Summary
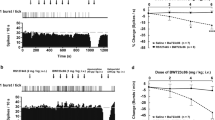
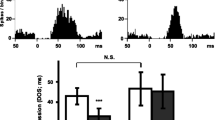
Citalopram (CIT), is a selective serotonin (5-HT) reuptake blocker and a clinically effective antidepressant. The present electrophysiological studies were undertaken to investigate in vivo the acute and long-term effects of CIT administration on 5-HT neurotransmission. In a first series of experiments, a single dose of CIT (0.05–0.5 mg/kg) was administered intravenously to naive rats while recording the activity of a 5-HT-containing neuron in the nucleus raphe dorsalis. A dose-response relationship of the inhibitory effect of CIT on the firing activity of 5-HT neurons was obtained with an ED50 of 0.23±0.03 mg/kg. In a second series of experiments, rats were treated with CIT (20 mg/kg/day, i.p.) for 2, 7 and 14 days. In rats treated for 2 days, there was a marked reduction in the firing activity of 5-HT neurons in the nucleus raphe dorsalis; there was a partial recovery after 7 days and a complete recovery after 14 days of treatment. The response of 5-HT neurons to intravenously administered LSD was decreased in rats treated for 14 days with CIT, indicating a desensitization of the somatodendritic 5-HT autoreceptor. In a third series of experiments, carried out in rats treated with CIT (20 mg/kg/day, i.p.) for 14 days, the suppression of firing activity of CA3 hippocampal pyramidal neurons produced by microiontophoretically-applied 5-HT and by the electrical activation of the ascending 5-HT pathway was measured. Long-term treatment with CIT did not modify the responsiveness of these neurons to microiontophoretically-applied 5-HT; however, the effect of the electrical activation of the ascending 5-HT pathway on these same neurons was enhanced. To determine if 5-HT reuptake blockade could be responsible for this enhancement, CIT (1 mg/kg) was injected intravenously in naive rats while stimulating the ascending 5-HT pathway; it failed to modify the effectiveness of the stimulation. To assess the involvement of the 5-HT terminal autoreceptor, methiothepin, a 5-HT autoreceptor antagonist, was injected intravenously (1 mg/kg) in naive rats and in rats treated for 14 days with CIT while stimulating the ascending 5-HT pathway. Methiothepin enhanced the effect of the stimulation in naive rats but failed to do so in the CIT-treated rats. It is concluded that long-term CIT treatment enhances 5-HT neurotransmission by desensitizing both the somatodendritic and terminal 5-HT autoreceptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK (1978) Feedback regulation of central monoaminergic neurons: evidence from single-cell recording studies. In: Youdim MBH, Lovenberg W, Lagnado JR, Sharman DF (eds) Essays in Neurochemistry and Neuropharmacology, vol 3. Wiley, New York, pp 1–32
Arnt J, Hyttel J, Fredricson Overø K (1983) Prolonged treatment with the specific 5-HT-uptake-inhibitor citalopram. Amphetamine hypersensitivity without receptor changes. Br J Pharmacol 79:411P
Arnt J, Hyttel J, Fredricson Overø K (1984a) Prolonged treatment with the specific 5-HT-uptake-inhibitor citalopram: Effect on dopaminergic and serotonergic functions. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm 36:221–230
Arnt J, Fredricson Overø K, Hyttel J, Olsen R (1984b) Changes in rat dopamine- and serotonin function in vivo after prolonged administration of the specific 5-HT uptake inhibitor, citalopram. Psychopharmacology 84:457–465
Baumann PA, Waldmeier PC (1984) Negative feedback control of serotonin release in vivo: comparison of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid levels measured by voltammetry in concious rats and by biochemical techniques. Neuroscience 11:195–204
Biegon A, Rainbow TC, McEwen BS (1982) Quantitative autoradiography of serotonin receptors in the rat brain. Brain Res 242:197–204
Blier P, de Montigny C (1983) Electrophysiological investigations on the effect of repeated zimelidine administration on serotonergic neurotransmission in the rat. J Neurosci 3:1270–1278
Blier P, de Montigny C, Tardif D (1984) Effects of the two antidepressant drugs mianserin and indalpine on the serotonergic system: single-cell studies in the rat. Psychopharmacology 84:242–249
Blier P, de Montigny C (1985) Serotonergic but not noradrenergic neurons in the rat central nervous system adapt to long-term treatment with monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Neuroscience 16:949–955
Cerrito F, Raiteri M (1979) Serotonin release is modulated by presynaptic autoreceptors. Eur J Pharmacol 57:427–430
Chaput Y, Blier P, de Montigny C (1986) In vivo electrophysiological evidence for the regulatory role of autoreceptors on serotonergic terminals. J. Neurosci (in press)
Chase TN, Katz RI, Kopin IJ (1969) Release of [3H] serotonin from brain slices. J Neurochem 16:607–615
Christensen AV, Fjalland B, Pedersen V, Danneskiold-Samsoe P, Svendsen JM (1977) Pharmacology of a new phtalane (LU 10-171), with specific 5-HT uptake inhibiting properties. Eur J Pharmacol 41:153–162
de Montigny C, Aghajanian GK (1977) Preferential action of 5-methoxytryptamine and 5-methoxydimethyltryptamine on presynaptic serotonin receptors: a comparative iontophoretic study with LSD and serotonin. Neuropharmacology 16:811–818
Dompert WU, Glaser T, Traber J (1985) 3H-TVXQ 7821: Identification of 5-HT1 binding sites as target for a novel putative anxiolytic. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 328: 467–470
Engel G, Göthert M, Hoyer D, Schlicker E, Hillenbrand K (1986) Identity of inhibitory presynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) autoreceptors in the rat brain cortex with 5-HT1B binding sites. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 332:1–7
Farnebo LO, Hamberger B (1971) Drug-induced changes in the release of 3H-monoamines from field stimulated rat brain slices. Acta Physiol Scand 371:35–44
Farnebo LO, Hamberger B (1974) Regulation of [3H]5-hydroxytryptamine release from rat brain slices. J Pharm Pharmacol 26:642–644
Fjalland B, Christensen AV, Hyttel J (1977) Peripheral and central muscarinic receptor affinity of psychotropic drugs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 301:5–9
Fredricson Overø K (1982a) Kinetics of citalopram in test animals: drug exposure in safety studies. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiat 6:297–309
Fredricson Overø K (1982b) Kinetics of citalopram in man. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiat 6:311–318
Galzin AM, Moret C, Verzier B, Langer SZ (1985) Interaction between tricyclic and nontricyclic 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake inhibitors and the presynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine inhibitory autoreceptors in the rat hypothalamus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 235:200–211
Gastpar M, Gastpar G (1982) Preliminary studies with citalopram (LU 10-171), a specific 5-HT-reuptake inhibitor, as antidepressant. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiat 6:319–325
Göthert M (1980) Serotonin-receptor-mediated modulation of Ca2+-dependent 5-hydroxytryptamine release from neurones of the rat brain cortex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 314:223–230
Gozlan H, Mestikawy SEI, Pichat L, Glowinski J, Hamon M (1983) Identification of presynaptic serotonin autoreceptors using a new ligand: 3H-PAT. Nature 305:140–142
Haigler HJ, Aghajanian GK (1974) Lysergic acid diethylamide and serotonin: a comparison of effects on serotonergic neurons and neurons receiving a serotonergic input. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 188:688–699
Hall H, Sällemark M, Wedel I (1984) Acute effects of atypical antidepressants on various receptors in the rat brain. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 54:379–384
Hamon M, Bourgoin S, Jagger J, Glowinski J (1974) Effects of LSD on synthesis and release of 5-HT in rat brain slices. Brain Res 69:265–280
Hyttel J (1977) Neurochemical characterization of a new potent and selective serotonin uptake inhibitor: LU 10-171. Psychopharmacology 51:225–233
Hyttel J (1978) Effect of a specific 5-HT uptake inhibitor, citalopram (LU 10-171), on 3H-5-HT uptake in rat brain synaptosomes in vitro. Psychopharmacology 60:13–18
Hyttel J (1982) Citalopram — pharmacological profile of a specific serotonin uptake inhibitor with antidepressant activity. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiat 6:277–295
Hyttel J, Fredricson Overø K, Arnt J (1984) Biochemical effects and drug levels in rats after long-term treatment with the specific 5-HT-uptake inhibitor, citalopram. Psychopharmacology 83: 20–27
Kandel ER, Spencer WA (1961) Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. II. After-potentials and repetitive firing. J Neurophysiol 24:243–259
Katz RI, Kopin IJ (1969) Effects of D-LSD and related compounds on release of norepinephrine-H3 and serotonin-H3 evoked from brain slices by electrical stimulation. Pharmacol Res Commun 1:54–61
Köhler C (1984) The distribution of serotonin binding sites in the hippocampal region of the rat brain. An autoradiographic study. Neuroscience 13:667–680
Kragh-Sørensen P (1983) A controlled double-blind multicenter trail comparing chlorimipramine and a new, highly selective 5-HT-uptake-inhibitor, citalopram (LU10-171). Abstract P175. VII World Congress in Psychiatry, Vienna, July 11–16, p 482
Kragh-Sørensen P, Fredricson Overø K, Lindegaard Petersen O, Jensen K, Parnas W (1981) The kinetics of citalopram: single and multiple dose studies in man. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 48:53–60
Langer SZ, Moret C (1982) Citalopram antagonizes the stimulation by lysergic acid diethylamide of presynaptic inhibitory serotonin autoreceptors in the rat hypothalamus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 222:220–226
Lindegaard Pedersen O, Kragh-Sørensen P, Bjerre M, Fredricson Overø K, Gram LF (1982) Citalopram, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor: clinical antidepressive and long-term effect — a phase II study. Psychopharmacology 77:199–204
Maître L, Baumann PA, Jackel J, Waldmeier PC (1982) 5-HT uptake inhibitors: pharmacological and neurobiochemical criteria of selectivity. In: Ho BT, Schoolar JC, Usdin E (eds) Serotonin in biological psychiatry. Raven Press, New York, pp 229–246
Martin LL, Sanders-Bush E (1982) Comparison of the pharmacological characteristics of 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 binding sites with those of serotonin autoreceptors which modulate serotonin release. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 321:165–170
Melzacka M, Rubak A, Adamus A, Daniel W (1984) Distribution of citalopram in the blood serum and in the central nervous system of rats after single and multiple dosage. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm 36:675–682
Middlemiss DN (1984a) 8-Hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin is devoid of activity at the 5-hydroxytryptamine autoreceptor in rat brain. Implications for the proposed link between autoreceptor and the [3H]5-HT recognition site. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 327:18–22
Middlemiss DN (1984b) Stereoselective blockade at [3H]5-HT binding sites at the 5-HT autoreceptor by propranol. Eur J Pharmacol 101:289–293
Moret C (1985) Pharmacology of the serotonin autoreceptor. In: Green AR (ed) Neuropharmacology of serotonin. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 21–49
Øfsti E (1982) Citalopram — a specific 5-HT-reuptake inhibitor — as an antidepressant drug: A phase II multicenter trial. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiat 6:327–335
Pawlowski L, Nowak G, Górka Z, MazelaH (1985) Ro 11-2465 (cyan-imipramine), citalopram and their N-desmethyl metabolites: Effects on the uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine and noradrenaline in vivo and related pharmacological activities. Psychopharmacology 86:156–163
Pettitbone DJ, Pflueger BA (1984) Effects of methiothepin and lysergic acid diethylamide on serotonin release in vitro and serotonin synthesis in vivo: possible relation to serotonin autoreceptor function. J Neurochem 43:83–90
Ropert R, Lôo H, Gay C (1984) Etude préliminaire en ouvert d'un nouveau composé antidépresseur: le citalopram. Encéphale 10:131–134
Scuvée-Moreau J, Dresse AR (1979) Effect of various antidepressant drugs on the spontaneous firing rate of locus coeruleus and dorsal raphe neurons of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 57:219–225
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaput, Y., de Montigny, C. & Blier, P. Effects of a selective 5-HT reuptake blocker, citalopram, on the sensitivity of 5-HT autoreceptors: Electrophysiological studies in the rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 333, 342–348 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500007
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500007