Abstract
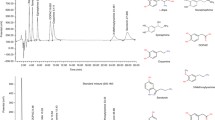
Purine and pyrimidine base and nucleoside levels were measured in adult rabbit cisternal CSF and plasma by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. The concentrations of bases, nucleosides, and nucleoside phosphates were similar in plasma and CSF except for the adenosine phosphates and uracil which were higher in the plasma. In plasma and CSF, adenosine levels were low (0.12 μM) and guanosine, deoxyadenosine, deoxyguanosine, and deoxyinosine were not detectable (<0.1 μM); inosine and xanthine concentrations were 1–2 μM and hypoxanthine concentrations were approximately 5 μM; uridine (∼8 μM), cytidine (2–3 μM), and thymidine, deoxyuridine, and deoxycytidine (0.5–1.4 μM) were easily detectable. In both plasma and CSF, guanine, and thymine were undetectable (<0.1 μM), adenine and cytosine were less than 0.2 μM, but uracil was present (>1 μM). Adenosine, inosine, and guanosine phosphates were also detectable at low concentrations in CSF and plasma. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that purine deoxyribonucleosides are synthesized in situ in the adult rabbit brain. In contrast, pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides and ribonucleosides, and purine and pyrimidine bases are available in the CSF for use by the brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- AUFS:
-
absorbance units full scale
- CSF:
-
cerebrospinal fluid
- CNS:
-
central nervous system
- ADA:
-
adenosine deaminase
- PNP:
-
purine nucleoside phosphorylase
- XOD:
-
xanthine oxidase
- UC:
-
uricase
- Alk. Phos:
-
alkaline phosphatase
References
Santos, J. N., Hempstead, K. W., Kopp, L. E., andMiech, R. P. 1968. Nucleotide metabolism in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 15:367–376.
McIlwain, H., andBachelard, H. 1971. Metabolism of nucleic acids and proteins Pages 222–265.in Biochemistry and the Central Nervous System. Churchill Livingstone, London.
Hopewell, J. W. 1971. A quantitative study of the mitotic activity in the subependymal plate of adult rat cell tissue. Cell Tissue Kinet. 4:273–278.
Kimberlin, R. H., Shirt, D. B., andCollis, S. C. 1974. The turnover of isotopically labeled DNA in vivo in developing, adult and scrapie-affected mouse brain. J. Neurochem. 23:241–248.
Wintzerith, M., Wittendorp, E., Rechenmann, R. V., andMandel, P. 1977. Nuclear, nucleolar repair or turnover of DNA in adult rat brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 3:217–230.
Schultze, B. 1981. Double labeling autoradiography: cell kinetic studies with [3H] and14C-thymidine. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 38:392–396.
Spector, R., Levy, P., andAbelson, H. T. 1977. The development and regional distribution of dihydrofolate reductase in rabbit brain. J. Neurochem. 29:919–921.
Suleiman, S. A., andSpector, R. 1982. Identification, development and regional distribution of thymidylate synthetase in adult rabbit brain. J. Neurochem. 38:392–396.
Sung, S. C. 1971. Thymidine kinase in the developing rat brain. Brain. Res. 35:268–271.
Yamada, N., Sawasaki, Y., andNakajima, H. 1979. Developmental changes in the subcellular distribution of thymidine kinase in the rat cerebellum. Brain Res. 168:393–397.
Eells, J. T., andSpector, R. 1982. Identification, development and regional distribution of ribonucleotide reductase in adult rat brain. J. Neurochem. 40:1008–1112.
Chiu, J., andSung, S. C. 1972. Pattern of developmental changes in two DNA polymerases in rat brain. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 269:364–369.
Millard, S. A. 1972. Ribonucleotide reductase in developing brain. J. Biol. Chem. 247:2395–2400.
Spector, R. 1980. Thymidine transport in the central nervous system. J. Neurochem. 35:1092–1098.
Spector, R. 1981. Development and localization of the thymidine phosphorylating systems in brain. J. Neurochem. 36:2019–2024.
Merlis, J. K. 1940. The effect of changes in the calcium content of cerebrospinal fluid on spinal reflex activity in the dog. Am. J. Physiol. 131:67–72.
Gehrke, C. W., Kuo, K. C., andZumwalt, R. W. 1980. Chromatography of Nucleosides. J. Chromatogr. 188:129–147.
Zakaria, M., andBrown, P. R. 1981. High-performance liquid column chromatography of nucleotides, nucleosides and bases. J. Chromotogr. 226:267–290.
Dixon, J. S., andLipkin, D. 1954. Spectrophotometric determination of vicinal glycols, application to the determination of ribofuranosides. Anal. Chem. 26:1092–1093.
Garrett, C., andSanti, D. 1979. A rapid and sensitive high pressure liquid chromatography assay for deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates in cell extracts. Anal. Biochem. 99:268–273.
Fernley, H. N., andWalker, P. G. 1967. Studies on alkaline phosphatase. Biochem. J. 104:1011–1018.
Fishman, R. A. 1980. Composition of cerebrospinal fluid Page 207in Cerebrospinal Fluid in Diseases of the Central Nervous System. W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia.
Berne, R. M., Rubio, R., andCurnish, R. R. 1974. Release of adenosine from ischemic brain; effect on cerebral vascular resistance and incorporation into cerebral adenine nucleotides. Circ. Res. 35:262–271.
Kuttesch, J. F., Schmalsteig, F. C., andNelson, J. A. 1978. Analysis of adenosine and other adenine compounds in patients with immunodeficiency diseases. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1:97–109.
Mills, G. C., Schmalstieg, F. C., Trimmer, K. B., Goldman, A. S., andGoldblum, R. M. 1976. Purine metabolism on adenosine deaminase deficiency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 73:2867–2871.
Leyva, A., Schornagel, J., andPinedo, H. H. M. 1980. High performance liquid chromatography of plasma pyrimidines and purines and its application in cancer chemotherapy, Pages 389–394,in Rapado, A., Watts, R. W. E., andDeBruyn, C. H. M. M. (eds.) Purine Metabolism in Man III. Plenum Press, New York.
Hartwick, R. A., Krstulovic, A. M., andBrown, P. R. 1979. Identification and quantitation of nucleosides, bases and other u.v. absorbing compounds in serum, using reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography II. Evaluation of human sera. J. Chromatogr. 186:659–676.
Assenza, S. P., andBrown, P. R. 1980. Comparison of high performance liquid chromatographic serum profiles of humans and dogs. J. Chromatogr. 181:169–176.
Simmonds, R. J., andHarkness, R. A. 1981. High-performance liquid chromatographic methods for base and nucleoside analysis in extracellular fluids and in cells. J. Chromagtogr. 226:369–381.
Wong, P. C. L., andHenderson, J. F. 1972. Purine ribonucleotide biosynthesis, interconversion and catabolism in mouse brain in vitro. Biochem. J. 129:1085–1094.
Hartwick, R. A., andBrown, P. R. 1977. Selective analysis for adenosine using reverse phase high pressure liquid chromotography. J. Chromatogr. 143:383–389.
Taylor, G. A., Dady, P. J., andHarrap, K. R. 1980. Quantitative high-performance liquid chromatography of nucleosides and bases in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. 183:421–431.
Koller, C. A., Stetson, P. L., Nichamin, L. D., andMitchell, B. S. 1980. An assay of deoxyadenosine and adenosine in human plasma by HPLC. Biochem. Med. 24:179–184.
Slowiaczek, P., andTattersall, M. H. N. 1982. The determination of purine levels in human and mouse plasma. Anal. Biochem. 125:6–12.
Karle, J. M., Anderson, L. W., Dietrick, D. D., andCysyk, R. L. 1980. Determination of serum and plasma uridine levels in mice, rats and humans by high pressure liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 109:41–46.
Moyer, J. D., Oliver, J. T., andHandschumacher, R. E. 1981. Salvage of circulating pyrimidine nucleosides in the rat. Cancer Res. 41:3010–3017.
Nottebrock, H., andThen, R. 1977. Thymidine concentrations in serum and urine of different animal species and man. Biochem. Pharmacol. 26:2175–2179.
Howell, S. B., Mansfield, S. J., andTaetle, R. 1981. Thymidine and hypoxanthine requirements for normal and malignant human cells for protection against methotrexate cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 41:945–950.
Dudman, N. P. B., Deveski, W. B., andTattersall, M. H. N. 1981. Radioimmunoassays of piasma thymidine, uridine, deoxyuridine and cytidine/deoxycytidine. Anal. Biochem. 115:428–437.
Chan, T., Lakhaura, B. D., andHsu, T. F. 1981. Differences in deoxycytidine metabolism in rat and mouse. Fed. Proc. 41:631.
Spector, R. 1982. Nucleoside transport in the choroid plexus: mechanism and specificity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 216:693–703.
Spector, R., andBerlinger, W. G. 1982. Localization and mechanism of thymidine transport into the central nervous system. J. Neurochem. 39:837–842.
Pappenheimer, J. R., andSetchell, B. P. 1973. Cerebral glucose transport and oxygen consumption in sheep and rabbits. J. Physiol. 223:529–551.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eells, J.T., Spector, R. Determination of ribonucleosides, deoxyribonucleosides, and purine and pyrimidine bases in adult rabbit cerebrospinal fluid and plasma. Neurochem Res 8, 1307–1320 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964000
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964000