Abstract
Purpose
Overactivity of the multidrug efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp) at the blood-brain barrier (BBB) is believed to play an important role in resistance to central nervous system drug treatment. (R)-[11C]verapamil (VPM) PET can be used to measure the function of P-gp at the BBB, but low brain uptake of VPM hampers the mapping of regional differences in cerebral P-gp function and expression. The aim of this study was to evaluate the dose-response relationship of two potent P-gp inhibitors and to investigate if increased brain uptake of VPM mediated by P-gp inhibition can be used to assess regional differences in P-gp activity.
Methods
Two groups of Sprague-Dawley rats (n = 12) underwent single VPM PET scans at 120 min after administration of different doses of the P-gp inhibitors tariquidar and elacridar. In an additional six rats, paired VPM PET scans were performed before and after administration of 3 mg/kg tariquidar.
Results
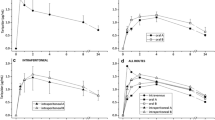
Inhibitor administration resulted in an up to 11-fold increase in VPM brain distribution volumes (DV) with half-maximum effective dose (ED50) values of 3.0 ± 0.2 and 1.2 ± 0.1 mg/kg for tariquidar and elacridar, respectively. In paired PET scans, 3 mg/kg tariquidar resulted in regionally different enhancement of brain activity distribution, with lowest DV in cerebellum and highest DV in thalamus.
Conclusion
Our data show that tariquidar and elacridar are able to increase VPM brain distribution in rat brain up to 11-fold over baseline at maximum effective doses, with elacridar being about three times more potent than tariquidar. Regional differences in tariquidar-induced modulation of VPM brain uptake point to regional differences in cerebral P-gp function and expression in rat brain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Löscher W, Potschka H. Role of drug efflux transporters in the brain for drug disposition and treatment of brain diseases. Prog Neurobiol 2005;76(1):22–76.
Lubberink M, Luurtsema G, van Berckel BN, Boellaard R, Toornvliet R, Windhorst AD, et al. Evaluation of tracer kinetic models for quantification of P-glycoprotein function using (R)-[(11)C]verapamil and PET. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2007;27(2):424–33.
Bankstahl JP, Kuntner C, Abrahim A, Karch R, Stanek J, Wanek T, et al. Tariquidar-induced P-glycoprotein inhibition at the rat blood-brain barrier studied with (R)-11C-verapamil and PET. J Nucl Med 2008;49(8):1328–35.
Bart J, Willemsen AT, Groen HJ, van der Graaf WT, Wegman TD, Vaalburg W, et al. Quantitative assessment of P-glycoprotein function in the rat blood-brain barrier by distribution volume of [11C]verapamil measured with PET. Neuroimage 2003;20(3):1775–82.
Bartels AL, van Berckel BN, Lubberink M, Luurtsema G, Lammertsma AA, Leenders KL. Blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein function is not impaired in early Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2008;14(6):505–8.
Langer O, Bauer M, Hammers A, Karch R, Pataraia E, Koepp MJ, et al. Pharmacoresistance in epilepsy: a pilot PET study with the P-glycoprotein substrate R-[(11)C]verapamil. Epilepsia 2007;48(9):1774–84.
Lee YJ, Maeda J, Kusuhara H, Okauchi T, Inaji M, Nagai Y, et al. In vivo evaluation of P-glycoprotein function at the blood-brain barrier in nonhuman primates using [11C]verapamil. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2006;316(2):647–53.
Sasongko L, Link JM, Muzi M, Mankoff DA, Yang X, Collier AC, et al. Imaging P-glycoprotein transport activity at the human blood-brain barrier with positron emission tomography. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2005;77(6):503–14.
Wagner CC, Bauer M, Karch R, Feurstein T, Kopp S, Chiba P, et al. A pilot study to assess the efficacy of tariquidar to inhibit P-glycoprotein at the human blood-brain barrier with (R)-11C-verapamil and PET. J Nucl Med 2009; in press.
Brunner M, Langer O, Sunder-Plassmann R, Dobrozemsky G, Müller U, Wadsak W, et al. Influence of functional haplotypes in the drug transporter gene ABCB1 on central nervous system drug distribution in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2005;78(2):182–90.
Tai YC, Ruangma A, Rowland D, Siegel S, Newport DF, Chow PL, et al. Performance evaluation of the microPET focus: a third-generation microPET scanner dedicated to animal imaging. J Nucl Med 2005;46(3):455–63.
Pauli-Magnus C, von Richter O, Burk O, Ziegler A, Mettang T, Eichelbaum M, et al. Characterization of the major metabolites of verapamil as substrates and inhibitors of P-glycoprotein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2000;293(2):376–82.
Abrahim A, Luurtsema G, Bauer M, Karch R, Lubberink M, Pataraia E, et al. Peripheral metabolism of (R)-[(11)C]verapamil in epilepsy patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;35:116–23.
Luurtsema G, Molthoff CF, Schuit RC, Windhorst AD, Lammertsma AA, Franssen EJ. Evaluation of (R)-[11C]verapamil as PET tracer of P-glycoprotein function in the blood-brain barrier: kinetics and metabolism in the rat. Nucl Med Biol 2005;32(1):87–93.
Loening AM, Gambhir SS. AMIDE: a free software tool for multimodality medical image analysis. Mol Imaging 2003;2(3):131–7.
Martin C, Berridge G, Mistry P, Higgins C, Charlton P, Callaghan R. The molecular interaction of the high affinity reversal agent XR9576 with P-glycoprotein. Br J Pharmacol 1999;128(2):403–11.
Polli JW, Wring SA, Humphreys JE, Huang L, Morgan JB, Webster LO, et al. Rational use of in vitro P-glycoprotein assays in drug discovery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2001;299(2):620–8.
Choo EF, Kurnik D, Muszkat M, Ohkubo T, Shay SD, Higginbotham JN, et al. Differential in vivo sensitivity to inhibition of P-glycoprotein located in lymphocytes, testes, and the blood-brain barrier. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2006;317(3):1012–8.
Cutler L, Howes C, Deeks NJ, Buck TL, Jeffrey P. Development of a P-glycoprotein knockout model in rodents to define species differences in its functional effect at the blood-brain barrier. J Pharm Sci 2006;95(9):1944–53.
Kühnle M, Egger M, Müller C, Mahringer A, Bernhardt G, Fricker G, et al. Potent and selective inhibitors of breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) derived from the p-glycoprotein (ABCB1) modulator tariquidar. J Med Chem 2009;52(4):1190–7.
Syvänen S, Lindhe O, Palner M, Kornum BR, Rahman O, Långström B, et al. Species differences in blood-brain barrier transport of three positron emission tomography radioligands with emphasis on P-glycoprotein transport. Drug Metab Dispos 2009;37(3):635–43.
Liow JS, Kreisl W, Zoghbi SS, Lazarova N, Seneca N, Gladding RL, et al. P-glycoprotein function at the blood-brain barrier imaged using 11C-N-desmethyl-loperamide in monkeys. J Nucl Med 2009;50(1):108–15.
van Vliet EA, van Schaik R, Edelbroek PM, Voskuyl RA, Redeker S, Aronica E, et al. Region-specific overexpression of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier affects brain uptake of phenytoin in epileptic rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2007;322(1):141–7.
Volk HA, Potschka H, Löscher W. Increased expression of the multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein in limbic brain regions after amygdala-kindled seizures in rats. Epilepsy Res 2004;58(1):67–79.
Laćan G, Plenevaux A, Rubins DJ, Way BM, Defraiteur C, Lemaire C, et al. Cyclosporine, a P-glycoprotein modulator, increases [18F]MPPF uptake in rat brain and peripheral tissues: microPET and ex vivo studies. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;35(12):2256–66.
Bauer M, Wagner CC, Kletter K, Zeitlinger M, Müller M, Langer O. Regional differences in P-glycoprotein function at the human blood-brain barrier [symposium abstract]. J Nucl Med 2009;50(Suppl 2):223P.
Paxinos G, Watson C. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. 6th ed. London: Academic; 2007.
Acknowledgments
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement number 201380 (“Euripides”) and from the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) project “Transmembrane Transporters in Health and Disease” (SFB F35). The authors thank Thomas Filip and Maria Zsebedics (Seibersdorf Laboratories GmbH) for their skilful help with laboratory animal handling and the staff of the radiochemistry laboratory (Seibersdorf Laboratories GmbH) for their continuous support. Thomas Flanitzer is gratefully acknowledged for help with the data analysis and Ronald Boellaard (VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) for advice on compartment modelling issues.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Claudia Kuntner and Jens P. Bankstahl contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuntner, C., Bankstahl, J.P., Bankstahl, M. et al. Dose-response assessment of tariquidar and elacridar and regional quantification of P-glycoprotein inhibition at the rat blood-brain barrier using (R)-[11C]verapamil PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37, 942–953 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-009-1332-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-009-1332-5