Abstract
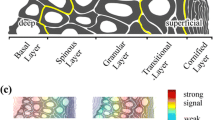
The topological relationships between erbB receptors and ligands of the epidermal growth factor family were characterized by immunocytochemistry in normal and psoriatic epidermis and in proliferating and differentiating human keratinocytes in culture. Spatial colocalization of receptors and ligands was assessed by dual immunostaining. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFr), erbB2, and erbB3, but not erbB4, was detected throughout the epidermis, although labeling for erbB2 and erbB3 was accentuated in the upper spinous layers, and EGFr was more strongly labeled in basal cells. Of the tested growth factors, heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (HB-EGF) was diffusely expressed throughout normal and psoriatic epidermis and sparsely colocalized with EGFr in all viable epidermal layers, with increased colocalization in psoriatic epidermis. In contrast, betacellulin and heregulin/neu differentiation factor (NDF) α were largely restricted in their distribution to the upper spinous and granular layers. Betacellulin was downregulated in psoriatic keratinocytes. Although heregulin/NDF-β was undetectable in normal epidermis, it was upregulated in psoriasis. Betacellulin and heregulin/NDF-α strikingly colocalized with EGFr and erbB3 receptors in the granular layer and in a declining gradient from the granular zone to the basal layer, respectively. Similar patterns were observed in cultured keratinocytes under proliferative conditions and upon differentiation in high-calcium medium. These morphological data collectively suggest divergent functions for members of the growth factor family, and in particular, we propose that betacellulin and heregulin/NDF-α are involved in epidermal morphogenesis and/or in maintenance of the differentiated phenotype.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed NU, Ueda M, Ichihashi M (1997) Increased level of c-erbB-2/neu/HER-2 protein in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol 136:908–912
Castagnino P, Lorenzi MV, Yeh J, Breckenridge D, Sakata H, Munz B, Werner S, Bottaro D (2000) Neu differentiation factor/heregulin induction by hepatocyte and keratinocytes growth factors. Oncogene 19:640–648
Cook PW, Piepkorn M, Clegg CH, Plowman GD, DeMay JM, Brown JR, Pittelkow MR (1997) Transgenic expression of the human amphiregulin gene induces a psoriasis-like phenotype. J Clin Invest 100:2286–2294
Danilenko DM, Ring BD, Lu JZ, Tarpley JE, Chang D, Liu N, Wen D, Pierce GF (1995) Neu differentiation factor upregulates epidermal migration and integrin expression in excisional wounds. J Clin Invest 95:842–851
De Potter IY, Poumay Y, Squillace KA, Pittelkow MR (2001) Human EGF receptor (HER) family and heregulin members are differentially expressed in epidermal keratinocytes and modulate differentiation. Exp Cell Res 271:315–328
Dlugosz AA, Cheng C, Williams EK, Darwiche N, Dempsey PJ, Mann B, Dunn AR, Coffey RJ Jr, Yuspa SH (1995) Autocrine transforming growth factor alpha is dispensible for v-rasHA-induced epidermal neoplasia: potential involvement of alternate epidermal growth factor receptor ligands. Cancer Res 55:1883–1893
Garach-Jehoshua O, Ravid A, Liberman UA, Koren R (1999) 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 increases the growth-promoting activity of autocrine epidermal growth factor receptor ligands in keratinocytes. Endocrinology 140:713–721
Hashimoto Y, Higashiyama S, Asada H, et al (1994) Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor is an autocrine growth factor for human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem 269:20060–20066
Kiguchi K, Beltran L, Rupp T, DiGiovanni J (1998) Altered expression of epidermal growth factor receptor ligands in tumor promoter-treated mouse epidermis and in primary mouse skin tumors induced by an initiation-promotion protocol. Mol Carcinog 22:73–83
Kilpi A, Rich AM, Konttinen YT, Reade PC (1995) The expression of c-erbB-2 protein in the keratinocytes of oral mucosal lichen planus. Br J Dermatol 133:847–852
Marikovsky M, Lavi S, Pinkas-Kramarski R, Karunagaran D, Liu N, Wen D, Yarden Y (1995) ErbB-3 mediates differential mitogenic effects of NDF/heregulin isoforms on mouse keratinocytes. Oncogene 10:1403–1411
Marques MM, Martinez N, Rodriguez-Garcia I, Alonso A (1999) EGFR family-mediated signal transduction in the human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT. Exp Cell Res 252:432–438
Miettinen PJ, Berger JE, Meneses J, Phung Y, Pedersen RA, Werb Z, Derynck R (1995) Epithelial immaturity and multiorgan failure in mice lacking epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature 376:337–341
Nanney LB, Stoscheck CM, King LE Jr, Underwood RA, Holbrook KA (1990) Immunolocalization of epidermal growth factor receptors in normal developing human skin. J Invest Dermatol 94:742–748
Nylander N, Smith LT, Underwood RA, Piepkorn M (1998) Topography of amphiregulin expression in cultured human keratinocytes: colocalization with the epidermal growth factor receptor and CD44. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 34:183–189
Peus D, Hamacher L, Pittelkow M (1997) EGF-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition induces keratinocyte growth arrest and terminal differentiation. J Invest Dermatol 109:751–756
Piepkorn M (1996) Overexpression of amphiregulin, a major autocrine growth factor for cultured human keratinocytes, in hyperproliferative skin diseases. Am J Dermatopathol 18:165–171
Piepkorn M, Lo C, Plowman G (1994) Amphiregulin-dependent proliferation of cultured human keratinocytes: autocrine growth, the effects of exogenous recombinant cytokine, and apparent requirement for heparin-like glycosaminoglycans. J Cell Physiol 159:114–120
Piepkorn M, Pittelkow MR, Cook PW (1998) Autocrine regulation of keratinocytes: the emerging role of heparin-binding, epidermal growth factor-related growth factors. J Invest Dermatol 111:715–721
Porter RM, Lunny DP, Ogden PH, Morley SM, McLean WHI, Evans A, Harrison DL, Rugg EL, Lane EB (2000) K15 expression implies lateral differentiation within stratified epithelial basal cells. Lab Invest 80:1701–1710
Sakai Y, Nelson KG, Snedeker S, Bossert NL, Walker W, McLachlan J, Di Augustine RP (1994) Expression of epidermal growth factor in suprabasal cells of stratified squamous epithelia: implications for a role in differentiation. Cell Growth Differ 5:527–535
Schelfhout VRJ, Coene ED, Delaey B, Thys S, Page DL, De Potter CR (2000) Pathogenesis of Paget's disease: epidermal heregulin α, motility factor, and the HER receptor family. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:622–627
Sibilia M, Wagner EF (1995) Strain-dependent epithelial defects in mice lacking the EGF receptor. Science 269:234–238
Stoll SW, Elder JT (1998) Retinoid regulation of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor gene expression in human keratinocytes and skin. Exp Dermatol 7:391–397
Stoll SW, Elder JT (1999) Differential regulation of EGF-like growth factor genes in human keratinocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 265:214–221
Stoll SW, Kansra S, Peshick S, Fry DW, Leopold WR, Wiesen JF, Sibilia M, Zhang T, Werb Z, Derynck R, Wagner EF, Elder JT (2001) Differential utilization and localization of erbB receptor tyrosine kinases in skin compared to normal and malignant keratinocytes. Neoplasia 3:339–350
Threadgill DW, Dlugosz AA, Hansen LA, et al (1995) Targeted disruption of mouse EGF receptor: effect of genetic background on mutant phenotype. Science 269:230–234
Xian W, Rosenberg MP, DiGiovanni J (1997) Activation of erbB2 and c-src in phorbol ester-treated mouse epidermis: possible role in mouse skin tumor promotion. Oncogene 14:1435–1444
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Public Health Service grant AR21557 from the National Institutes of Health and by the Odland Research Endowment, University of Washington Division of Dermatology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piepkorn, M., Predd, H., Underwood, R. et al. Proliferation–differentiation relationships in the expression of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-related factors and erbB receptors by normal and psoriatic human keratinocytes. Arch Dermatol Res 295, 93–101 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-003-0391-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-003-0391-x