Abstract
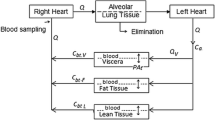
A physiological flow model simulating the pregnant rat is constructed for methadone. The model includes brain, fetal, hepatic, intestinal, muscular, pulmonar, and renal tissues. Since methadone kinetics may provide valuable information for optimal therapy, an attempt is made to describe methadone kinetics in brain and other tissues simultaneously. The concentration-time profiles of methadone in various tissues after an i.v. bolus dose of 2 rng/kg are reasonably described by the model. The role of the different organs in the disposition of methadone is further explored by simulations. It is found that methadone is initially sequestered in lung tissues immediately after intravenous administration. Therefore, both venous and arterial blood pools are included in the model. Rapid uptake then takes place into vascular-rich organs, including kidneys, liver, and muscle, followed by redistribution into less penetrable organs, such as brain, fetal, and intestinal tissues. Data indicate that diffusional resistance governs the transfer of drug into brain, fetal, and intestinal tissues. Simulations suggest that muscular tissues play an important role in the rat and in man, becoming the major methadone reservoir. The tissue-to-blood partition coefficients derived from equilibrium conditions in this study are generally higher than those reported hitherto. The model is scaled up to a human to investigate whether it can be used to predict the concentration of methadone in different organs after a certain dose. Volume of distribution (Vdss) and biological half-life are consistent with earlier findings in man. The study is done by means of the GC-MS method with selected ion-monitoring where deuterated methadone is used as an internal standard.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Isbell, A. J. Eisenman, A. Wilder, M. Daingerfield, and K. Frank. Treatment of the morphine abstinence syndrome with 10820 (4,4-diphenyl-6-dimentylamino-heptanone-3).Fed. Proc. 6:340 (1947).
V. P. Dole and M. E. Nyswander. A medical treatment of diacetylmorphine (herione) addiction: A clinical trial with methadone hydrochloride.J. Am. Med. Assoc. 193:646 (1965).
M. A. Peters, M. Turnbow, and D. Buchenauer. The distribution of methadone in the nonpregnant, pregnant and fetal rat after acute methadone treatment.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 181:273–278 (1972).
M. I. Nilsson, E. Widerlöv, U. Meresaar, and E. Änggard. The effect of urinary pH on the disposition of methadone in man.Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 22:337–342 (1982).
K. Bischoff. Some fundamental considerations of the application of pharmacokinetics to cancer therapy.Cancer Chemother. Rep. 59:777–793 (1975).
J. V. Wait and F. Clarke III. DARE-P, A Portable Digital Simulation System, University of Arizona, 1974.
L. Jansky and J. S. Hart. Cardiac output and organ blood flow in warm- and cold-acclimated rats exposed to cold.Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 46:653–659 (1968).
Y. Lundgren, K. Karlsson, and U. Ljungblad. Circulatory changes during pregnancy, in spontaneously and renal hypertensive rats.Clin. Sci. 57:337–339 (1979).
E. D. Adolph. Quantitative relations in the physiological constitutions of mammals.Science 109:579–585 (1949).
S. J. Liu, K. Z. C. Chen, and R. I. H. Wang. Effects of desipramine, fecal and urinary excretion of methadone in the rat.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 198:308–317 (1976).
G. S. F. Ling, J. G. Umans, and C. E. Inturrisi. Methodone: Radioimmunoassay and pharmacokinetics in the rat.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 217:147–151 (1980).
S. G. Avery.Drug Treatment, 2nd ed., Churchill Livingstone, New York, 1982.
A. L. Misra, R. Bloch, N. L. Vadlamani, and S. J. Mule. Physiological disposition and biotransformation of levo-methadone-1-3H in the dog.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 188:34–44 (1974).
A. E. Robinson and F. M. Williams. The distribution of methadone in man.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 23:353–358 (1971).
J. J. Kaufman, N. M. Semo, and Walter S. Koski. Microelectrometric titration measurements of the pKa's and partition and drug distribution coefficients of narcotics and narcotic antagonists and their pH and temperature dependence.J. Med. Chem. 18:647–655 (1975).
M. Rowland. Physiologic pharmacokinetic models: Relevance, experience, and future trends,Drug Metab. Rev. 15:55–74 (1984).
W. A. Calder III and S. L. Lindstedt. Body size, physiological time, and longevity of homeothermic animals.Q. Rev. Biol. 56:1–16 (1981).
C. A. Guyton.Textbook of Medical Physiology, 5th ed., W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, 1975, p. 251.
G. S. Dawes.Foetal and Neonatal Physiology, Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago, 1968.
G. D. Olsen. Metadone binding to human plasma proteins.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 14:338–343 (1972).
H. R. Sullivan and D. A. Blake. Quantitative determination of methadone concentrations in human blood, plasma and urine by gas chromatography.Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 3:467–478 (1972).
W. T. Beaver, S. L. Wallenstein, R. W. Houde, and A. Rodgers. A clinical comparison of the analgesic effect of methadone and morphine administered intra muscularly, and of orally and parentally administered methadone.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.,8:415–426 (1966).
F. Reynolds. Transfer of drugs. In G. V. P. Chamberlain and A. W. Wilkinson (eds.),Placental Transfer, Pitman, London, 1979.
N. S. Shah and A. B. Shah. Age-dependent alterations in the accumulation of 1-methadone in brain synaptosomes and other subcellular fractions.Dev. Pharmacol. Ther. 7:109–120 (1984).
T. Johannesson and T. A. Becker. Morphine analgesia in rats at various ages.Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 33:429–441 (1973).
H. J. Kupferberg and E. L. Way. Pharmacologic basis for the increased sensitivity of the newborn rat to morphine.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 141:105–112 (1963).
J. L. Gabrielsson and L. K. Paalzow. A physiological pharmacokinetic model for morphine disposition in the pregnant rat.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 11:147–163 (1983).
G. K. Gburlay, R. J. Willis, and P. R. Wilson. Postoperative pain control with methadone: Influence of supplementary methadone doses and blood concentration-response relationships.Anaesthesiology 61:19–26 (1984).
William H. Horns, Madeline Rado, and Avram Goldstein. Plasma levels and symptoms complaints in patients maintained on daily dosage of methadone hydrochloride.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 17:636–649 (1975).
G. K. Gourlay, P. R. Wilson, and C. J. Glynn. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of methadone during the peri-operative period.Anaesthesiology 57:458–467 (1982).
Cheng-Nan Chen, Materials for Extracorporeal Poisoning Treatment—A Novel Pharmacokinetic Analysis, PhD Thesis, University of Utah (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gabrielsson, J.L., Johansson, P., Bondesson, U. et al. Analysis of methadone disposition in the pregnant rat by means of a physiological flow model. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 13, 355–372 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061474
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061474