Abstract
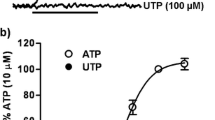
The actions of monovalent and divalent ions on the P2X7 receptor have been assessed by measuring their effect on responses to the P2 receptor agonist, 2’- and 3’-O-(4-benzoyl-benzoyl)-ATP (DbATP), in HEK293 cells expressing the human recombinant P2X7 receptor. In these cells, DbATP increased the cellular accumulation of the DNA binding, fluorescent dye, YO-PRO-1. The potency of DbATP to elicit this effect was decreased by both calcium and magnesium ions. In addition, when the pH was increased above 8 or reduced below 6.5, the potency of DbATP was less than obtained at pH 7.5. Monovalent ions also affected the P2X7 receptor such that the potency of DbATP was 19-fold higher in NaCl-free buffer containing 280 mM sucrose (pEC50=6.48) than in 140 mM NaCl containing buffer (pEC50=5.19). Monovalent cations differentially affected the potency of DbATP. Thus, when the chloride concentration was maintained at 140 mM, pEC50 values for DbATP were 6.14, 5.87 and 5.19 when the counter cation was 140 mM choline, potassium or sodium, respectively. Monovalent anions also differentially affected the potency of DbATP and in the presence of 140 mM sodium ions, pEC50 values for DbATP were 6.14, 6.07, 5.19 and 4.53, respectively, when the counter anion was 140 mM aspartate, glutamate, chloride or iodide. The inhibitory effect of monovalent anions on P2X7 receptor function was also observed in electrophysiological studies. Thus in sodium glutamate containing buffer the potency of DbATP (pEC50=5.55) was approximately 22-fold higher than in NaCl containing buffer (pEC50=4.20). This study has demonstrated that P2X7 receptor function can be markedly affected by a wide range of ions and that physiological concentrations of sodium and chloride ions, as well as divalent cations, contribute to the low potency of ATP as an agonist at this receptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 27 July 1998 / Accepted: 18 November 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michel, A., Chessell, I. & Humphrey, P. Ionic effects on human recombinant P2X7 receptor function. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 359, 102–109 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005328
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005328