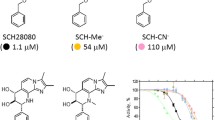
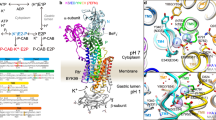
Abstract
The gastric H,K-ATPase, a member of the P2-type ATPase family, is the integral membrane protein responsible for gastric acid secretion. It is an α,β-heterodimeric enzyme that exchanges cytoplasmic hydronium with extracellular potassium. The catalytic α subunit has ten transmembrane segments with a cluster of intramembranal carboxylic amino acids located in the middle of the transmembrane segments TM4, TM5,TM6, and TM8. Comparison to the known structure of the SERCA pump, mutagenesis, and molecular modeling has identified these as constituents of the ion binding domain. The β subunit has one transmembrane segment with N terminus in cytoplasmic region. The extracellular domain of the β subunit contains six or seven N-linked glycosylation sites. N-glycosylation is important for the enzyme assembly, maturation, and sorting. The enzyme pumps acid by a series of conformational changes from an E1 (ion site in) to an E2 (ion site out) configuration following binding of MgATP and phosphorylation. Several experimental observations support the hypothesis that expulsion of the proton at 160 mM (pH 0.8) results from movement of lysine 791 into the ion binding site in the E2P configuration. Potassium access from the lumen depends on activation of a K and Cl conductance via a KCNQ1/KCNE2 complex and Clic6. K movement through the luminal channel in E2P is proposed to displace the lysine along with dephosphorylation to return the enzyme to the E1 configuration. This enzyme is inhibited by the unique proton pump inhibitor class of drug, allowing therapy of acid-related diseases.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Kaya S, Taniguchi K, Hayashi Y, Imagawa T, Kikumoto M, Oiwa K, Sakaguchi K (2005) Evidence for a relationship between activity and the tetraprotomeric assembly of solubilized pig gastric H/K-ATPase. J Biochem (Tokyo) 138:293–301
Andersson K, Carlsson E (2005) Potassium-competitive acid blockade: a new therapeutic strategy in acid-related diseases. Pharmacol Ther 108:294–307
Asano S, Yoshida A, Yashiro H, Kobayashi Y, Morisato A, Ogawa H, Takeguchi N, Morii M (2004) The cavity structure for docking the K(+)-competitive inhibitors in the gastric proton pump. J Biol Chem 279:13968–13975
Bamberg K, Mercier F, Reuben MA, Kobayashi Y, Munson KB, Sachs G (1992) cDNA cloning and membrane topology of the rabbit gastric H+/K(+)-ATPase alpha-subunit. Biochim Biophys Acta 1131:69–77
Besancon M, Shin JM, Mercier F, Munson K, Miller M, Hersey S, Sachs G (1993) Membrane topology and omeprazole labeling of the gastric H+,K(+)-adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry 32:2345–2355
Black JW, Duncan WAM, Durant CJ, Ganellin CR, Parsons ME (1972) Definition and antagonism of histamine H2 receptors. Nature 236:385–390
Burnay M, Crambert G, Kharoubi-Hess S, Geering K, Horisberger JD (2003) Electrogenicity of Na,K- and H,K-ATPase activity and presence of a positively charged amino acid in the fifth transmembrane segment. J Biol Chem 278:19237–19244
Codina J, Li J, Dubose TD Jr (2004) A carboxy-terminus motif of HKalpha2 is necessary for assembly and function. Kidney Int 66:2283–2292
Dammann HG, Burkhardt F (1999) Pantoprazole versus omeprazole: influence on meal-stimulated gastric acid secretion. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 11:1277–1282
Dempski RE, Hartung K, Friedrich T, Bamberg E (2006) Fluorometric measurements of intermolecular distances between the alpha- and beta-subunits of the Na+/K+-ATPase. J Biol Chem 281:36338–36346
Fellenius E, Berglindh T, Sachs G, Olbe L, Elander B, Sjostrand SE, Wallmark B (1981) Substituted benzimidazoles inhibit gastric acid secretion by blocking (H+ + K+)ATPase. Nature 290:159–161
Ferron GM, McKeand W, Mayer PR (2001) Pharmacodynamic modeling of pantoprazole’s irreversible effect on gastric acid secretion in humans and rats. J Clin Pharmacol 41:149–156
Forte JG, Forte TM, Black JA, Okamoto C, Wolosin JM (1983) Correlation of parietal cell structure and function. J Clin Gastroenterol 5(Suppl 1):17–27
Galmiche JP, Bruley Des Varannes S, Ducrotte P, Sacher-Huvelin S, Vavasseur F, Taccoen A, Fiorentini P, Homerin M (2004) Tenatoprazole, a novel proton pump inhibitor with a prolonged plasma half-life: effects on intragastric pH and comparison with esomeprazole in healthy volunteers. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 19:655–662
Gedda K, Scott D, Besancon M, Lorentzon P, Sachs G (1995) Turnover of the gastric H+,K(+)-adenosine triphosphatase alpha subunit and its effect on inhibition of rat gastric acid secretion. Gastroenterology 109:1134–1141
Grishin AV, Caplan MJ (1998) ATP1AL1, a member of the non-gastric H,K-ATPase family, functions as a sodium pump. J Biol Chem 273:27772–27778
Han KS, Kim YG, Yoo JK, Lee JW, Lee MG (1998) Pharmacokinetics of a new reversible proton pump inhibitor, YH1885, after intravenous and oral administrations to rats and dogs: hepatic first-pass effect in rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos 19:493–500
Hersey SJ, Steiner L, Mendlein J, Rabon E, Sachs G (1988) SCH28080 prevents omeprazole inhibition of the gastric H+/K+-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta 956:49–57
Im WB, Blakeman DP, Davis JP (1985) Irreversible inactivation of rat gastric (H+–K+)-ATPase in vivo by omeprazole. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 126:78–82
Ito K, Kinoshita K, Tomizawa A, Inaba F, Morikawa-Inomata Y, Makino M, Tabata K, Shibakawa N (2007) Pharmacological profile of novel acid pump antagonist 7-(4-fluorobenzyloxy)-2,3-dimethyl-1-{[(1S,2S)-2-methyl cyclopropyl]methyl}-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyridazine (CS-526). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 323:308–317
Kahrilas PJ, Dent J, Lauritsen K, Malfertheiner P, Denison H, Franzen S, Hasselgren G (2007) A randomized, comparative study of three doses of AZD0865 and esomeprazole for healing of reflux esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:1385–1391
Kaminski JJ, Bristol JA, Puchalski C, Lovey RG, Elliott AJ, Guzik H, Solomon DM, Conn DJ, Domalski MS, Wong SC, Gold EH, Long JF, Chiu PJ, Steinberg M, McPhail AT (1985) Antiulcer agents. 1. Gastric antisecretory and cytoprotective properties of substituted imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines. J Med Chem 28:876–892
Katashima M, Yamamoto K, Tokuma Y, Hata T, Sawada Y, Iga T (1998) Comparative pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis of proton pump inhibitors omeprazole, lansoprazole and pantoprazole, in humans. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 23:19–26
Kirchhoff P, Andersson K, Socrates T, Sidani S, Kosiek O, Geibel JP (2006) Characteristics of the K+-competitive H+,K+-ATPase inhibitor AZD0865 in isolated rat gastric glands. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 291:G838–G843
Lambrecht NW, Yakubov I, Scott D, Sachs G (2005) Identification of the K efflux channel coupled to the gastric H–K-ATPase during acid secretion. Physiol Genomics 21:81–91
Maeda M, Ishizaki J, Futai M (1988) cDNA cloning and sequence determination of pig gastric (H+ + K+)-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 157:203–209
Maeda M, Oshiman K, Tamura S, Futai M (1990) Human gastric (H+ + K+)-ATPase gene. Similarity to (Na+ + K+)-ATPase genes in exon/intron organization but difference in control region. J Biol Chem 265:9027–9032
Melle-Milovanovic D, Milovanovic M, Nagpal S, Sachs G, Shin JM (1998) Regions of association between the alpha and the beta subunit of the gastric H,K-ATPase. J Biol Chem 273:11075–11081
Mizukawa Y, Nishizawa T, Nagao T, Kitamura K, Urushidani T (2002) Cellular distribution of parchorin, a chloride intracellular channel-related protein, in various tissues. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282:C786–C795
Morth JP, Pedersen BP, Toustrup-Jensen MS, Sorensen TL, Petersen J, Andersen JP, Vilsen B, Nissen P (2007) Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump. Nature 450:1043–1049
Munson KB, Gutierrez C, Balaji VN, Ramnarayan K, Sachs G (1991) Identification of an extracytoplasmic region of H+,K(+)-ATPase labeled by a K(+)-competitive photoaffinity inhibitor. J Biol Chem 266:18976–18988
Munson K, Vagin O, Sachs G, Karlish S (2003) Molecular modeling of SCH28080 binding to the gastric H,K-ATPase and MgATP interactions with SERCA- and Na,K-ATPases. Ann N Y Acad Sci 986:106–110
Munson K, Garcia R, Sachs G (2005) Inhibitor and ion binding sites on the gastric H,K-ATPase. Biochemistry 44:5267–5284
Munson K, Law RJ, Sachs G (2007) Analysis of the gastric H,K ATPase for ion pathways and inhibitor binding sites. Biochemistry 46:5398–5417
Olesen C, Picard M, Winther AM, Gyrup C, Morth JP, Oxvig C, Moller JV, Nissen P (2007) The structural basis of calcium transport by the calcium pump. Nature 450:1036–1042
Purhonen P, Thomsen K, Maunsbach AB, Hebert H (2006) Association of renal Na,K-ATPase alpha-subunit with the beta- and gamma-subunits based on cryoelectron microscopy. J Membr Biol 214:139–146
Rabon EC, McFall TL, Sachs G (1982) The gastric [H,K]ATPase:H+/ATP stoichiometry. J Biol Chem 257:6296–6299
Reenstra WW, Forte JG (1981) H+/ATP stoichiometry for the gastric (K+ + H+)-ATPase. J Membr Biol 61:55–60
Reenstra WW, Crothers J Jr, Forte JG (2007) The conformation of H,K-ATPase determines the nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) selectivity for active proton transport. Biochemistry 46:10145–10152
Reuben MA, Lasater LS, Sachs G (1990) Characterization of a beta subunit of the gastric H+/K(+)-transporting ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87:6767–6771
Sachs G, Chang HH, Rabon E, Schackman R, Lewin M, Saccomani G (1976) A nonelectrogenic H+ pump in plasma membranes of hog stomach. J Biol Chem 251:7690–7698
Sachs G, Shin JM, Besancon M, Prinz C (1993) The continuing development of gastric acid pump inhibitors. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 7:4–12; discussion 29-31
Sachs G, Shin JM, Howden CW (2006) Review article: the clinical pharmacology of proton pump inhibitors. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 23(Suppl 2):2–8
Sachs G, Shin JM, Vagin O, Lambrecht N, Yakubov I, Munson K (2007) The gastric H,K ATPase as a drug target: past, present, and future. J Clin Gastroenterol 41:S226–S242
Sawaguchi A, Aoyama F, Ide S, Suganuma T (2005) The cryofixation of isolated rat gastric mucosa provides new insights into the functional transformation of gastric parietal cells: an in vitro experimental model study. Arch Histol Cytol 68:151–160
Shin JM, Sachs G (1994) Identification of a region of the H,K-ATPase alpha subunit associated with the beta subunit. J Biol Chem 269:8642–8646
Shin JM, Sachs G (2002) Restoration of acid secretion following treatment with proton pump inhibitors. Gastroenterology 123:1588–1597
Shin JM, Sachs G (2004) Differences in binding properties of two proton pump inhibitors on the gastric H+,K+-ATPase in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol 68:2117–2127
Shin JM, Besancon M, Simon A, Sachs G (1993) The site of action of pantoprazole in the gastric H+/K(+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1148:223–233
Shin JM, Cho YM, Sachs G (2004) Chemistry of covalent inhibition of the gastric (H+, K+)-ATPase by proton pump inhibitors. J Am Chem Soc 126:7800–7811
Shin JM, Grundler G, Senn-Bilfinger J, Simon WA, Sachs G (2005) Functional consequences of the oligomeric form of the membrane-bound gastric H,K-ATPase. Biochemistry 44:16321–16332
Shin JM, Homerin M, Domagala F, Ficheux H, Sachs G (2006) Characterization of the inhibitory activity of tenatoprazole on the gastric H+,K+-ATPase in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol 71:837–849
Shull GE (1990) cDNA cloning of the beta-subunit of the rat gastric H,K-ATPase. J Biol Chem 265:12123–12126
Shull GE, Lingrel JB (1986) Molecular cloning of the rat stomach (H+ + K+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem 261:16788–16791
Simon WA, Herrmann M, Klein T, Shin JM, Huber R, Senn-Bilfinger J, Postius S (2007) Soraprazan: setting new standards in inhibition of gastric acid secretion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321:866–874
Skrabanja AT, Asty P, Soumarmon A, Joep J, de Pont HH, Lewin MJ (1986) H+ transport by reconstituted gastric (H+ + K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta 860:131–136
Song I, Mortell MP, Gantz I, Brown DR, Yamada T (1993) Molecular cloning and structural analysis of canine gastric H+,K(+)-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 196:1240–1247
Swarts HG, Koenderink JB, Willems PH, Krieger E, De Pont JJ (2005) Asn792 participates in the hydrogen bond network around the K+-binding pocket of gastric H,K-ATPase. J Biol Chem 280:11488–11494
Sweadner KJ, Donnet C (2001) Structural similarities of Na,K-ATPase and SERCA, the Ca(2+)-ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J 356:685–704
Toh BH, Gleeson PA, Simpson RJ, Moritz RL, Callaghan JM, Goldkorn I, Jones CM, Martinelli TM, Mu FT, Humphris DC et al (1990) The 60- to 90-kDa parietal cell autoantigen associated with autoimmune gastritis is a beta subunit of the gastric H+/K(+)-ATPase (proton pump). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87:6418–6422
Toyoshima C, Nakasako M, Nomura H, Ogawa H (2000) Crystal structure of the calcium pump of sarcoplasmic reticulum at 2.6 A resolution. Nature 405:647–655
Toyoshima C, Asahi M, Sugita Y, Khanna R, Tsuda T, MacLennan DH (2003) Modeling of the inhibitory interaction of phospholamban with the Ca2+ ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:467–472
Toyoshima C, Nomura H, Sugita Y (2003) Crystal structures of Ca2+-ATPase in various physiological states. Ann N Y Acad Sci 986:1–8
Vagin O, Munson K, Lambrecht N, Karlish SJ, Sachs G (2001) Mutational analysis of the K+-competitive inhibitor site of gastric H,K-ATPase. Biochemistry 40:7480–7490
Vagin O, Denevich S, Munson K, Sachs G (2002) SCH28080, a K+-competitive inhibitor of the gastric H,K-ATPase, binds near the M5-6 luminal loop, preventing K+ access to the ion binding domain. Biochemistry 41:12755–12762
Vagin O, Denevich S, Sachs G (2003) Plasma membrane delivery of the gastric H,K-ATPase: the role of beta-subunit glycosylation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 285:C968–C976
Vagin O, Turdikulova S, Sachs G (2004) The H,K-ATPase beta subunit as a model to study the role of N-glycosylation in membrane trafficking and apical sorting. J Biol Chem 279:39026–39034
Vagin O, Turdikulova S, Yakubov I, Sachs G (2005) Use of the H,K-ATPase beta subunit to identify multiple sorting pathways for plasma membrane delivery in polarized cells. J Biol Chem 280:14741–14754
Wallmark B, Sachs G, Mardh S, Fellenius E (1983) Inhibition of gastric (H+ + K+)-ATPase by the substituted benzimidazole, picoprazole. Biochim Biophys Acta 728:31–38
Wallmark B, Larsson H, Humble L (1985) The relationship between gastric acid secretion and gastric H+,K+-ATPase activity. J Biol Chem 260:13681–13684
Wallmark B, Briving C, Fryklund J, Munson K, Jackson R, Mendlein J, Rabon E, Sachs G (1987) Inhibition of gastric H+,K+-ATPase and acid secretion by SCH 28080, a substituted pyridyl(1,2a)imidazole. J Biol Chem 262:2077–2084
Wolosin JM, Forte JG (1985) K+ and Cl− conductances in the apical membrane from secreting oxyntic cells are concurrently inhibited by divalent cations. J Membr Biol 83:261–272
Yu KS, Bae KS, Shon JH, Cho JY, Yi SY, Chung JY, Lim HS, Jang IJ, Shin SG, Song KS, Moon BS (2004) Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of a novel proton pump inhibitor, YH1885, in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 44:73–82
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00424-010-0907-0
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, J.M., Munson, K., Vagin, O. et al. The gastric HK-ATPase: structure, function, and inhibition. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 457, 609–622 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0495-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0495-4