Abstract
Rationale
Neuropeptide S (NPS) and its receptor (NPSR) comprise a recently deorphaned G protein-coupled receptor system. Recent reports implicate NPS in the mediation of anxiolytic-like activity in rodents.
Objectives
To extend the characterization of NPS, the present studies examined the in vitro pharmacology of mouse NPSR and the in vivo pharmacology of NPS in three preclinical mouse models predictive of anxiolytic action: the four-plate test (FPT), elevated zero maze (EZM), and stress-induced hyperthermia (SIH). The ability of NPS to produce antidepressant-like effects in the tail suspension test (TST) was also investigated.
Results
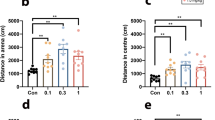
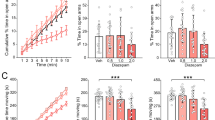
In vitro, mouse NPS1–20 (mNPS1–20) and the C-terminal glutamine-truncated mouse NPS1–19 bound mNPSR with high affinity (K i = 0.203 ± 0.060, 0.635 ± 0.141 nM, respectively) and potently activated intracellular calcium release (EC50 = 3.73 ± 1.08, 4.10 ± 1.25 nM). NPS produced effects in vivo consistent with anxiolytic-like activity. In FPT, NPS increased punished crossings (minimal effective dose [MED]: mNPS1–20 = 0.2 μg, mNPS1–19 = 0.02 μg), similar to the reference anxiolytic, alprazolam (MED 0.5 μg). NPS increased the percentage of time spent in the open quadrants of EZM (MED: mNPS1–20 = 0.1 μg, mNPS1–19 = 1.0 μg), like the reference anxiolytic, chlordiazepoxide (MED 56 μg). In SIH, NPS attenuated stress-induced increases in body temperature similar to alprazolam but with a large potency difference between the NPS peptides (MED: mNPS1–20 = 2.0 μg, mNPS1–19 = 0.0002 μg) and mNPS1–20 increased baseline temperature. Unlike fluoxetine, NPS did not effect immobility time in TST, indicating a lack of antidepressant-like activity.
Conclusions
These data provide an important confirmation and expansion of the anxiolytic-like effects of NPS and implicate the NPS system as a novel target for anxiolytic drug discovery.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aron C, Simon P, Larousse C, Boissier JR (1971) Evaluation of a rapid technique for detecting minor tranquilizers. Neuropharmacology 10:459–469
Beck B, Fernette B, Stricker-Krongrad A (2005) Peptide S is a novel potent inhibitor of voluntary and fast-induced food intake in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 332:859–865
Bernier V, Stocco R, Bogusky MJ, Joyce JG, Parachoniak C, Grenier K, Arget M, Mathieu MC, O’Neill GP, Slipetz D, Crackower MA, Tan CM, Therien AG (2006) Structure–function relationships in the neuropeptide S receptor: molecular consequences of the asthma-associated mutation N107I. J Biol Chem 281:24704–24712
Borsini F, Lecci A, Volterra G, Meli A (1989) A model to measure anticipatory anxiety in mice? Psychopharmacology (Berl) 98:207–211
Boules M, Shaw A, Fredrickson P, Richelson E (2007) Neurotensin agonists: potential in the treatment of schizophrenia. CNS Drugs 21:13–23
Bourin M, Hascoet M, Mansouri B, Colombel MC, Bradwejn J (1992) Comparison of behavioral effects after single and repeated administrations of four benzodiazepines in three mice behavioral models. J Psychiatry Neurosci 17:72–77
Bouwknecht JA, Olivier B, Paylor RE (2007) The stress-induced hyperthermia paradigm as a physiological animal model for anxiety: a review of pharmacological and genetic studies in the mouse. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 31:41–59
Bystritsky A (2006) Treatment-resistant anxiety disorders. Mol Psychiatry 11:805–814
Cheng Y, Prusoff WH (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 22:3099–3108
Chiou LC, Liao YY, Fan PC, Kuo PH, Wang CH, Riemer C, Prinssen EP (2007) Nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide receptors: pharmacology and clinical implications. Curr Drug Targets 8:117–135
Cryan JF, Mombereau C, Vassout A (2005) The tail suspension test as a model for assessing antidepressant activity: review of pharmacological and genetic studies in mice. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:571–625
Gupte J, Cutler G, Chen JL, Tian H (2004) Elucidation of signaling properties of vasopressin receptor-related receptor 1 by using the chimeric receptor approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:1508–1513
Hascoet M, Bourin M, Colombel MC, Fiocco AJ, Baker GB (2000) Anxiolytic-like effects of antidepressants after acute administration in a four-plate test in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 65:339–344
Hunkeler W, Mohler H, Pieri L, Polc P, Bonetti EP, Cumin R, Schaffner R, Haefely W (1981) Selective antagonists of benzodiazepines. Nature 290:514–516
Kash SF, Tecott LH, Hodge C, Baekkeskov S (1999) Increased anxiety and altered responses to anxiolytics in mice deficient in the 65-kDa isoform of glutamic acid decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:1698–1703
Kinkead B, Nemeroff CB (2006) Novel treatments of schizophrenia: targeting the neurotensin system. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 5:205–218
Koob GF, Greenwell TN (2004) Neuropeptide S: a novel activating anxiolytic? Neuron 43:441–442
Malberg JE, Platt B, Rizzo SJ, Ring RH, Lucki I, Schechter LE, Rosenzweig-Lipson S (2007) Increasing the levels of insulin-like growth factor-i by an igf binding protein inhibitor produces anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:2360–2368
Mori M, Hayashi K, Miya H, Sato S, Kitada C, Matsumoto H, Nagi T, Shimomura T (2002) Novel polypeptide, DNA thereof and use of the same. European Patent EP1433849
Nielsen DM (2006) Corticotropin-releasing factor type-1 receptor antagonists: the next class of antidepressants? Life Sci 78:909–919
Olivier B, Zethof T, Pattij T, van Boogaert M, van Oorschot R, Leahy C, Oosting R, Bouwknecht A, Veening J, van der Gugten J, Groenink L (2003) Stress-induced hyperthermia and anxiety: pharmacological validation. Eur J Pharmacol 463:117–132
Pellow S, Chopin P, File SE, Briley M (1985) Validation of open:closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 14:149–67
Porsolt RD, Deniel M, Jalfre M (1979) Forced swimming in rats: hypothermia, immobility and the effects of imipramine. Eur J Pharmacol 57:431–436
Pulkkinen V, Majuri ML, Wang G, Holopainen P, Obase Y, Vendelin J, Wolff H, Rytila P, Laitinen LA, Haahtela T, Laitinen T, Alenius H, Kere J, Rehn M (2006) Neuropeptide S and G protein-coupled receptor 154 modulate macrophage immune responses. Hum Mol Genet 15:1667–1679
Rajarao SJ, Platt B, Sukoff SJ, Lin Q, Bender CN, Nieuwenhuijsen BW, Ring RH, Schechter LE, Rosenzweig-Lipson S, Beyer CE (2007) Anxiolytic-like activity of the non-selective galanin receptor agonist, galnon. Neuropeptides 41:307–320
Reinscheid RK (2007) Phylogenetic appearance of neuropeptide S precursor proteins in tetrapods. Peptides 28:830–837
Ring RH (2005) The central vasopressinergic system: examining the opportunities for psychiatric drug development. Curr Pharm Des 11:205–225
Ring RH, Malberg JE, Potestio L, Ping J, Boikess S, Luo B, Schechter LE, Rizzo S, Rahman Z, Rosenzweig-Lipson S (2006) Anxiolytic-like activity of oxytocin in male mice: behavioral and autonomic evidence, therapeutic implications. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 185:218–225
Roth AL, Marzola E, Rizzi A, Arduin M, Trapella C, Corti C, Vergura R, Martinelli P, Salvadori S, Regoli D, Corsi M, Cavanni P, Calo G, Guerrini R (2006) Structure-activity studies on neuropeptide S: identification of the amino acid residues crucial for receptor activation. J Biol Chem 281:20809–20816
Sakurai T, Amemiya A, Ishii M, Matsuzaki I, Chemelli RM, Tanaka H, Williams SC, Richarson JA, Kozlowski GP, Wilson S, Arch JR, Buckingham RE, Haynes AC, Carr SA, Annan RS, McNulty DE, Liu WS, Terrett JA, Elshourbagy NA, Bergsma DJ, Yanagisawa M (1998) Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell 92:1 (page following 696)
Shepherd JK, Grewal SS, Fletcher A, Bill DJ, Dourish CT (1994) Behavioural and pharmacological characterisation of the elevated “zero-maze” as an animal model of anxiety. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 116:56–64
Shimazaki T, Yoshimizu T, Chaki S (2006) Melanin-concentrating hormone MCH1 receptor antagonists: a potential new approach to the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. CNS Drugs 20:801–811
Smith KL, Patterson M, Dhillo WS, Patel SR, Semjonous NM, Gardiner JV, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR (2006) Neuropeptide S stimulates the hypothalamo–pituitary–adrenal axis and inhibits food intake. Endocrinology 147:3510–3518
Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B, Simon P (1985) The tail suspension test: a new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 85:367–370
Valdez GR (2006) Development of CRF1 receptor antagonists as antidepressants and anxiolytics: progress to date. CNS Drugs 20:887–896
Varty GB, Cohen-Williams ME, Hunter JC (2003) The antidepressant-like effects of neurokinin NK1 receptor antagonists in a gerbil tail suspension test. Behav Pharmacol 14:87–95
Vendelin J, Pulkkinen V, Rehn M, Pirskanen A, Raisanen-Sokolowski A, Laitinen A, Laitinen LA, Kere J, Laitinen T (2005) Characterization of GPRA, a novel G protein-coupled receptor related to asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 33:262–270
Xu YL, Reinscheid RK, Huitron-Resendiz S, Clark SD, Wang Z, Lin SH, Brucher FA, Zeng J, Ly NK, Henriksen SJ, de Lecea L, Civelli O (2004) Neuropeptide S: a neuropeptide promoting arousal and anxiolytic-like effects. Neuron 43:487–497
Xu YL, Gall CM, Jackson VR, Civelli O, Reinscheid RK (2007) Distribution of neuropeptide S receptor mRNA and neurochemical characteristics of neuropeptide S-expressing neurons in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 500:84–102
Zhang Y, Kowal D, Kramer A, Dunlop J (2003) Evaluation of FLIPR Calcium 3 Assay Kit—a new no-wash fluorescence calcium indicator reagent. J Biomol Screen 8:571–577
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leonard, S.K., Dwyer, J.M., Sukoff Rizzo, S.J. et al. Pharmacology of neuropeptide S in mice: therapeutic relevance to anxiety disorders. Psychopharmacology 197, 601–611 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1080-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1080-4