Abstract
Rationale
Phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) and neuroimmune signaling have been posited to regulate alcohol drinking.
Objectives
This study evaluated the involvement of PDE4 and Il22ra2 on ethanol (EtOH) intake by alcohol-preferring (P) and high-alcohol-drinking (HAD1) rats.
Methods
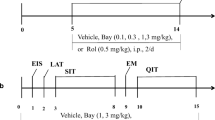
Exp 1 determined the dose-response effects of PDE4 inhibitors, rolipram, and Ro 20-1724, on 2 h/day free-choice EtOH intake by adult P and HAD1 rats. Exps 2–3 examined the effects of repeated administration with the PDE4 inhibitors on EtOH or sucrose intake and locomotor behavior. Exp 4 determined Pde4-associated gene expression differences in subregions of the extended amygdala, between high- and low-alcohol-consuming rat lines. Exp 5 evaluated the effects of infusing short hairpin RNA to knock down Il22ra2 in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) shell on a 24-h free-choice EtOH drinking by P rats.
Results
Administration of rolipram or Ro 20-1724 reduced EtOH intake by P rats; Ro 20-1724 reduced EtOH intake by HAD1 rats. Repeated rolipram or Ro 20-1724 exposure reduced EtOH intake by P and HAD1 rats. PDE4 inhibition induced motor impairment during the first hour of EtOH intake by P rats. Higher gene expression levels for PDE4A were found in the NAc shell of P vs NP rats. ShRNAs targeting Il22ra2 in the NAc shell significantly reduced chronic EtOH intake.
Conclusions
PDE4 and neuroinflammatory/immune signaling pathways could represent molecular targets for the treatment of alcohol use disorders in genetically predisposed subjects. This study underscores the importance of testing compounds over multiple days and rat lines when determining efficacy to disrupt excessive alcohol intake.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen CD, Lee S, Koob GF, Rivier C (2011) Immediate and prolonged effects of alcohol exposure on the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in adult and adolescent rats. Brain Behav Immun 25:S50–S60
Baumer W, Hoppmann J, Rundfeldt C, Kietzmann M (2007) Highly selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors for the treatment of allergic skin diseases and psoriasis. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 6:17–26
Bell RL, Rodd ZA, Smith RJ, Toalston JE, Franklin KM, McBride WJ (2011) Modeling binge-like EtOH drinking by peri-adolescent and adult P rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 100:90–97
Bell RL, Sable HJ, Colombo G, Hyytia P, Rodd ZA, Lumeng L (2012) Animal models for medications development targeting alcohol abuse using selectively bred rat lines: neurobiological and pharmacological validity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 103:119–155
Bell RL, Lopez MF, Cui C, Egli M, Johnson KW, Franklin KM, Becker HC (2014a) Ibudilast reduces alcohol drinking in multiple animal models of alcohol dependence. Addict Biol In Press
Bell RL, Rodd ZA, Engleman EA, Toalston JE, McBride WJ (2014b) Scheduled access alcohol drinking by alcohol-preferring (P) and high alcohol-drinking (HAD) rats: modeling adolescent and adult binge-like drinking. Alcohol 48:225–234
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP (2003) A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 19:185–193
Boudreau AC, Ferrario CR, Glucksman MJ, Wolf ME (2009) Signaling pathway adaptations and novel protein kinase A substrates related to behavioral sensitization to cocaine. J Neurochem 110:363–377
Cherry JA, Davis RL (1999) Cyclic AMP phosphodiesterases are localized in regions of the mouse brain associated with reinforcement, movement, and affect. J Comp Neurol 407:287–301
Conti M, Beavo J (2007) Biochemistry and physiology of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: essential components in cyclic nucleotide signaling. Annu Rev Biochem 76:481–511
Crews FT, Nixon K (2009) Mechanisms of neurodegeneration and regeneration in alcoholism. Alcohol Alcohol 44:115–127
Crews FT, Zou J, Qin L (2011) Induction of innate immune genes in brain create the neurobiology of addiction. Brain Behav Immun 25:S4–S12
Engleman EA, Ding ZM, Oster SM, Toalston JE, Bell RL, Murphy JM, McBride WJ, Rodd ZA (2009) Ethanol is self-administered into the nucleus accumbens shell, but not the core: evidence of genetic sensitivity. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:2162–2171
Fernandez-Lizarbe S, Pascual M, Guerri C (2009) Critical role of TLR4 response in the activation of microglia induced by EtOH. J Immunol 183:4733–4744
Frank MG, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2011) Stress- and glucocorticoid-induced priming of neuroinflammatory responses: potential mechanisms of stress-induced vulnerability to drugs of abuse. Brain Behav Immun 25:S21–S28
Genain CP, Roberts T, Davis RL, Nguyen MH, Uccelli A, Faulds D, Li Y, Hedgpeth J, Hauser SL (1995) Prevention of autoimmune demyelination in non-human primates by a cAMP-specific phospodiesterase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:3601–3605
Gobejishvili L, Barve S, Joshi-Barve S, McClain C (2008) Enhanced PDE4B expression augments LPS-inducible TNF expression in EtOH-primed monocytes: relevance to alcoholic liver disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 295:G718–G724
He J, Crews FT (2008) Increased MCP-1 and microglia in various regions of the human alcoholic brain. Exp Neurol 210:349–358
Houslay MD, Adams DR (2003) PDE4 cAMP phosphodiesterases: modular enzymes that orchestrate signalling cross-talk, desensitization and compartmentalization. Biochem J 370:1–18
Hu W, Lu T, Chen A, Huang Y, Hansen R, Chandler LJ, Zhang HT (2011) Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 decreases EtOH intake in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 218:331–339
Hu TM, Lee RP, Lee CJ, Subeq YM, Lin NT, Hsu BG (2013) Heavy EtOH intoxication increases proinflammatory cytokines and aggravates hemorrhagic shock-induced organ damage in rats. Mediators Inflamm 2013:121786
Hutchinson MR, Bland ST, Johnson KW, Rice KC, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2007) Opioid-induced glial activation: mechanisms of activation and implications for opioid analgesia, dependence, and reward. Sci World J 7:98–111
Janes AC, Kantak KM, Cherry JA (2009) The involvement of type IV phosphodiesterases in cocaine-induced sensitization and subsequent pERK expression in the mouse nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 206:177–185
Jin SL, Ding SL, Lin SC (2012) Phosphodiesterase 4 and its inhibitors in inflammatory diseases. Chang Gung Med J 35:197–210
Kelley KW, Dantzer R (2011) Alcoholism and inflammation: neuroimmunology of behavioral and mood disorders. Brain Behav Immun 25:S13–S20
Kenk M, Thomas A, Lortie M, Dekemp R, Beanlands RS, Dasilva JN (2011) PET measurements of cAMP-mediated phosphodiesterase-4 with (R)-[11C] rolipram. Curr Radiopharm 4:44–58
Knapp CM, Foye MM, Ciraulo DA, Kornetsky C (1999) The type IV phosphodiesterase inhibitors, Ro 20-1724 and rolipram, block the initiation of cocaine self-administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 62:151–158
Kotenko SV, Izotova LS, Mirochnitchenko OV, Esterova E, Dickensheets H, Donnelly RP, Pestka S (2001) Identification, cloning, and characterization of a novel soluble receptor that binds IL-22 and neutralizes its activity. J Immunol 166:7096–7103
Krause W, Kuhne G (1988) Pharmacokinetics of rolipram in the rhesus and cynomolgus monkeys, the rat and the rabbit. Studies on species differences. Xenobiotica 18:561–571
McBride WJ, Kimpel MW, McClintick JN, Ding ZM, Hauser SR, Edenberg HJ, Bell RL, Rodd ZA (2013a) Changes in gene expression within the ventral tegmental area following repeated excessive binge-like alcohol drinking by alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Alcohol 47:367–380
McBride WJ, Kimpel MW, McClintick JN, Ding ZM, Hyytia P, Colombo G, Liang T, Edenberg HJ, Lumeng L, Bell RL (2013b) Gene expression within the extended amygdala of 5 pairs of rat lines selectively bred for high or low EtOH consumption. Alcohol 47:517–529
McBride WJ, Rodd ZA, Bell RL, Lumeng L, Li T-K (2014) The alcohol-preferring (P) and high-alcohol-drinking (HAD) rats—animal models of alcoholism. Alcohol 48:209–215
Misra K, Pandey SC (2006) The decreased cyclic-AMP dependent-protein kinase A function in the nucleus accumbens: a role in alcohol drinking but not in anxiety-like behaviors in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1406–1419
Mori T, Baba J, Ichimaru Y, Suzuki T (2000) Effects of rolipram, a selective inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4, on hyperlocomotion induced by several abused drugs in mice. Jpn J Pharmacol 83:113–118
Narita M, Miyatake M, Shibasaki M, Shindo K, Nakamura A, Kuzumaki N, Nagumo Y, Suzuki T (2006) Direct evidence of astrocytic modulation in the development of rewarding effects induced by drugs of abuse. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:2476–2488
Oger S, Mehats C, Dallot E, Cabrol D, Leroy MJ (2005) Evidence for a role of phosphodiesterase 4 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated prostaglandin E2 production and matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity in human amniochorionic membranes. J Immunol 174:8082–8089
Page CP, Spina D (2011) Phosphodiesterase inhibitors in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Handb Exp Pharmacol 204:391–414
Pandey SC, Mittal N, Lumeng L, Li TK (1999) Involvement of the cyclic AMP-responsive element binding protein gene transcription factor in genetic preference for alcohol drinking behavior. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23:1425–1434
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, New York
Perez-Torres S, Miro X, Palacios JM, Cortes R, Puigdomenech P, Mengod G (2000) Phosphodiesterase type 4 isozymes expression in human brain examined by in situ hybridization histochemistry and [3H] rolipram binding autoradiography. Comparison with monkey and rat brain. J Chem Neuroanat 20:349–374
Qin L, He J, Hanes RN, Pluzarev O, Hong JS, Crews FT (2008) Increased systemic and brain cytokine production and neuroinflammation by endotoxin following EtOH treatment. J Neuroinflammation 5:10
Research Institute for Laboratory Animal Research (2011) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals, 8th edn. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Rosi S (2011) Neuroinflammation and the plasticity-related immediate-early gene Arc. Brain Behav Immun 25:S39–S49
Sanjabi S, Zenewicz LA, Kamanaka M, Flavell RA (2009) Anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory roles of TGF-beta, IL-10, and IL-22 in immunity and autoimmunity. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9:447–453
Schaal SM, Garg MS, Ghosh M, Lovera L, Lopez M, Patel M, Louro J, Patel S, Tuesta L, Chan WM, Pearse DD (2012) The therapeutic profile of rolipram, PDE target and mechanism of action as a neuroprotectant following spinal cord injury. PLoS One 7:e43634
Sekut L, Yarnall D, Stimpson SA, Noel LS, Bateman-Fite R, Clark RL, Brackeen MF, Menius JA Jr, Connolly KM (1995) Anti-inflammatory activity of phosphodiesterase (PDE)-IV inhibitors in acute and chronic models of inflammation. Clin Experiment Immunol 100:126–132
Smith DF (1990) Effects of lithium and rolipram enantiomers on locomotor activity in inbred mice. Pharmacol Toxicol 66:142–145
Snider SE, Hendrick ES, Beardsley PM (2013) Glial cell modulators attenuate methamphetamine self-administration in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 701:124–130
Souness JE, Villamil ME, Scott LC, Tomkinson A, Giembycz MA, Raeburn D (1994) Possible role of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterases in the actions of ibudilast on eosinophil thromboxane generation and airways smooth muscle tone. Br J Pharmacol 111:1081–1088
Souness JE, Aldous D, Sargent C (2000) Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory effects of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase (PDE) type 4 inhibitors. Immunopharmacology 47:127–162
Sousa LP, Lopes F, Silva DM, Tavares LP, Vieira AT, Rezende BM, Carmo AF, Russo RC, Garcia CC, Bonjardim CA, Alessandri AL, Rossi AG, Pinho V, Teixeira MM (2010) PDE4 inhibition drives resolution of neutrophilic inflammation by inducing apoptosis in PKA-PI3K/Akt-dependent and NF-kappaB-independent manner. J Leukoc Biol 87:895–904
Teixeira MM, Gristwood RW, Cooper N, Hellewell PG (1997) Phosphodiesterase (PDE)4 inhibitors: anti-inflammatory drugs of the future? Trends Pharmacol Sci 8:164–171
Terwilliger RZ, Beitner-Johnson D, Sevarino KA, Crain SM, Nestler EJ (1991) A general role for adaptations in G-proteins and the cyclic AMP system in mediating the chronic actions of morphine and cocaine on neuronal function. Brain Res 548:100–110
Thiele TE, Willis B, Stadler J, Reynolds JG, Bernstein IL, McKnight GS (2000) High EtOH consumption and low sensitivity to EtOH-induced sedation in protein kinase A-mutant mice. J Neurosci 20:RC75
Thompson BE, Sachs BD, Kantak KM, Cherry JA (2004) The type IV phosphodiesterase inhibitor rolipram interferes with drug-induced conditioned place preference but not immediate early gene induction in mice. Eur J Neurosci 19:2561–2568
Wachtel H (1983) Species differences in behavioural effects of rolipram and other adenosine cyclic 3H, 5H-monophosphate phosphodiesterase inhibitors. J Neural Transm 56:139–152
Wang C, Yang XM, Zhuo YY, Zhou H, Lin HB, Cheng YFm Xy JP, Zhang HT (2012) The phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor rolipram reverses Aβ-induced cognitive impairment and neuroinflammatory and apoptotic responses in rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15:749–766
Wen RT, Zhang M, Qin WJ, Liu Q, Wang WP, Lawrence AJ, Zhang HT, Liang JH (2012) The phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor rolipram decreases EtOH seeking and consumption in alcohol-preferring fawn-hooded rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 36:2157–2167
Yakovleva T, Bazov I, Watanabe H, Hauser KF, Bakalkin G (2011) Transcriptional control of maladaptive and protective responses in alcoholics: a role of the NF-kappaB system. Brain Behav Immun 25:S29–S38
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by the National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) grants AA07611, AA013522, AA016654, and NIAAA contract HHSN267200700037C. Kelle Franklin and Sheketha Hauser share first authorship on this manuscript. The authors would like to thank Thomas H. Ewing, Jason D. Pope, and Ian S. Roberts for their technical support with this research. None of the authors has a conflict of interest associated with this research. The content of this manuscript is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of NIAAA or NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franklin, K.M., Hauser, S.R., Lasek, A.W. et al. Reduction of alcohol drinking of alcohol-preferring (P) and high-alcohol drinking (HAD1) rats by targeting phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4). Psychopharmacology 232, 2251–2262 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3852-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3852-3