Summary
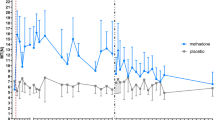
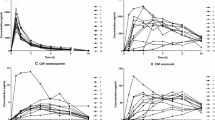
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma morphine concentrations were determined in 5 patients after epidural administration of 6 mg morphine; plasma samples were collected frequently during the initial 6 h and 6–7 CSF samples were obtained from each patient over a 24 h period. Morphine was analysed using gas chromatography and electron capture detection. Individual morphine concentration-time curves were plotted for plasma and CSF and various pharmacokinetic variables were calculated. Plasma morphine concentrations after epidural injection were similar to those found after intramuscular administration; Cmax (66±8 mg/ml: mean±SEM) appeared within 12±3 min, and the terminal elimination half-life in plasma was 213±24 min. In CSF, morphine reached a peak (1575±359 ng/ml) after 135±40 min. The terminal elimination half-life for morphine in CSF was 239±10 min. The CSF bioavailability of morphine after epidural administration was calculated to be 1.9±0.5%.
The study showed that epidural administration of morphine resulted in CSF concentrations many times higher than those in plasma, but still only 2% of the dose administered was available to the CSF compartment. Morphine was eliminated with similar speed from CSF and plasma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behar M, Olshwang D, Magora I, Davidson JT (1979) Epidural morphine in treatment of pain. Lancet 1: 527–529
Rawal N, Sjöstrand U, Dahlström B, Nydahl P-A, Ostelius J (1982) Epidural morphine for postoperative pain relief: a comparative study with intramuscular narcotic and intercostal nerve block. Anesth Analg 61: 93–98
Martin R, Salbaing J, Blaise G, Tétrault J-P, Tétrault L (1982) Epidural morphine for postoperative pain relief: a dose response curve. Anesthesiology 56: 423–426
Yaksh TL (1981) Spinal opiate analgesia: principles and mechanisms of action. Pain 11: 293–346
Hökfelt T, Elde R, Johansson O et al. (1977) The distribution of enkephalin immunoreactive cell bodies in the rat central nervous system. Neurosci Lett 5: 25–31
Hunt SP, Ninkovic M, Gleave JWR, Iversen SD, Iversen LL (1982) Inter-relationships between enkephalin and opiate receptors in the spinal cord. In: Fink GR, Whalley L (eds) Neuropeptides, basic and clinical aspects. Edinburgh, Churchill Livingstone, pp 13–23
Nordberg G, Hedner T, Mellstrand T, Dahlström B (1983) Pharmacokinetic aspects of epidural morphine analgesia. Anesthesiology 58: 545–551
Nordberg G, Hedner T, Mellstrand T, Dahlström B (1984) Pharmacokinetic aspects of intrathecal morphine analgesia. Anesthesiology (in press)
Edlund PO (1982) Determination of opiates in biological samples by glass capillary gas chromatography with electron capture detection. J Chromatogr 206: 109–116
Brunk F, Delle M (1974) Morphine metabolism in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther 16: 51–57
Weddel SI, Ritter RR (1981) Serum levels following epidural administration of morphine and correlation with relief of post-surgical pain. Anesthesiology 54: 210–214
Dahlström B, Tamsen A, Paalzow L, Hartvig P (1982) Patient controlled analgesic therapy. IV: pharmacokinetics and analgesic plasma concentrations of morphine. Clin Pharmacokinet 7: 266–279
Bromage PR, Camporesi E, Chestnut D (1980) Epidural narcotics for postoperative analgesia. Anesth Analg 59: 473–480
Youngstrom P, Cowan R, Suthermer C, Eastwood DW, James CM (1982) Pain relief and plasma concentrations from epidural and intramuscular morphine in post-cesarean patients. Anesthesiology 57: 404–409
Gustafsson LL, Friberg-Nielsen S, Garle M, Mohall A, Rane A, Schildt B, Sumreng T (1982) Extradural and parenteral morphine: kinetics and effects in postoperative pain. A controlled clinical study. Br J Anaesth 54: 1167–1174
Rawal N, Möllefors K, Axelsson K, Lingårdh G, Widman B (1983) An experimental study of urodynamic effects of epidural morphine and of naloxone reversal. Anesth Analg 62: 641–647
Glynn CI, Mather LE, Cousíns MI, Graham JR, Wilson PR (1981) Peridural meperidine in humans. Anesthesiology 55: 520–526
Bromage P, Comparesi E, Durant P, Nielsen C (1982) Rostral spread of epidural morphine. Anesthesiology 56: 431–436
Bromage P, Camporesi E, Durant P, Nielsen C (1982) Non-respiratory side effects of epidural morphine. Anesth Analg 61: 490–495
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nordberg, G., Hedner, T., Mellstrand, T. et al. Pharmacokinetics of epidural morphine in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 26, 233–237 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00630291
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00630291