Summary
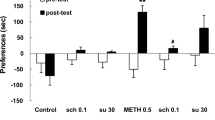
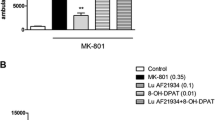
The effects of typical and atypical neuroleptics on MK-801-induced locomotor activity and stereotyped sniffing were tested. Pretreatment with the typical neuroleptic haloperidol (0.01,0.05, 0.1,0.5 mg/kg SC) and the dopamine D 2 receptor selective antagonist eticlopride (0.005, 0.01, 0.05 mg/kg SC) each resulted in significant and dose-dependent reductions of locomotor activity and sniffing. The atypical neuroleptic clozapine (1.0, 5.0, 10.0 mg/kg SC) was some-what unique in that all doses reduced locomotor activity, but only the highest dose (10.0 mg/kg) significantly reduced sniffing. The data support a functional interaction between glutamate and dopamine systems, and suggest that the behavioral activation associated with MK-801 may represent a valid model for detecting potential therapeutic agents in the treatment of schizophrenia. The data should be viewed as preliminary, however, until neuroleptics are characterized in other glutamate-based models that minimize or exclude the possible influence of nonspecific motor effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RM, Young SJ (1978) Phencyclidine-induced psychosis. Am J Psychiatry 135: 1081–1084
Carlsson M, Carlsson A (1989) The NMDA antagonist MK-801 causes marked locomotor stimulation in monoamine-depleted mice. J Neural Transm 75: 221–226
Clow DW, Jhamandas K (1989) Characterization of L-glutamate action on the release of endogenous dopamine from the rat caudate-putamen. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 248: 722–728
Contreras PC, Rice KC, Jacobson AE, O'Donohue TL (1986) Stereotyped behavior correlates better than ataxia with phencyclidine-receptor interactions. Eur J Pharmacol 121: 9–18
Costall B, Naylor RJ (1975) Detection of the neuroleptic properties of clozapine, sulpiride and thioridazine, Psychopharmacologia (Berlin) 43: 69–74
Costall B, Naylor RJ, Nohria V (1978) Climbing behavior induced by apomorphine in mice: a potential model for the detection of neuroleptic activity. Eur J Pharmacol 50: 39–50
de Paulis T, Kumar Y, Johansson L, Ramsby S, Hall H, Sallemark M, Angeby-Moller K, Ogren SO (1986) Potential neuroleptic agents. 4. Chemistry, behavioral pharmacology, and inhibition of [3 H]spiperone binding of 3,5-disubstituted N-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-6-methoxysalicylamides. J Med Chem 29: 61–69
Deutch A, Moghaddam B, Innis RB, Krystal JH, Aghajanian GK, Bunney BS, Charney DS (1991) Mechanisms of action of atypical antipsychotic drugs. Implications for novel therapeutic strategies for schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 4: 121–156
Deutsch SI, Mastropaolo J, Schwartz BL, Rosse RB, Morihisa JM (1989) A “glutamatergic hypothesis” of schizophrenia. Rationale for pharmacotherapy with glycine. Clin Neuropharmacol 12: 1–13
Ellenbroek BA, Cools AR (1990) Animal models with construct validity for schizophrenia. Behav Pharmacol 1: 469–490
Elliott PJ, Close SP, Walsh DM, Hayes AG, Marriott AS (1990) Neuroleptic-induced catalepsy as a model of Parkinson's disease. II. Effect of glutamate antagonists. J Neural Transm [PD-Sect] 2: 91–100
Ford LM, Norman AB, Sanberg PR (1989) The topography of MK-801-induced locomotor patterns in rats. Physiol Behav 46: 755–758
French ED, Ceci A (1990) Non-competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonists are potent activators of ventral tegmental A 10 dopamine neurons. Neurosci Lett 19: 159–162
Grace AA (1991) Phasic versus tonic dopamine release and the modulation of dopamine system responsivity: a hypothesis for the etiology of schizophrenia. Neuroscience 41: 1–24
Hauber W, Schmidt WJ (1990) The NMDA antagonist dizocilpine (MK-801) reverses haloperidol-induced movement initiation deficits. Behav Brain Res 41: 161–166
Hogberg T, Ramsby S, Ogren SO, Norinder U (1987) New selective dopamine D 2 antagonists as antipsychotic agents. Acta Pharm Suec 24: 289–328
Imperato A, Scrocco MG, Bacchi S, Angelucci L (1990) NMDA receptors and in vivo dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and caudatus. Eur J Pharmacol 187: 555–556
Kalivas PW, Duffy P, Barrow J (1989) Regulation of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system by glutamic acid receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 251: 378–387
Kim JS, Kornhuber HH, Schmid-Burgk W, Holzmüller B (1980) Low cerebrospinal fluid glutamate in schizophrenic patients and a new hypothesis on schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett 20: 379–382
Koek W, Woods JH, Winger GD (1988) MK-801, a proposed noncompetitive antagonist of excitatory amino acid neurotransmission, produces phencyclidine-like behavioral effects in pigeons, rats and rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 245: 969–974
Kornhuber J, Kornhuber ME (1986) Presynaptic dopaminergic modulation of cortical input to the striatum. Life Sci 39: 669–674
Leviel V, Gobert A, Guibert B (1990) The glutamate-mediated release of dopamine in the rat striatum: further characterization of the dual excitatory-inhibitory function. Neuroscience 39: 305–312
Ljungberg T, Ungerstedt U (1978) Classification of neuroleptic drugs according to their ability to inhibit apomorphine-induced locomotion and gnawing: evidence for two different mechanisms of action. Psychopharmacology 56: 239–247
Maura G, Giardi A, Raiteri M (1988) Release-regulating D 2 dopamine receptors are located on striatal glutamatergic nerve terminals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 247: 680–684
McKinney WT (1989) Animal models of schizophrenic disorders. In: Schulz SC, Tamminga CA (eds) Schizophrenia: scientific progress. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 141–154
Monahan JB, Contreras PC, Lanthorn TH, DiMaggio DA, Handelmann GE, Pullan LM, Gray NM, O'Donohue TL (1989) The Phencyclidine receptor complex: Interaction with excitatory amino acids and endogenous ligands. In: Schulz SC, Tamminga CA (eds) Schizophrenia: scientific progress. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 155–162
Ogren SO, Hall H, Kohler C, Magnusson O, Lindbom L-O, Angeby K, Florvall L (1984) Remoxipride, a new potential antipsychotic compound with selective antidopaminergic actions in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 102: 459–474
Ogren SO, Hall H, Kohler C, Magnusson O, Sjostrand S (1986) The selective dopamine D 2 receptor antagonist raclopride discriminates between dopamine-mediated motor functions. Psychopharmacology 90: 287–294
O'Neill KA, Liebman JM (1987) Unique behavioral effects of the NMDA antagonist, CPP, upon injection into the medial pre-frontal cortex of rats. Brain Res 435: 371–376
O'Neill KA, Carelli RM, Jarvis MF, Liebman JM (1989) Hyperactivity induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate injections into nucleus accumbens: lack of evidence for mediation by dopaminergic neurons. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 34: 739–745
Raffa RB, Ortegon ME, Robisch DM, Martin GE (1989) In vivo demonstration of the enhancement of MK-801 by L-glutamate. Life Sci 44: 1593–1599
Robertson A, MacDonald C (1984) Atypical neuroleptics clozapine and thioridazine enhance amphetamine-induced stereotypy. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 21: 97–101
Schmidt WJ (1986) Intrastriatal injection of DL-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (AP-5) induces sniffing stereotypy that is antagonized by haloperidol and clozapine. Psychopharmacology 90: 123–130
Schmidt WJ, Bubser M (1989) Anticataleptic effects of the N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist MK-801 in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 32: 621–623
Seeman P (1981) Brain dopamine receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 32: 229–313
Seeman P (1987) Dopamine receptors and dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Synapse 1: 133–152
Tiedtke PI, Bischoff C, Schmidt WJ (1990) MK-801-induced stereotypy and its antagonism by neuroleptic drugs. J Neural Transm 81: 173–182
Werling LL, Jacocks III HM, McMahon PN (1990) Regulation of [3H] dopamine release from guinea pig striatum by NMDA receptor/channel activators and inhibitors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 255: 40–45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffman, D.C. Typical and atypical neuroleptics antagonize MK-801-induced locomotion and stereotypy in rats. J. Neural Transmission 89, 1–10 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01245347
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01245347