoes e Silva AC (2008) Immune mediators in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: evidence for a relation between interleukin 8 and proteinuria. Pediatr Res 64:637–642
Garin EH (2000) Circulating mediators of proteinuria in idiopathic minimal lesion nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 14:872–878
Hogg RJ, Furth S, Lemley KV, Portman R, Schwartz GJ, Coresh J, Balk E, Lau J, Levin A, Kausz AT, Eknoyan G, Levey AS (2003) National Kidney Foundation’s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease in children and adolescents: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Pediatrics 111:1416–1421
Soares CM, Diniz JS, Lima EM, Silva JM, Oliveira GR, Canhestro MR, Colosimo EA, Simoes e Silva AC, Oliveira EA (2008) Clinical outcome of children with chronic kidney disease in a pre-dialysis interdisciplinary program. Pediatr Nephrol 23:2039–2046
Soares CM, Diniz JS, Lima EM, Oliveira GR, Canhestro MR, Colosimo EA, Simoes e Silva AC, Oliveira EA (2009) Predictive factors of progression to chronic kidney disease stage 5 in a predialysis interdisciplinary programme. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:848–855
Schwartz GJ, Haycock GB, Edelmann CM Jr, Spitzer A (1976) A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics 58:259–263
Institute of Medicien of the National Academies (2003) Dietary reference intakes: applications in dietary planning. The National Academies Press, Washington DC
Levin A, Rocco MV (2006) KDOQI clinical practice guidelines and clinical practice recommendations for anemia in chronic kidney disease—foreword. Am J Kidney Dis 47:S9–S145
Langman CB, Salusky IB (2005) K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for bone metabolism and disease in children with chronic kidney disease—foreword. Ame J Kidney Dis 46:S6–S121
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood in Children and Adolescents (2004) The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 114:555–576
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH (2000) Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. Br Med J 320:1240–1243
Leung AK, Wong AH (2010) Proteinuria in children. Am Fam Physician 82:645–651
Wada T, Furuichi K, Sakai N, Iwata Y, Yoshimoto K, Shimizu M, Takeda SI, Takasawa K, Yoshimura M, Kida H, Kobayashi KI, Mukaida N, Naito T, Matsushima K, Yokoyama H (2000) Up-regulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in tubulointerstitial lesions of human diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 58:1492–1499
Bobkova IN, Chebotareva NV, Kozlovskaia LV, Varshavskii VA, Golitsyna EP (2006) Urine excretion of a monocytic chemotaxic protein-1 and a transforming growth factor beta1 as an indicator of chronic glomerulonephritis progression. Ter Arkh 78:9–14
Eddy AA, Warren JS (1996) Expression and function of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in experimental nephrotic syndrome. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 78:140–151
Stangou M, Alexopoulos E, Papagianni A, Pantzaki A, Bantis C, Dovas S, Economidou D, Leontsini M, Memmos D (2009) Urinary levels of epidermal growth factor, interleukin-6 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 may act as predictor markers of renal function outcome in immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Nephrology (Carlton) 14:613–620
Kim MJ, Tam FWK (2011) Urinary monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in renal disease. Clin Chim Acta 412:2022–2030
Yadav A, Saini V, Arora S (2010) MCP-1: chemoattractant with a role beyond immunity: a review. Clin Chim Acta 411:1570–1579
Giunti S, Pinach S, Arnaldi L, Viberti G, Perin PC, Camussi G, Gruden G (2006) The MCP-1/CCR2 system has direct proinflammatory effects in human mesangial cells. Kidney Int 69:856–863
Hunley TE, Ma LJ, Kon V (2010) Scope and mechanisms of obesity-related renal disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 19:227–234
Kershaw EE, Flier JS (2004) Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2548–2556
Chow FY, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Ozols E, Atkins RC, Rollin BJ, Tesch GH (2006) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 promotes the development of diabetic renal injury in streptozotocin-treated mice. Kidney Int 69:73–80
Lloyd CM, Dorf ME, Proudfoot A, Salant DJ, Gutierrez-Ramos JC (1997) Role of MCP-1 and RANTES in inflammation and progression to fibrosis during murine crescentic nephritis. J Leukoc Biol 62:676–680
Erman A, Veksler S, Gafter U, Boner G, Wittenberg C, van Dijk DJ (2004) Renin Angiotensin System blockade prevents the increase in transforming growth factor beta 1 and reduces proteinuria and kidney hypertrophy in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 5:146–151
Zaki Mel S (2008) Interleukin 8 is a surrogate marker for rapid diagnosis of bacteriuria. Immunol Invest 37:694–703
Mohkam M, Karimi A, Karimi H, Sharifian M, Armin S, Dalirani R, Abdollah Gorgi F (2008) Urinary interleukin-8 in acute pyelonephritis of children: a before-after study. Iran J Kidney Dis 2:193–196
Sheu JN, Chen SM, Meng MH, Lue KH (2009) The role of serum and urine interleukin-8 on acute pyelonephritis and subsequent renal scarring in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J 28:885–890
Galanakis E, Bitsori M, Dimitriou H, Giannakopoulou C, Karkavitsas NS, Kalmanti M (2006) Urine interleukin-8 as a marker of vesicoureteral reflux in infants. Pediatrics 117:e863–e867
Gokce I, Alpay H, Biyikli N, Unluguzel G, Dede F, Topuzoglu A (2010) Urinary levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in patients with vesicoureteral reflux and renal parenchymal scar. Pediatr Nephrol 25:905–912
Grenda R, Wuhl E, Litwin M, Janas R, Sladowska J, Arbeiter K, Berg U, Caldas-Afonso A, Fischbach M, Mehls O, Sallay P, Schaefer F (2007) Urinary excretion of endothelin-1 (ET-1), transforming growth factor- beta1 (TGF- beta1) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF165) in paediatric chronic kidney diseases: results of the ESCAPE trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant 22:3487–3494
Chevalier RL, Thornhill BA, Forbes MS, Kiley SC (2010) Mechanisms of renal injury and progression of renal disease in congenital obstructive nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 25:687–697
Wasilewska A, Zoch-Zwierz W, Taranta-Janusz K (2009) Urinary transforming growth factor beta1 in children and adolescents with congenital solitary kidney. Pediatr Nephrol 24:753–759
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, Brazil) and FAPEMIG (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais, Brazil) by the Grant INCT-MM (Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia–Medicina Molecular: FAPEMIG: CBB-APQ-00075-09/CNPq 573646/2008-2). GSE and PMM were recipients of CNPq fellowships. Dr. AC Simões e Silva and Dr. MM Teixeira received a research grant from CNPq.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vianna, H.R., Soares, C.M.B.M., Silveira, K.D. et al. Cytokines in chronic kidney disease: potential link of MCP-1 and dyslipidemia in glomerular diseases. Pediatr Nephrol 28, 463–469 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-012-2363-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-012-2363-x