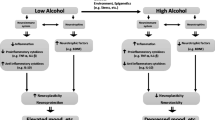
Abstract
A potential role for nitric oxide in alcohol-induced changes in brain function is discussed. Chronic alcohol exposure may lead to excitotoxicity partially due to increased levels of nitric oxide (NO). Excessive NO has been linked to cytotoxicity in neurons, glia and myelin. Cytokines produced in response to cell injury may trigger increased production of NO. These events may be involved in alcohol-induced brain damage. Formation of NO has recently been linked to increased preference for and tolerance to alcohol. A hypothesis for prevention and treatment of alcohol-induced brain damage, and craving and alcohol intake by alcoholics is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, M. L., Meyer, E. R., Sewing, B. N., and Cicero, T. J. (1994). Effects of nitric oxide-related agents on alcohol narcosis.Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 18:969–975.
Adams, M. L., Nock, B., Truong, R., and Cicero, T. J. (1992). Nitric oxide control of steroidogenesis: Endocrine effects of NG-nitro-L-arginine and comparisons to alcohol.Life Sci. 50:PL35-PL40.
Afework, M., Tomlinson, A., and Burnstock, G. (1994). Distribution and colocalization of nitric oxide synthase and NADPH-diaphorase in adrenal gland of developing, adult and aging Sprague-Dawley rats.Cell Tissue Res. 276:133–141.
Akira, T., Henry, D., and Wasterlain, C. G. (1994). Nitric oxide mediates the sustained opening of NMDA receptor-gated ionic channels which follows transient excitotoxic exposure in hippocampal slices.Brain Res. 652:190–194.
Beauge, F. J., Sebire, N., and Vesperini, D. (1994). Involvement of nitric oxide (NO) in ethanol intake and preference in rats.International Society for Biomedical Research on Alcoholism, Gold Coast, Australia, Abstract 6.14.
Bondy, S. C., and Naderi, S. (1994). The formation of reactive oxygen species in a fraction of rat brain by metabolism of nitric oxide.Neurosci. Lett. 168:34–36.
Bredt, D. S., Glatt, C. E., Hwang, P. M., Fotuhi, M., Dawson, T. M., and Snyder, S. H. (1991). Nitric oxide synthase protein and mRNA are discretely localized in neuronal populations of the mammalian CNS together with NADPH diaphorase.Neuron 7:615–624.
Bredt, D. S., Hwang, P. M., and Snyder, S. H. (1990). Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neuronal role for nitric oxide.Nature 347:768–770.
Bredt, D. S., and Snyder, S. H. (1992). Nitric oxide, a novel neuronal messenger.Neuron 8:3–11.
Brenner, T., Yamin, A., and Gallily, R. (1994). Mycoplasma triggering of nitric oxide production by central nervous system glial cells and its inhibition by glucocorticoids.Brain Res. 641:51–56.
Buxton, I. L., Cheek, D. J., Eckman, D., Westfall, D. F., Sanders, K. M., and Keef, K. D. (1993). NG-nitro L-arginine methyl ester and other alkyl esters of arginine are muscarinic receptor antagonists.Circ. Res. 72:387–395.
Chandler, L. J., Guzman, N., Sumners, C., and Crews, F. T. (1994a). Induction of nitric oxide synthase in brain glial cells: Possible interaction with ethanol in reactive neuronal injury.In Lancaster, F. E. (ed)Alcohol and Glial Cells. National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism Research, Monograph 27. NIH Pub. No. 94-3742. Bethesda, Maryland: National Institutes of Health, pp. 195–214.
Chandler, L. J., Guzman, N. J., Sumners, C., and Crews, F. T. (1994b). Magnesium and zinc potentiate ethanol inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate-stimulated nitric oxide synthase in cortical neurons.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 271:67–75.
Chandler, L. J., Sumners, C., and Crews, F. T. (1994c). Effects of chronic ethanol exposure on nitric oxide formation in primary neuronal and astroglial cultures.Research Society on Alcoholism, Maui, HI, Abstract 154.
Clark, I. A., Rockett, K. A., and Cowden, W. B. (1992). Possible central role of nitric oxide in conditions clinically similar to cerebral malaria.Lancet 340:894–896.
Crews, F. T., and Chandler, L. J. (1993). Excitotoxicity and the neuropathology of ethanol.In Hunt W. A. and Nixon S. J. (eds)Alcohol-induced Brain Damage. NIH Pub. No. 93-3549. Bethesda, Maryland: National Institutes of Health, pp. 355–371.
Davda, R. K., Chandler, L. J., Crews, F. T., and Guzman, N. J. (1993). Ethanol enhances the endothelial nitric oxide synthase response to agonists.Hypertension 21:939–943.
D'Souza, N. B., Nelson, S., Summer, W. R., and Deaciuc, I. V. (1994). Alcohol-induced inhibition of alveolar macrophage reactive nitrogen intermediates (RNI) release.Research Society on Alcoholism, Maui, HI, Abstract 119.
Feinstein, D. L., Galea, E., Roberts, S., Berquist, H., Wang, H., and Reis, D. J. (1994). Induction of nitric oxide synthase in rat C6 glioma cells.J. Neurochem. 62:315–321.
Forstermann, U., Schmidt, H. H., Pollock, J. S., Sheng, H., Mitchell, J. A., Warner, T. D., Nakane, M., and Murad, F. (1991). Isoforms of nitric oxide synthase. Characterization and purification from different cells types.Biochem. Pharmacol. 42:1849–1857.
Galea, E., Reis, D. J., and Feinstein, D. L. (1994). Cloning and expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase from rat astrocytes.J. Neurosci. Res. 37:406–414.
Gonzalez-Hernandez, T., Gonzalez-Gonzalez, B., Mantolan-Sarmiento, B., Medez-Medina, R., Ferres-Torres, R., and Meyer, G. (1994). Transient NADPH-diaphorase activity in motor nuclei of the foetal human brain stem.NeuroReport 5:758–760.
Greenberg S., Kolls, J., Bagby, G., Nelson, S., Summer, W., Greenberg, J., and Xie, J. (1994). Ethanol metabolism is required for inhibition of nitric oxide gene expression by endotoxin in lung macrophage.Research Society on Alcoholism, Maui, HI, Abstract 111.
Grossman, A. (1994). Editorial: NO news is good news.Endocrinol. 134:1003–1005.
Grossman, A. B., Rossmanith, W. G., Kabigting, E. B., Cadd, G., Clifton, D., and Steiner, R. A. (1994). The distribution of hypothalamic nitric oxide synthase mRNA in relation to gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neurons.J. Endocrinol. 140:R5-R8.
Guevara-Guzman, R., Emson, P. C., and Kendrick, K. M. (1994). Modulation ofin vivo striatal transmitter release by nitric oxide and cyclic GMP.J. Neurochem. 62:807–810.
Hecker, M., Mulsch, A., and Busse, R. (1994). Subcellular localization and characterization of neuronal nitric oxide synthase.J. Neurochem. 62:1524–1529.
Horn, T., Smith, P. M., McLaughlin, B. E., Bauce, L., Marks, G. S., Pittman, Q. J., and Ferguson, A. V. (1994). Nitric oxide actions in paraventricular nucleus: Cardiovascular and neurochemical implications.Am. J. Physiol. 266:(Regulatory Integrative Comp. Physiol. 35) R306-R313.
Jia, Y.-S., Wang, X.-A., and Ju, G. (1994). Nitric oxide synthase expression in vagal complex following vagotomy in the rat.NeuroReport 5:793–796.
Kadowaki, K., Kishimoto, J., Leng, G., and Emson, P. C. (1994). Up-regulation of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) gene expression together with NOS activity in the rat hypothalamo-hypophysial system after chronic salt loading: Evidence of a neuromodulatory role of nitric oxide in arginine vasopressin and oxytocin secretion.Endocrinol 134:1011–1017.
Khanna, J. M., Morato, G. S., Shah, G., Chau, A., and Kalant, H. (1993). Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis impairs rapid tolerance to ethanol.Brain Res. Bull. 32:43–47.
Kimelberg, H. K. and Aschner, M. (1994). Astrocytes and their functions, past and present.In Lancaster F. E. (ed)Alcohol and Glial Cells, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism Research, Monograph 27. NIH Pub. No. 94-3742, Bethesda, Maryland, pp. 1–40.
Knowles, R. G., and Moncada, S. (1994). Nitric oxide synthases in mammals.Biochem. J. 299:249–258.
Lancaster, F. E. (1992). Alcohol, nitric oxide, and neurotoxicity: Is there a connection? - A review.Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 16:539–541.
Lancaster, F. E. (1993a). Nitric oxide and ethanol-induced brain damage-A hypothesis.In Hunt W. A. and Nixon S. J. (eds)Alcohol-induced Brain Damage, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism Research, Monograph 22. NIH Pub. No. 93-3549, Bethesda, Maryland, pp. 373–386.
Lancaster, F. E. (1993b). Ethanol and white matter damage in the brain.In Hunt W. A. and Nixon S. J. (eds)Alcohol-induced Brain Damage, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism Research, Monograph 22. NIH Pub. No. 93-3549, Bethesda, Maryland, pp. 387–399.
Li, P., Tong, C., Eisenach, J. C., and Figueroa, J. P. (1994). NMDA causes the release of nitric oxide from rat spinal cordin vitro.Brain Res. 637:287–291.
Miyagawa, A., Okamura, H., and Ibata, Y. (1994). Coexistence of oxytocin and NADPH-diaphorase in magnocellular neurons of the paraventricular and the supraoptic nuclei of the rat hypothalamus.Neurosci. Lett. 171:13–16.
Mufson, E. J., and Brandabur, M. M. (1994). Sparing of NADPH-diaphorase striatal neurons in Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases.NeuroReport 5:705–708.
Munoz-Fernandez, M. A., Cano, E., O'Donnell, C. A., Doyle, J., Liew, F. Y., and Fresno, M. (1994). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interferon-gamma, and interleukin-6 but not TNF-beta induce differentiation of neuroblastoma cells: the role of nitric oxide.J. Neurochem. 62:1330–1336.
Persson, M. G., and Gustafsson, L. E. (1992). Ethanol can inhibit nitric oxide production.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 224:99–100.
Rajfer, J., Aronson, W. J., Bush, P. A., Dorey, F. J., and Ignarro, L. J. (1992). Nitric oxide as a mediator of relaxation of the corpus cavernosum in response to nonadrenergic, noncholinergic neurotransmission.N. Engl. J. Med. 326:90–94.
Rettori, V., Kamat, A., and McCann, S. M. (1994). Nitric oxide mediates the stimulation of luteinizing hormone releasing hormone release induced by glutamic acidin vitro.Brain Res. Bull. 33:501–503.
Sanchez, F., Alonso, J. R., Arevalo, R., Blanco, E., Aijon, J., Vazquez, R. (1994). Coexistence of NADPH-diaphorase with vasopressin and oxytocin in the hypothalamic magnocellular neurosecretory nuclei of the rat.Cell Tissue Res. 276:31–34.
Saxon, D. W., and Beitz, A. J. (1994). Cerebellar injury induces NOS in Purkinje cells and cerebellar afferent neurons.NeuroReport 5:809–812.
Schilling, J., Holzer, P., Guggenbach, M., Gyurech, D., Mrathia, K., and Geroulanos, S. (1994). Reduced endogenous nitric oxide in the exhaled air of smokers and hypertensives.Eur. Respir. J. 7:467–471.
Schoedon, G., Blau, N., Schneemann, M., Flury, G., and Schaffer, A. (1994). Nitric oxide production depends on preceding tetrahydrobiopterin synthesis by endothelial cells: selective suppression of induced nitric oxide production by sepiapterin reductase inhibitors.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 199:504–510.
Schoedon, G., Schneemann, M., Hofe, S., Guerrero, L., Blau, N., and Schaffner, A. (1993). Regulation of the L-arginine dependent and tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent biosynthesis of nitric oxide in murine macrophages.Eur. J. Biochem. 213:833–839.
Snyder, S. H. (1992). Nitric oxide: First in a new class of neurotransmitters.Science 257:494–496.
Steuhr, D. J., Fasehun, O. A., Kwon, N. S., Gross, S. S., Gonzalez, J. A., Levi, R., and Nathan, C. F. (1991). Inhibition of macrophage and endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase by diphenyleneiodonium and its analogs.FASEB J. 5:98–103.
Sugaya, K., and McKinney, M. (1994). Nitric oxide synthase gene expression in cholinergic neurons in the rat brain examined by combined immunocytochemistry andin situ hybridization histochemistry.Mol. Brain Res. 23:111–125.
Trevisan, S., Fitzgerald, L. W., Brose, N., Gasic, G. P., Heinemann, S. F., Duman, R. S., and Nestler, E. J. (1994). Chronic ingestion of ethanol up-regulates NMDARI receptor subunit immunoreactivity in rat hippocampus.J. Neurochem. 62:1635–1638.
Vincent, S. R. (1994). Nitric oxide: A radical neurotransmitter in the central nervous system.Prog. Neurobiol. 42:129–160.
Wang, Y.-X., and Pang, C. C. Y. (1993). Suppression by ethanol of pressor response caused by the inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 233:275–278.
Wang, S. Z., Zhu, S. Z., and El-Fakahany, E. E. (1994). Efficient coupling of m5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors to activation of nitric oxide synthase.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 268:552–557.
Werner, E. R., Werner-Felmayer, G., and Wachter, H. (1993). Tetrahydrobiopterin and cytokines (43566A).Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 203:1–12.
Xie, J., Kolls, J., Bagby, G., Nelson, S., Summer, W., and Greenberg, S. (1994). Ethanol down-regulates LPS-induced mRNA for nitric oxide synthase in lung macrophages independent of TNFα.Research Society on Alcoholism, Maui, HI, Abstract 110.
Xu, Z.-Q., Peribone, V. A., Zhang, X., Grillner, S., and Hokfelt, T. (1994). A functional role for nitric oxide in locus coeruleus: Immunohistochemical and electrophysiological studies.Exp. Brain Res. 98:75–83.
Zhang, X., Verge, V., Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z., Ju, G., Bredt, D., Snyder, S. H., and Hokfelt, T. (1994). Nitric oxide synthase-like immunoreactivity in lumbar dorsal root ganglial and spinal cord of rat and monkey and effect of peripheral axotomy.J. Comp. Neurol. 335:563–575.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lancaster, F.E. Alcohol and the brain: what's NO got to do with it?. Metab Brain Dis 10, 125–133 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01991860
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01991860