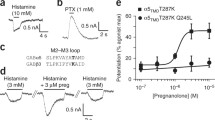
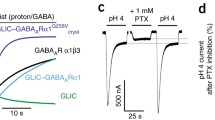
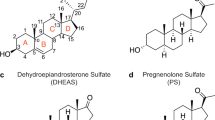
Summary
1. The pioneering work of Hans Selye over 50 years ago demonstrated that certain steroid metabolites can produce a rapid depression of central nervous system activity.
2. Research during the last 10 years has established that such effects are mediated by a nongenomic and specific interaction of these steroids with the brain's major inhibitory receptor, the GABAA receptor.
3. Here we describe the molecular mechanism of action of such steroids and review attempts to define the steroid binding site on the receptor protein. The therapeutic potential of such neurosteroids is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Backus, K. H., Arigoni, M., Drescher, U., Scheurer, L., Malherbe, P., Möhler, H., and Benson, J. A. (1993). Stoichiometry of a recombinant GABAA receptor deduced from mutation-induced rectification.NeuroReport 5285–288.
Barker, J. L., Harrison, N. L., Lange, G. D., and Owen, D. G. (1987). Potentiation of γ-aminobutyric-acid-activated chloride conductance by a steroid anaesthetic in cultured rat spinal neurones.J. Physiol. 386485–501.
Belelli, D., Lambert, J. J., Peters, J. A., Lan, N. C., and Gee, K. W. (1994a). Modulation of mammalian GABAA receptors by the neurosteroid 5α-pregnan-3α,20α-diol.Br. J. Pharmacol. 111:182P.
Belelli, D., Lambert, J. J., Peters, J. A., Lan, N. C., and Gee, K. W. (1994b). Modulation of human (α1β1γ2L) recombinant GABAA receptors by pregnanediols.Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 72339.
Belelli, D., Callachan, H., Lambert, J. Peters, J. A., Hill-Venning, C., and Lan, N. C. (1994c). A comparative study of the influence of allosteric modulators upon human (α3β1γ2L) andDrosophila recombinant GABA receptors.Br. J. Pharmacol. 112:257P.
Bertrand, P. P., and Galligan, J. J. (1992). Alfaxalone, pentobarbital and diazepam potentiate γ-aminobutyric acid-induced depolarizations in single myenteric neurons of guinea-pig intestine.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 262677–682.
Bormann, J. (1987). Electrophysiology of GABAA and GABAB receptor subtypes.Trends Neurosci. 11112–116.
Bormann, J., and Clapham, D. E. (1985). γ-Aminobutyric acid receptor channels in adrenal chromaffin cells: A patch-clamp study.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 822168–2172.
Bureau, M., and Olsen, R. W. (1990). Multiple distinct subunits of the γ-aminobutyric acid-A receptor protein show different ligand binding affinities.Mol. Pharmacol. 37497–502.
Callachan, H., Cottrell, G. A., Hather, N. Y., Lambert, J. J., Nooney, J. M., and Peters, J. A. (1987). Modulation of the GABAA receptor by progesterone metabolites.Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 231359–369.
Carboni, E., Wieland, S., Lan, N. C., and Gee, K. W. (1994). Effect of endogenously occurring pregnandiols in animal models of anxiety.Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 72449.
Carl, P., Høgskilde, S., Lang-Jensen, T., Bach, V., Jacobsen, J., Sorensen, M. B., Gralls, M., and Widlund, L. (1994). Pharmacokinetics and pharamcodynamics of eltanolone (pregnanolone), a new steroid intravenous anaesthetic, in humans.Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 38734–741.
Celotti, F., Melcangi, R. C., and Martini, L. (1992). The 5α-reductase in the brain: Molecular aspects and relation to brain function.Front. Neuroendocrinol. 13163–215.
Chen, R., Belelli, D., Lambert, J. J., Peters, J. A., Reyes, A., and Lan, N. C. (1994). Cloning and functional expression of aDrosophila γ-aminobutyric acid receptor.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 916069–6074.
Chvátal, A., and Kettenman, H. (1991). Effects of steroids on γ-aminobutyrate-induced currents in cultured rat astrocytes.Pflugers Arch. 419263–266.
Cottrell, G. A., Lambert, J. J., and Peters, J. A. (1987). Modulation of GABAA receptor activity by alphaxalone.Br. J. Pharmacol. 90491–501.
Ebert, B., Wafford, K. A., Whiting, P. J., Krogsgaard-Larsen, P., and Kemp, J. A. (1994). Molecular pharmacology of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor agonists and partial agonists in oocytes injected with different α, β and γ receptor subunit combinations.Mol. Pharmacol. 46957–963.
Ennis, C., and Minchin, M. C. W. (1993). Modulation of the GABAA-like autoreceptor by barbiturates but not by steroids.Neuropharmacology 32355–357.
ffrench-Constant, R. H., Rocheleau, T. A., Steichen, J. C., and Chalmers, A. E. (1993). A point mutation in aDrosophila GABA receptor confers insecticide resistance.Nature 363449–451.
ffrench-Mullen, J. M. H., Danks, P., and Spence, K. (1994). Neurosteroids modulate calcium currents in hippocampal CA1 neurons via a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein-coupled mechanism.J. Neurosci. 141963–1977.
Figdor, S. K., Kodet, M. T., Bloom, B. M., Agnello, E. J., P'An, S. Y., and Laubach, G. D. (1957). Central activity and structure in a series of water soluble steroids.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 119299–309.
Galzi, J.-L., and Changeux, J.-P. (1994). Neurotransmitter-gated ion channels as unconventional allosteric proteins.Current Opin. Struct. Biol. 4554–565.
Gee, K. W., Bolger, M. B., Brinton, R. E., Coirini, H., and McEwen, B. S. (1988). Steroid regulation of the chloride ionophore in rat brain: Structure activity requirements, regional dependence and mechanism of action.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 241346–353.
Gee, K. W., McCauley, L., and Lan, N. C. (1995). A putative receptor for neurosteroids on the GABAA receptor complex; The pharmacological properties and thereapeutic potential of epalons.Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 9207–227.
Gyenes, M., Wang, Q., Gibbs, T., and Farb, D. H. (1994). Phosphorylation factors control neurotransmitter and neuromodulator actions at the γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor.Mol. Pharmacol. 46542–549.
Hadingham, K. L., Wingrove, P. B., Wafford, K. A., Bain, C., Kemp, J. A., Palmer, K. J., Wilson, A. W., Wilcox, A. S., Sikela, J. M., Ragan, C. I., and Whiting, P. J. (1993). Role of the β subunit in determining the pharmacology of human γ-aminobutyric type A receptors.Mol. Pharmacol. 441211–1218.
Harris, B. D., Wang, G., Moody, E. J., and Skolnick, P. (1995). Different subunit requirements for volatile and nonvolatile anesthetics at γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors.Mol. Pharmacol. 47363–367.
Harrison, N. L., and Simmonds, M. A. (1984). Modulation of the GABAA receptor complex by a steroid anaesthetic.Brain Res. 323287–292.
Harrison, N. L., Majewska, M. D., Harrington, J. W., and Barker, J. L. (1987a). Structure activity relationships for steroid interaction with the γ-amino-butyric acidA receptor complex.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 241346–353.
Harrison, N. L., Vicini, S., and Barker, J. L. (1987b). A steroid anaesthetic prolongs inhibitory postsynaptic currents in cultured rat hippocampal neurons.J. Neurosci. 7604–609.
Hawkinson, J. E., Kimbrough, C. L., McCauley, L. D., Bolger, M. B., Lan, N. C., and Gee, K. W. (1994a). The neuroactive steroid 3α-hydroxy-5β-pregnan-20-one is a two-component modulator of ligand binding to the GABAA receptor.Eur. J. Pharmacol. (Mol. Pharmacol. Sect.) 269157–163.
Hawkinson, J. E., Kimbrough, C. L., Belelli, D., Lambert, J. J., Purdy, R. H., and Lan, N. C. (1994b). Correlation of neuroactive steroid modulation of [35S]t-butylbicyclophosphorothionate and [3H]flunitrazepam binding and γ-aminobutyric acidA receptor function.Mol. Pharmacol. 46977–985.
Hill-Venning, C., Lambert, J. J., Peters, J. A., and Hales, T. G. (1991). The actions of neurosteroids on inhibitory amino acid receptors. InNeurosteroids and Brain Function, Fidia Research Symposium Series Vol. 8 (E. Costa and S. M. Paul, Eds), Thieme, New York, pp. 77–85.
Hill-Venning, C., Lambert, J. J., Peters, J. A., Hales, T. G., Gill, C., Callachan, H., and Sturgess, N. C. (1992). The actions of endogenous and synthetic pregnane steroids on GABAA receptors. InGABAergic Synaptic Transmission. Molecular, Pharmacological and Clinical Aspects, Advances in Biochemical Psychopharmacology Vol. 47 (G. Biggio, A. Concas, and E. Costa, Eds.), Raven Press, New York, pp. 93–102.
Hill-Venning, C., Callachan, H., Peters, J. A., Lambert, J. J., Gemmell, D. K., and Campbell, A. C. (1994a). Modulation of the GABAA receptor by ORG20599: A water-soluble pregnane steroid.Br. J. Pharmacol. 111:183P.
Hill-Venning, C., Callachan, H., Peters, J. A., Lambert, J. J., Gemmell, D. K., Campbell, A. C., Anderson, A., Byford, A., and Marshall, R. J. (1994b). The novel water soluble steroid ORG 20599 modulates GABAA receptors.Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 72 (Suppl. 1):340.
Hill-Venning, C., Belelli, D., Peters, J. A., and Lambert, J. J. (1994c). Electrophysiological studies of neurosteroid modulation of the γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor. InNeurobiology of Steroids, Methods in Neurosciences Vol. 22, (R. de Kloet and W. Sutanto, Eds.), Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 446–467.
Kirkness, E. F., and Fraser, C. M. (1993). A strong promoter element is located between alternative exons of a gene encoding the GABRβ3 subunit (GABRB3).J. Biol. Chem. 2684420–4428.
Korpi, E. R., and Lüddens, H. (1993). Regional γ-aminobutyric acid sensitivity of t-butylbicyclophosphorol[35S]thionate binding depends upon γ-aminobutyric acidA receptor α subunit.Mol. Pharmacol. 4487–92.
Lambert, J. J., Peters, J. A., and Cottrell, G. A. (1987). Actions of synthetic and endogenous steroids on the GABAA receptor.Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 8224–227.
Lambert, J. J., Peters, J. A., Sturgess, N. C., and Hales, T. G. (1990). Steroid modulation of the GABAA receptor complex: Electrophysiological studies. InSteroids and Neuronal Activity, CIBA Foundation Symposium 153 (K. Widdows and D. Chadwick, Eds.), Wiley Chichester, pp. 56–82.
Lambert, J. J., Hill-Venning, C., Peters, J. A., Sturgess, N. C., and Hales, T. G. (1991). The actions of anesthetic steroids on inhibitory and excitatory aminno acid receptors. InTransmitter Amino Acid Receptors: Structure, Transduction and Models for Drug Development. Fidia Research Foundation Symposium Series Vol. 6 (E. A. Barnard and E. Costa, Eds.), Thieme, New York, pp. 219–236.
Lan, N. C., Gee, K. W., Bolger, M. B., and Chen, J. S. (1991). Differential responses of expressed recombinant human γ-aminobutyric acidA receptors to neurosteroids.J. Neurochem. 571818–1821.
Laurie, D. J., Seeburg, P. H., and Wisden, W. (1992). The distribution of 13 GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in rat brain. II. Olfactory bulb and cerebellum.J. Neurosci. 121063–1076.
Lin, L. H., Whiting, P., and Harris, R. A. (1993). Molecular determinants of general anaesthetic action: Role of GABAA receptor structure.J. Neurochem. 601548–1553.
Lüddens, H., Korpi, E. R., and Seeburg, P. H. (1995). GABAA/benzodiazepine receptor heterogeneity: Neurophysiological implications.Neuropharmacology 34245–254.
MacDonald, R. L., and Olsen, R. W. (1994). GABAA receptor channels.Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 17569–602.
MacDonald, R. L., Rogers, C. J., and Twyman, R. E. (1989). Barbiturate modulation of kinetic properties of the GABAA receptor channel of mouse spinal neurones in culture.J. Physiol. 417483–5000.
Majewska, M. D. (1992). Neurosteroids: Endogenous bimodal modulators of the GABAA receptor. Mechanism of action and physiological significance.Prog. Neurobiol. 38379–395.
Majewska, M. D., Mienville, J.-M., and Vicini, S. (1987). Neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate antagonises electrophysiological responses to GABA in neurons.Neurosci. Lett. 90279–284.
Makriyannis, A., Yang, D.-P., and Mavromoustakos, T. (1990). The molecular features of membrane perturbation by anaesthetic steroids: A study using differential scanning calorimetry, small angle X-ray diffraction and solid state2H NMR. InSteroids and Neuronal Activity, CIBA Foundation Symposium 153 (K. Widdows and D. Chadwick, Eds.), Wiley, Chichester, pp. 172–189.
McCauley, L. D., and Gee, K. W. (1994). Detection and characterization of epalon receptors: Novel recognition sites for neuroactive steroids that modulate the GABAA receptor complex. InNeurobiology of Steroids, Methods in Neurosciences Vol. 22 (R. de Kloet and W. Sutanto, eds.), Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 211–225.
McCauley, L. D., Liu, V., Chen, J.-S., Hawkinson, J. E., Lan, N. C., and Gee, K. W. (1995). Selective actions of certain neuroactive pregnanediols at the γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor complex in rat brain.Mol. Pharmacol. 47354–362.
McNeil, R. G., Gee, K. W., Bolger, M. B., Lan, N. C., Wieland, S., Belelli, D., Purdy, R. H., and Paul, S. M. (1992). Neuroactive steroids that act at GABAA receptors.Drugs News Perspect.5145–152.
Melcangi, R. C., Celotti, F., and Martini, L. (1994). Progesterone 5-α reduction in neuronal and in different types of glial cell cultures: type 1 and 2 astrocytes and oligodendrocytes.Brain Res. 639202–206.
Mienville, J. M., and Vicini, S. (1989). Pregnenolone sulfate antagonizes GABAA receptor-mediated currents via a reduction of channel opening frequency.Brain Res. 489190–194.
Mody, I., De Koninck, Y., Otis, T. S., and Soltesz, I. (1994). Bridging the cleft at GABA synapses in the brain.Trends Neurosci. 17517–525.
Morrow, L. A., Pace, J. R., Purdy, R. H., and Paul, S. M. (1990). Characterization of steroid interactions with γ-aminobutyric acid receptor-gated chloride ion channels: Evidence for multiple steroid recognition sites.Mol. Pharmacol. 37263–269.
Nayeem, N., Green, T. P., Martin, I. L., and Barnard, E. A. (1994). Quaternary structure of the native GABAA receptor determined by electron microscopic image analysis.J. Neurochem. 62815–818.
Nguyen, Q., Sapp, D. W., Van Ness, P. C., and Olsen, R. W. (1995). Modulation of GABAA receptor binding in human brain by neuroactive steroids: Species and brain regional differences.Synapse 1977–87.
Oliver, A. E., Deamer, D. W., and Akeson, M. (1991). Evidence that sensitivity to steroid anesthetics appears late in evolution.Brain Res. 557298–302.
Olsen, R. W., and Sapp, D. W. (1995). Neuroactive steroid modulation of GABAA receptors. InGABA A Receptors and Anxiety; From Neurobiology to Treatment (G. Biggio, E. Sanna, M. Serra, and E. Costa, Eds.), Raven Press, New York, pp. 57–74.
Ong, J., Kerr, D. I. B., and Johnston, G. A. R. (1987). Cortisol: A potent biphasic modulator at GABAA-receptor complexes in the guinea-pig isolated ileum.Neurosci. Lett. 82101–106.
Paul, S. M., and Purdy, R. H. (1992). Neuroactive steroids.FASEB J. 62311–2322.
Peters, J. A., Kirkness, E. F., Callachan, H., Lambert, J. J., and Turner, A. J. (1988). Modulation of the GABAA receptor by depressant barbiturates and pregnane steroids.Br. J. Pharmacol. 941257–1269.
Peters, J. A., Lambert, J. J., and Cottrell, G. A. (1989). An electrophysiological investigation of the characteristics and function of GABAA receptors on bovine adrenomedullary chromaffin cells.Pflugers Arch. 41595–103.
Prince, R. J., and Simmonds, M. A. (1992). Steroid modulation of the strychnine-sensitive glycine receptor.Neuropharmacology 31201–205.
Prince, R. J., and Simmonds, M. A. (1993). Differential antagonism by epipregnanolone of alphaxalone and pregnanolone potentiation of [3H]flunitrazepam binding suggests more than one class of binding site for steroids at GABAA receptors.Neuropharmacology 3259–63.
Puia, G., Santi, M. R., Vicini, S., Pritchett, D. B., Purdy, R. H., Paul, S. M., Seeburg, P. H., and Costa, E. (1990). Neurosteroids act on recombinant human GABAA receptors.Neuron 4759–765.
Puia, G., Ducic, I., Vicini, S., and Costa, E. (1993). Does neurosteroid modulatory efficacy depend upon GABAA receptor subunit composition?Receptors Channels 1135–142.
Quirk, K., Gillard, N. P., Ragan, I. C., Whiting, P. J., and McKernan, R. M. (1994). γ-Aminobutyric acid type A receptors in the rat brain can contain bothγ2 andγ3 subunits, butγ1 does not exist in combination with anotherγ subunit.Mol. Pharmacol. 451061–1070.
Rauh, J. J., Lummis, S. C. R., and Sattelle, D. B. (1990). Pharmacological and biochemical properties of insect GABA receptors.Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 11325–329.
Robel, P., and Baulieu, E.-E. (1994). Neurosteroids: biosynthesis and function. InNeurobiology of Steroids, Methods in Neurosciences Vol. 22 (R. de Kloet and W. Sutanto, Eds.), Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 36–50.
Rogers, C. J., Twyman, R. E., and MacDonald, R. L. (1994). Benzodiazepine andβ-carboline regulation of single GABAA receptor channels of mouse spinal neurones in culture.J. Physiol. 475(1):69–82.
Selye, H. (1941). Anaesthetic effects of steroid hormones.Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 46116–121.
Shimada, S., Cutting, G., and Uhl, G. R. (1992).γ-Aminobutyric acid A or C recptor?γ-Aminobutyric acidρ1 receptor RNA induces bicuculline-, barbiturate-, and benzodiazepine-insensitiveγ-aminobutyric acid responses inXenopus oocytes.Mol. Pharmacol. 41683–687.
Shingai, R., Sutherland, M. L., and Barnard, E. A. (1991). Effects of subunit types of the cloned GABAA receptor on the response to a neurosteroid.Eur. J. Pharmacol. (Mol. Pharmacol. Sect.) 20677–80.
Sieghart, W. (1992). GABAA receptors: Ligand-gated Cl− ion channels modulated by multiple drug-binding sites.Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 13445–450.
Simmonds, M. A. (1991). Modulation of the GABAA receptor by steroids.Semin. Neurosci. 3231–239.
Sivilotti, L., and Nistri, A. (1991). GABA receptor mechanisms in the central nervous system.Prog. Neurobiol. 3635–92.
Smith, S. (1994). Female sex steroid hormones: From receptors to networks to performance-actions on the sensorimotor system.Prog. Neurobiol. 4455–86.
Turner, D. M., Ransom, R. W., Yang, J. S.-J., and Olsen, R. W. (1989). Steroid anesthetics and naturally occurring analogs modulate theγ-aminobutyric acid receptor complex at a site distinct from barbiturates.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 248960–966.
Twyman, R. E., and MacDonald, R. L. (1992). Neurosteroid regulation of GABAA receptor single channel kinetic properties of mouse spinal cord neurones in culture.J. Physiol. 456215–245.
Tyndale, R. F., Olsen, R. W., and Tobin, A. J. (1995). GABAA receptors. InHandbook of Receptors and Channels; Ligand- and Voltage-Gated Ion Channels (R. A. North, Ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 265–290.
Valeyev, A. Y., Barker, J. L., Cruciani, R. A., Lange, D. G., Smallwood, V. V., and Mahan, L. C. (1993). Characterization of theγ-aminobutyric acidA receptor-channel complex composed ofα1β2 andα1β3 subunits from rat brain.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 265985–991.
Wingrove, P. B., Wafford, K. A., Bain, C., and Whiting, P. J. (1994). The modulatory action of loreclezole at theγ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor is determined by a single amino acid in theβ2 andβ3 subunit.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 914569–4573.
Woodward, R. M., Polenzani, L., and Miledi, R. (1992). Effects of steroids onγ-aminobutyric acid receptors expressed inXenopus oocytes by poly(A)+ RNA from mammalian brain and retina.Mol. Pharmacol. 4189–103.
Zaman, S. H., Shingai, R., Harvey, R. J., Darlison, M. G., and Barnard, E. A. (1992). Effects of subunit types of the recombinant GABAA receptor on the response to a neurosteroid.Eur. J. Pharmacol. (Mol. Pharmacol. Sect.) 225321–330.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lambert, J.J., Belelli, D., Hill-Venning, C. et al. Neurosteroid modulation of native and recombinant GABAA receptors. Cell Mol Neurobiol 16, 155–174 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02088174
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02088174