Abstract
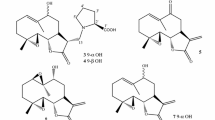
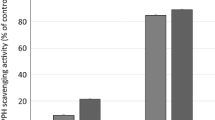
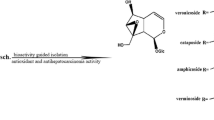
The methanol extract of the Oriental medicinal plantVitis coignetiae (Vitaceae) showed hepatoprotective activity in the in vitro assay method using primary cultured rat hepatocytes. Activity-guided fractionation of the extract afforded ɛ-viniferin as an active principle. The protective effect of ɛ-viniferin against mice carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury in mice was shown by serum enzyme assay as well as by pathological examination. In addition to ɛ-viniferin, plant oligostilbenes, ampelopsins A, C, F and the mixture of vitisin A andcis-vitisin A were also present in the extract. Among them, ampelopsin C and the mixture of vitisin A andcis-vitisin A were found to be powerful hepatotoxins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hikino, H., and Kiso, Y., in: Economic and Medicinal Plant Research, vol. 2: Natural Products for Liver Diseases, p. 39. Eds H. Wagner, H. Hikino, and N. R. Farnsworth, Academic Press 1988.
Yang, L.-L., Yen, K.-Y., Kiso, Y., and Hikino, H., J. Ethnopharmac.19 (1987) 103.
Langcake, P. L., and Pryce, R. J., Experientia33 (1977) 151. Physicochemical data: amorphous powder, [α]D+38° (c=1.83, MeOH); EIMSm/z 454 [M+]; UV λ max (MeOH): 324 nm (log ɛ 4.36); IR ν max (KBr): 3300, 960 cm−1;1H NMR (100 MHz, acetone-d 6): δ 4.44, 5.40 (each 1H, d, J=5.5 Hz), 6.22 (3H, s), 6.31 (1H, d, J=2.0 Hz) 6.65 (1H, d, J=16.0 Hz), 6.70 (1H, d, J=2.0 Hz), 6.71, 6.80 (each 2H, d, J=8.5 Hz), 6.91 (1H, d, J=16.0 Hz), 7.15, 7.19 (each 2H, d, J=8.5 Hz);13C NMR (25MHz, acetone-d6):, δ 57.5 (d), 94.2 (d), 97.2 (d), 102.5 (d), 104.6 (d), 107.4 (2C, d), 116.5 (2C, d), 116.7 (2C, d), 120.1 (s), 123.8 (d), 128.2 (2C, s), 159.7 (s), 160.0 (2C, s), 162.6 (s).
Kiso, Y., Tohkin, M., and Hikino, H., Plant Med.49 (1983) 222.
Kiso, Y., Tohkin, M., and Hikino, H., J. nat. Prod.46 (1983) 841.
Karmen, A., Wroblewski, F., and Ladue, J., J. clin. Invest.34 (1955) 126.
Oshima, Y., Ueno, Y., Hikino, H., Yang, L.-L., and Yen, K.-Y., Tetrahedron46 (1990) 5121. Physicochemical data: (ampelopsin A) amorphous powder, [α]D+167° (c=2.0, MeOH); FABMSm/z 471 [MH+]; UV λ max (MeOH): 283 nm (log ɛ 3.86); IR ν max (KBr): 3300, 1605, 1515, 1450 cm−1,1H NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d 6): δ 4.17 (1H, d, J=11.7 Hz), 5.42 (1H, br s), 5.45 (1H, d, J=5.0 Hz), 5.77 (1H, d, J=11.7 Hz), 6.16, 6.24, 6.43, 6.62 (each 1H, d, J=2.3 Hz), 6.65, 6.78, 6.90, 7.12 (each 2H, J=8.3 Hz), (ampelopsin C) amorphous powder, [α]D+24° (c=1.0, MeOH); FABMSm/z 681 [MH+]; UV λ max (MeOH): 282 nm (log ɛ 4.03); IR ν max (KBr): 3400, 1610, 1515, 1450 cm−1;1H NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d 6): δ 3.67 (1H, br d, J=12.0 Hz), 3.78 (1H, dd, J=12.0 and 9.5 Hz), 4.26 (1H, d, J=9.5 Hz), 4.48 (1H, d, J=12.0 Hz), 5.29 (1H, d, J=3.5 Hz), 5.85 (1H, d, J=12.0 Hz), 6.17 (1H, s), 6.18 (1H, br s), 6.20 (1H, t, J=2.0 Hz), 6.22 (2H, d, J=2.0 Hz), 6.37 (1H, d, J=2.0 Hz), 6.70, 6.75, 6.82, 7.03, 7.20, 7.28 (each 2H, d, J=8.5 Hz).
Oshima, Y., Ueno, Y., Hisamichi, K., and Takeshita, M., Tetrahedron49 (1993) 5801. Physicochemical data: amorphouse powder, [α]D+14° (c=2.0, MeOH); EIMSm/z 454 [M+]; UV λ max (MeOH): 281 nm (log ɛ 3.89); IR ν max (KBr): 3300, 1610, 1510, 1460 cm−1,1H NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d 6): δ 3.23, 3.52, 4.01, 4.07 (each 1H, br s), 5.94, 6.03, 6.32, 6.39 (each 1H, d, J=2.5 Hz), 6.44, 6.63, 6.66, 6.97 (each 2H, d, J=7.5 Hz).
Oshima, Y., Kamijou, A., Moritani, H., Namao, K., and Ohizumi, Y., J. org. Chem.58 (1993) 850. Approximate ratio of vitisin A andcis-vitisin A was estimated at 3∶2 by the1H NMR spectrum. Physicochemical data: amorphous powder, FABMSm/z 907 [MH+]; UV λ max (MeOH): 283 (log ɛ 4.40), 320 nm (4.22); IR ν max (KBr): 3160, 1600, 1510, 1450 cm−1;1H NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d 6): (vitisin A) δ 4.26 (1H, d, J=10.5 Hz), 4.43, 5.38 (each 1H, d, J=5.0 Hz), 5.41, 5.50 (each 1H, d, J=3.0 Hz), 5.91 (1H, d, J=10.5 Hz), 6.06, 6.08, 6.11, 6.12 (each 1H, d, J=2.0 Hz), 6.19 (2H, d, J=2.0 Hz), 6.24 (1H, t, J=2.0 Hz), 6.27, 6.28 (each 1H, d, J=2.0 Hz), 6.41 (2H, br s), 6.55 (1H, d, J=2.0 Hz), 6.68 (2H, d, J=8.5 Hz), 6.71 (1H, d, J=8.5 Hz), 6.80, 6.86 (each 2H, d, J=8.5 Hz), 6.89 (1H, dd, J=8.5 and 2.0 Hz), 7.06, 7.17, 7.22 (each 2H, d, J=8.5 Hz); (cis-vitisin A) δ 4.09 (1H, d, J=5.0 Hz), 4.25 (1H, d, J=10.5 Hz), 5.29 (1H, d, J=5.0 Hz), 5.41, 5.54 (each 1H, d, J=3.0 Hz), 5.83 (2H, br s), 5.85 (1H, d, J=10.5 Hz), 5.98 (1H, br s), 6.05 (2H, d, J=2.0 Hz), 6.14, 6.20 (each 1H, d, J=2.0 Hz), 6.22 (1H, t, J=2.0 Hz), 6.23, 6.24, 6.30, 6.55 (each 1H, d, J=2.0 Hz), 6.56 (1H, d, J=8.5 Hz), 6.69 (1H, dd, J=8.5 and 2.0 Hz), 6.69, 6.78, 6.87, 7.06 (each 2H, d, J=8.5 Hz), 7.13 (4H, d, J=8.5 Hz).
Slater, T. F., Nature209 (1966) 36.
Recknagel, R. O., Pharmac. Rev.4 (1967) 145.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oshima, Y., Namao, K., Kamijou, A. et al. Powerful hepatoprotective and hepatotoxic plant oligostilbenes, isolated from the Oriental medicinal plantVitis coignetiae (Vitaceae). Experientia 51, 63–66 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01964921
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01964921