Summary
The disposition of dl-propranolol was studied in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR), both after subcutaneous (s.c.) and intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injection of 1 mg/kg.
-
1.
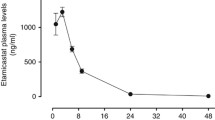
Upon s.c. injection propranolol appeared rapidly in plasma. A maximum concentration of 374 ± 33 ng/ml (N=10) was reached 5 min after injection. After a distribution phase with a half-life of t 1/2α=17 min propranolol was eliminated with a t 1/2β=59 min.
-
2.
Both propranolol and its metabolites were taken up rapidly into all tissues studied. Highest concentrations (10.4±1.5 μg/g, N=5) were found in lungs 30 min after injection.
-
3.
Neither propranolol nor its metabolites accumulated in any of the tissues examined.
-
4.
Upon i.c.v. injection of propranolol, a maximal concentration of 573±47 ng/ml (N=3) was reached in plasma already 2 min after injection. In this case t 1/2α was 13 min and t 1/2β was 80 min.
-
5.
Dialysis experiments indicated that propranolol is bound to plasma proteins for 92% in the concentration range of 20–100 ng/ml. With increasing concentrations binding diminishes progressively. At the highest concentration tested (345 ng/ml) only 76% was bound.
It is concluded that s.c. and i.c.v. injection of an identical dose of propranolol gives a similar plasma concentration-time profile. Moreover, it is suggested that the pharmacokinetic behaviour of propranolol in SHR does not explain the delayed antihypertensive effect of this drug.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, W. P., Korner, P. I., Bobik, A., Chalmers, J. P.: Leakage of dl-propranolol from cerebrospinal fluid to the bloodstream in the rabbit. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 202, 320–325 (1977)
Bakke, O. M., Dollery, C. T., Lewis, P. J., Myers, M. G., Reid, J. L.: Regional brain concentration of propranolol and its hypotensive effect in the conscious rabbit. Br. J. Pharmacol. 51, 148P (1974)
Day, M. D., Roach, A. G.: Cardiovascular effects of beta-adrenoceptor blocking agents after intracerebroventricular administration in conscious normotensive cats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1, 333–339 (1974)
Evans, G. H., Nies, A. S., Shand, D. G.: The disposition of propranolol. III. Decreased half-life as result of plasma binding in man, monkey, dog and rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 186, 114–122 (1973)
Fitzgerald, J. D., Ruffin, R., Smedstadt, K. G., Roberts, R., McAinsh, J.: Studies on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of atenolol in man. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 13, 81–91 (1978)
Forman, B. H., Mulrow, P. J.: Effect of propranolol on blood pressure and plasma renin activity in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Circ. Res. 35, 215–221 (1974)
Garvey, H. L., Ram, N.: Comparative antihypertensive effects and tissue distribution of beta-adrenergic blocking drugs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 194, 220–230 (1975)
Gibaldi, M.: Biopharmaceutics and clinical pharmacokinetics. Philadelphia: Lea and Fehiger 1977
Hansson, L., Zweifler, A. J., Julius, S., Hunyor, S. N.: Hemodynamic effects of acute and prolonged beta-adrenergic blockade in essential hypertension. Acta Med. Scand. 196, 27–34 (1974)
Harrison, L. I., Gibaldi, M.: Physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for digoxin distribution and elimination in the rat. J. Pharm. Sci. 66, 1138–1142 (1977)
Migdalof, B. H.: Methods for obtaining drug time course data from individual small laboratory animals: Serial microblood sampling and assay. Drug Metab. Rev. 5, 295–310 (1976)
Myers, M. G., Lewis, P. J., Reid, J. L., Dollery, C. T.: Brain concentrations of propranolol in relation to its hypotensive effect in the rabbit with observations on brain propranolol levels in man. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 192, 327–335 (1975)
Reid, J. L., Lewis, P. J., Myers, M. G., Dollery, C. T.: Cardiovascular effects of intracerebroventricular d-, and l- and dl-propranolol in the conscious rabbit. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 188, 394–399 (1974)
Shand, D. G.: Pharmacokinetic properties of the beta-adrenergic receptor blocking drugs. Drugs 7, 39–47 (1974)
Shand, D. G., Rango, R. G., Evans, G. H.: The disposition of propranolol. II. Hepatic elimination in the rat. Pharmacology 8, 344–352 (1972)
Smits, J. F. M., Struyker Boudier, H. A. J.: Steady-state disposition of propranolol and its metabolites in the spontaneously hypertensive rat: chronic subcutaneous versus intracerebroventricular infusion with osmotic minipumps. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 209, 317–322 (1979)
Smits, J. F. M., van Essen, H., Struyker Boudier, H. A. J.: Propranolol in conscious hypertensive rats. I. Cardiovascular effects of subcutaneous and intracerebroventricular administration. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 309, 13–18 (1979)
Struyker Boudier, H. A. J.: Cardiovascular actions and pharmacokinetics of propranolol in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Naunyn-Schmideberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 302, R40 (1978)
Struyker Boudier, H. A. J., Smits, J. F. M.: The osmotic minipump: a new tool in the study of steady-state kinetics of drug distribution and metabolism. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 30, 576–578 (1978)
Struyker Boudier, H. A. J., Smits, J. F. M., van Essen, H.: The role of the baroreceptor reflex in the cardiovascular effects of propranolol in the conscious spontaneously hypertensive rat. Clin. Sci. Mol. Med. 56, 163–167 (1979)
Stumpe, K. O., Kolloch, R., Vetter, H., Gramann, W., Krück, F., Ressel, C., Higuchi, M.: Acute and long-term studies of the mechanism of action of beta-blocking drugs in lowering blood pressure. Am. J. Med. 60, 853–865 (1976)
Sweet, C. S., Wenger, H. C.: Central antihypertensive effects of propranolol in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Neuropharmacology 15, 511–513 (1976)
Tarazi, R. C., Dustan, H. P.: Beta-adrenergic blockade in hypertension. Am. J. Cardiol. 29, 633–640 (1972)
Ulrych, M., Frolich, E. D., Dustan, H. P., Page, I. H.: Immediate hemodynamic effects of beta-adrenergic blockade with propranolol in normotensive and hypertensive man. Circ. Res. 37, 411–417 (1968)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smits, J.F.M., Struyker-Boudier, H.A.J. Propranolol in conscious spontaneously hypertensive rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 309, 19–24 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498752
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498752