Abstract.
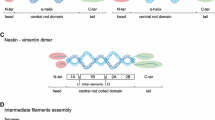
Tissue-specific progenitor cells are characterized by proliferation and differentiation, but, in contrast to embryonic stem (ES) cells, have limited capacities for self-renewal and no tumourigenic potential. These latter traits make progenitor cells an ideal source for regenerative cell therapies. In this review, we describe what is currently known about nestin, an intermediate filament first identified in neuroepithelial stem cells. During embryogenesis, nestin is expressed in migrating and proliferating cells, whereas in adult tissues, nestin is mainly restricted to areas of regeneration. We show that nestin is abundant in ES-derived progenitor cells that have the potential to develop into neuroectodermal, endodermal and mesodermal lineages. Although it remains unclear what factors regulate in vitro and in vivo expression of nestin, we conclude that nestin represents a characteristic marker of multi-lineage progenitor cells and suggest that its presence in cells may indicate multi-potentiality and regenerative potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 1 April 2004; received after revision 17 May 2004; accepted 8 June 2004
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiese, C., Rolletschek, A., Kania, G. et al. Nestin expression – a property of multi-lineage progenitor cells?. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 61, 2510–2522 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4144-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4144-6