Abstract
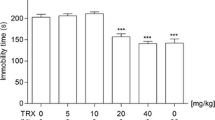
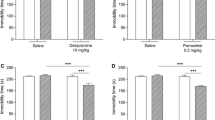
Recent clinical data suggest that buspirone may enhance the efficacy and/or reduce the latency to therapeutic effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in unipolar major depressive disorder. The present study, using the mouse forced swimming test, was performed to investigate further the mechanisms involved in the potential antidepressant-enhancing effects of buspirone. Prior administration of buspirone (0.06 mg kg−1, IP) significantly enhanced the anti-immobility effects of subactive doses of fluvoxamine (4 mg kg−1, IP; P < 0.01), paroxetine (4 mg kg−1, IP; P < 0.01), citalopram (4 mg kg−1, IP; P < 0.01) and sertraline (2 mg kg−1, IP; P < 0.01) in the forced swimming test. However, pretreatment with buspirone did not induce antidepressant-like effects when tested in combination with fluoxetine (4 mg kg−1, IP). Each antidepressant tested reduced immobility time in the forced swimming test [citalopram (16 mg kg−1, IP; P < 0.01), fluoxetine (32 mg kg−1, IP; P < 0.01), fluvoxamine (32 mg kg−1, IP; P < 0.01), paroxetine (16 mg kg−1, IP; P < 0.01) and sertraline (16 mg kg−1, IP; P < 0.01)]. Pretreatment with buspirone (0.5 mg kg−1, IP), or its major metabolite 1-PP (0.5 mg kg−1, IP), attenuated all SSRI-induced anti-immobility effects (P < 0.01). Concomitant studies of locomotor activity ruled out any stimulant or sedative effects of the interactions. The results of the present study suggested that low dose buspirone enhanced the activity of subactive doses of SSRIs in the mouse forced swimming test, probably via an action at 5-HT1A receptors. On the other hand, a high dose of buspirone attenuated the antidepressant-like effects of active doses of these drugs, possibly via the generation of an active metabolite (1-PP) acting at alpha2-adrenoreceptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 19 October 1997 / Final version: 16 December 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Redrobe, J., Bourin, M. Dose-dependent influence of buspirone on the activities of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the mouse forced swimming test. Psychopharmacology 138, 198–206 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050663
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050663