Summary
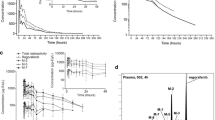
The disposition kinetics of bezafibrate, a newly developed drug of great lipid-lowering potency, were investigated in normal male subjects. Five male volunteers received14C-labelled bezafibrate orally in solution, and a further 10 were given the same dose (300 mg) of un-labelled drug as tablets. The concentration of bezafibrate in serum and urine from the latter was determined by GC, and in the former total radioactivity in serum, urine and feces was followed for 48 h, and urinary excretion products were analysed by TLC and GC-MS. Rapid absorption from the gastrointestinal tract led to peak serum levels 30 min and 2 h after administration of solution and tablets, respectively. Since approximately 95% of the administered14C-bezafibrate was excreted in urine within 48 h, and almost all the remainder was detected in feces, absorption can be regarded as complete after administration in solution. The relative optimal bioavailability from the tablets was also complete, since in both cases approximately 50% of the administered dose was detected as unchanged bezafibrate in urine within 24 h by GC in the tablet study, and by TLC in the solution study. Of the decomposition products, more than 20% of the dose was present as glucuronides and the remainder consisted of several more polar compounds, one of which was identified as a hydroxyderivative of bezafibrate. Since the apparent halflife of bezafibrate in serum was 2.1 h, this new drug possesses favourable pharmacokinetic features: rapid and complete absorption, even from tablets, combined with a conveniently short half-life, and clearance which is half renal (56 ml/min) and half metabolic (43 ml/min), giving a total clearance of 99 ml/min.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, O., Wolfram, G., Lang, P. D., Zöllner, N.: Dosiswirkungsuntersuchung mit Bezafibrat an Patienten mit Hypercholesterinämie und Hypertriglyzeridämie. Münch. Med. Wocheschr.121, 319–322 (1979)
Arntz, H.-R., Klemens, U. H., Lang, P. D., Vollmar, J.: Vergleich von Clofibrat und Bezafibrat bei Hyperlipoproteinämie Typ IIa und IIb. Med. Klin.73, 1731–1737 (1978)
Ayerst, C. M.: Plasma concentrations of clofibrate in normal men after single oral doses and comparison of a twice and four times daily dosage regimen. Clin. Res.25, 547 A (1977)
Billet, S., Lietmann, P. S., Fenselan, C.: Mass spectral analysis of glucuronides. J. Med. Chem.16, 30–33 (1973)
Bolzano, K., Krempler, F., Schellenberg, B., Schlierf, G.: Eine vergleichende Studie von Bezafibrat und Clofibrat bei Patienten mit Hyperlipoproteinämie vom Typ IIB und IV. Acta Med. Austriaca (in press)
Cailleux, A., Allain, P., Tadei, A.: Etude pharmacocinétique des hypolipémiants dériés de l'acide clofibrique chez l'Homme aprés administration unique et réjétée. Thérapie31, 637–645 (1976)
Endele, R.: A gas chromatographic method for the determination of bezafibrate. J. Chromatogr.154, 261–263 (1978)
Gugler, R., Shoemann, D. W., Huffman, D. H., Cohlmia, J. B., Azarnoff, D. L.: Pharmacokinetics of drugs in patients with the nephrotic syndrome. J. clin. Invest.55, 1182–1189 (1975)
Hartlapp, J. H., Gugler, R.: Single versus multiple dose pharmacokinetics of clofibrate. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.293, Suppl. 63 (1976)
Houin, G., Thebault, J. J., d'athis, P., Tillement, J. P., Beaumont, J. L.: A GLC method for estimation of chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid in plasma. Pharmacokinetics of a single oral dose of clofibrate in man. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol.8, 433–437 (1975)
Kaffarnik, H., Schneider, J., Schubotz, R., Mühlfellner, O., Mühlfellner, G., Hausmann, L., Zöfel, P.: Long-term results with bezafibrate, a new derivate of clofibrate. International Conference on Atherosclerosis. L. A. Carlson, R. Paoletti, G. Weber (eds.), p. 129–133. New York, N. Y.: Raven Press 1978
Kösters, W., Abshagen, U., Lang, P. D., Endele, R.: Pharmakokinetik und Metabolismus von Bezafibrat bei Patienten mit eingeschränkter Nierenfunktion. Verhandlungsbericht des Internationalen Symposiums: Neue Aspekte in Diagnostik und Therapie von Fettstoffwechselstörungen. 12./13. Mai 1979 Wien. G. Witzstrock-Verlag Baden-Baden, Köln, New York (in press)
Lageder, H., Irsigler, K.: Double-blind comparison of bezafibrate and clofibrate in patients with primary hyperlipoproteinaemia. International Conference on Atherosclerosis. L. A. Carlson, R. Paoletti, G. Weber (eds.), p. 726. New York, N. Y.: Raven Press 1978
Olsson, A. G., Rössner, S., Walldius, G., Carlson, L. A., Lang, P. D.: Effect of BM 15.075 on lipoprotein concentrations in different types of hyperlipoproteinaemia. Atherosclerosis27, 279–287 (1977)
Olsson, A. G., Lang, P. D.: Dose-response study of bezafibrate on serum lipoprotein concentrations in hyperlipoproteinaemia. Atherosclerosis31, 421–428 (1978)
Olsson, A. G., Lang, P. D.: One-year study of bezafibrate on serum lipoprotein concentrations in hyperlipoproteinaemia. Atherosclerosis31, 429–433 (1978)
Oster, P., Schlierf, G., Mordasini, R., Heuck, C. C., Raetzer, H., Schellenberg, B.: Diurnal lipid and lipoprotein profiles with bezafibrate and clofibrate. Ad. Exp. Med. Biol.109, 400–401 (1978)
Pichardo, R., Boulet, L., Davignon, J.: Pharmacokinetics of clofibrate in familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis26, 573–582 (1977)
Stork, H., Lang, P. D.: Some characteristics of a new hypolipidemic agent — BM 15.075. In: Lipids, Lipoproteins, and Drugs. Eds.: D. Kritschevsky, R. Paoletti, and W. L. Holmes. Plenum Press. New York and London, 1975, p. 485
Wahl, P., Hasslacher, Ch., Lang, P. D., Vollmar, J.: Der lipidsenkende Effekt von Bezafibrat bei Patienten mit Diabetes mellitus und Hyperlipidämie. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr.103, 1233–1237 (1978)
Wechsler, J. G., Hutt, V., Klör, H. U., Schönborn, J., Jäger, H., Ditschuneit, H.: Changes in plasma lipids and lipoprotein concentration and composition in hyperlipidemias type IIa, IIb, IV abd V upon treatment with bezafibrate. International Conference on Atherosclerosis. L. A. Carlson, R. Paoletti, G. Weber (eds.), p. 726. New York, N. Y.: Raven Press 1978
Wechsler, J. G., Hutt, V., Klör, H. U., Jäger, H., Schönborn, J., Ditschuneit, H.: Plasma lipids and lipoprotein concentration and composition in hyperlipidemias type IIb and IV upon treatment with bezafibrate. Ad. Exp. Med. Biol.109, 726 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abshagen, U., Bablok, W., Koch, K. et al. Disposition pharmacokinetics of bezafibrate in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 16, 31–38 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00644963
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00644963