Summary
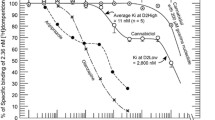
In order to label dopamine D2 receptors selectively we tritiated the potent benzamide neuroleptic, YM-09151-2 (26.7 Ci/mmol). The binding of [3H]-YM-09151-2 to canine striatal membranes was saturable and specific with a K D of 57 pmol/l and B max of 36 pmol/g tissue as determined by Scatchard analysis. The K D, but not the B max, of [3H]-YM-09151-2 increased 6-fold in the absence of sodium chloride. [3H]-YM-09151-2 labeled 40% more sites than [3H]-spiperone in the same tissue homogenate. [3H]-YM-09151-2 binding was inhibited by dopaminergic drugs in a concentration and stereoselective manner with the appropriate dopamine D2 receptor profile. Thus, dopamine agonists inhibited [3H]-YM-09151-2 binding to canine striatal membranes with the following rank order of potency: (−)-N-n-propylnorapomorphine > apomorphine > (±)-6,7-dihydroxy-2-aminotetralin > (+)-N-n-propylnorapomorphine > dopamine > (−)-noradrenaline > serotonin > (−)-isoprenaline. Dopaminergic antagonists competed for [3H]-YM-09151-2 binding with the following order of potency: spiperone > (+)-butaclamol > haloperidol > clebopride > (−)-sulpiride > SCH-23390 > (−)-butaclamol. Furthermore, dopamine agonists recognized 2 states of the receptor labeled by [3H]-YM-09151-2, D high2 and D low2 . The D high2 state of the receptor could be converted to D low2 by guanine nucleotides and sodium ions as is the case for [3H]-spiperone binding to D2 receptors. [3H]-YM-09151-2 appears to be a more selective ligand for dopamine D2 receptors than [3H]-spiperone, since YM-09151-2 displays approximately 9-fold lower affinity than spiperone for cortical serotonergic (S2) receptors. [3H]-YM-09151-2 may become a useful tool for the selective characterization of dopamine D2 receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- (±)ADTN:
-
(±)-2-amino-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene
- NPA:
-
N-n-propylnorapomorphine
- Gpp(NH)p:
-
5′-guanylylimidodiphosphate
References
Creese I, Hamblin MW, Leff SE, Sibley DR (1983) CNS dopamine receptors. In: Iversen LL, Iversen SD, Snyder SH (eds) Handbook for psychopharmacology, vol 17. Plenum Press, New York, pp 81–138
Elliott PNC, Jenner P, Huizing G, Marsden CD, Miller R (1977) Substituted benzamides as cerebral dopamine antagonists in rodents. Neuropharmacology 16:332–342
Fleminger S, Van De Waterbeemd H, Rupniak NMJ, Reavill C, Testa B, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1983) Potent lipophillic substituted benzamide drugs are not selective D1 dopamine receptor antagonists in the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol 55:363–368
Freedman SB, Poat JA, Woodruff GN (1981) The effect of guanosine nucleotides on [3H]-sulpiride binding to rat striatal membranes. Eur J Pharmacol 69:117–118
Freedman SB, Poat JA, Woodruff GN (1982) Influence of sodium and sulphydryl groups on [3H]-sulpiride binding sites in rat striatal membranes. J Neurochem 38:1459–1465
Grewe CW, Frey EA, Cote TE, Kebabian JW (1982) YM-09151-2: A potent antagonist for a peripheral D2 dopamine receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 81:149–152
Grigoriadis D, Seeman P (1985) Complete conversion of brain D2 dopamine receptors from the high- to the low-affinity state for dopamine agonists using sodium ions and guanine nucleotides. J Neurochem (in press)
Hadley MS (1982) Substituted benzamides as dopamine antagonists. In: Creighton AM, Turner S (eds) The chemical regulation of biological mechanisms. R Soc Chem. Special publication no. 42 London, pp 140–153
Hamblin MW, Leff SE, Creese I (1984) Interactions of agonists with D2 dopamine receptors: Evidence for a single receptor population existing in multiple agonist affinity-states in rat striatal membranes. Biochem Pharmacol 33:877–887
Hyttel J (1978) Effects of neuroleptics on [3H]-haloperidol and [3H]-cis-flupenthixol binding and on adenylate cyclase activity in vitro. Life Sci 23:551–556
Hyttel J (1983) SCH-23390 — the first selective dopamine D1 antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 91:153–154
Iorio LC, Barnett A, Leitz FH, Houser VP, Korduba CA (1983) SCH-23390, a potent benzazepine anti-psychotic with unique interactions on dopaminergic systems. J Pharm Exp Ther 226:462–468
Iwanami S, Takashima M, Hirata Y, Hasegawa O, Usuda S (1981) Synthesis and neuroleptic activity of benzamides. cis-N-(1-benzyl-2-methylpyrrolidin-3-yl)-5-chloro-2-methoxy-4-(methylamino) benzamide and related compounds. J Med Chem 24:1224–1230
Jenner P, Marsden CD (1981) Substituted benzamide drugs as selective neuroleptic agents. Neuropharmacology 20:1285–1293
Jenner P, Elliott PNC, Clow A, Reavill C, Marsden CD (1978) A comparison of in vitro and in vivo dopamine receptor antagonism produced by substituted benzamide drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol 30:46–48
Jenner P, Clow A, Reavill C, Theodorou A, Marsden CD (1980) Stereoselective actions of substituted benzamide drugs on cerebral dopamine mechanisms. J Pharm Pharmacol 32:39–44
Kebabian JW, Calne DB (1979) Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature 277:93–96
Leysen JE, Gommeren W, Laduron PM (1978) Spiperone: A ligand of choice for neuroleptic receptors. 1. Kinetics and characteristics of in vitro binding. Biochem Pharmacol 27:307–316
Leysen JE, Niemegeers CJE, Van Neuten JM, Laduron PM (1982) [3H]-Ketanserin (R41468), a selective [3H]-ligand for serotonin2 receptor binding sites. Mol Pharmacol 21:301–314
List SJ, Seeman P (1981) Resolution of dopamine and serotonin receptor components of [3H]-spiperone binding to rat brain regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:2620–2624
Martres MP, Sokoloff P, Delandre M, Schwartz JC, Protais P, Costentin J (1984) Selection of dopamine antagonists discriminating various behavioural responses and radioligand binding sites. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 325:102–115
Meltzer HY, Mikuni M, Simonovic M, Gudelsky GA (1983) Effect of a novel benzamide, YM-09151-2, on rat serum prolactin levels. Life Sci 32:1015–1021
Mizuchi A, Kitagawa N, Saruta S, Miyachi Y (1982) Characteristics of [3H]-sultopride binding to rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 84:51–59
Munson PJ, Rodbard D (1980) A versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem 107:220–239
Nakajima T, Iwata K (1984) [3H]R0-22-1319 (Piquindone) binds to the D2 dopaminergic receptor subtype in a sodium-dependent manner. Mol Pharmacol 26:430–438
Niznik HB, Grigoriadis D, Pri-Bar I, Buchman O, Seeman P (1984) Dopamine D2 receptors labeled by a new high affinity ligand: [3H]-YM-09151-2. Soc Neurosci Abstr 10 (1):277
Onali P, Olianas MC, Gessa GL (1984) Selective blockade of dopamine D1 receptors by SCH-23390 discloses striatal dopamine D2 receptors mediating the inhibition of adenylate cyclase in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 99:127–128
Rumigny JF, Benedetti MS, Dostert P (1984) Investigation on central dopaminergic receptors (D2) using the antagonistic properties of new benzamides. J Pharm Pharmacol 36:373–377
Seeman P (1980) Brain dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 32:229–313
Seeman P, Ulpian C, Wreggett KA, Wells JW (1984) Dopamine receptor parameters detected by [3H]-spiperone depend on tissue concentration: Analysis and examples. J Neurochem 43:221–235
Sokoloff P, Martres MP, Delandre M, Redouane K, Schwartz JC (1984) [3H]-Domperidone binding sites differ in rat striatum and pituitary. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 327:221–227
Stefanini E, Marchisto AM, Devoto P, Vernaleone F, Collu R, Spano PF (1980) Sodium dependent interactions of benzamides with dopamine receptors. Brain Res 198:229–233
Stoof JC, Kebabian JW (1981) Opposing roles for D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in efflux of cyclic AMP from rat neostriatum. Nature 294:366–368
Templeton WW, Woodruff GN (1983) A comparison of some of the properties of the [3H]-sulpiride binding site in soluble and native membrane preparations of dog striatum. Br J Pharmacol 78:5–7
Terai M, Ususa S, Kuroiwa I, Noshiro O, Maeno H (1983) Selective binding of YM-09151-2, a new potent neuroleptic, to D2 dopaminergic receptors. Jpn J Pharmacol 33:749–755
Theodorou A, Crockett M, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1979) Specific binding of [3H]-sulpiride to rat striatal preparations. J Pharm Pharmacol 31:424–426
Theodorou A, Hall MD, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1980) Cation regulation differentiates specific binding of [3H]-sulpiride and [3H]-spiperone to rat striatal preparations. J Pharm Pharmacol 32:441–444
Theodorou AE, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1983) Cation specificity of [3H]-sulpiride binding involves alteration in the number of striatal binding sites. Life Sci 32:1243–1254
Usuda S, Nishikori K, Noshiro O, Maeno H (1981) Neuroleptic properties of cis-N-(1-benzyl-2-methylpyrrolidin-3-yl)-5-chloro-2-methoxy-4-methylaminobenzamide (YM-09151-2) with selective anti-dopaminergic activity. Psychopharmacol 73:103–109
Woodruff GN, Freedman SB (1981) Binding of [3H]-sulpiride to purified rat striatal synaptic membranes. Neuroscience 6:407–410
Wreggett KA, Seeman P (1984) Agonist high- and low-affinity states of the D2 dopamine receptor in calf brain: Partial conversion by guanine nucleotide. Mol Pharmacol 25:10–17
Yamamoto M, Usuda S, Tachikawa S, Maeno H (1982) Pharmacological studies on a new benzamide derivative, YM-09151-2, with potential neuroleptic properties. Neuropharmacology 21:945–951
Zahniser NR, Dubocovich ML (1983) Comparison of dopamine receptor sites labeled by [3H]-sulpiride and [3H]-spiperone in striatum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:592–599
Zahniser NR, Molinoff PB (1978) Effect of guanine nucleotides on striatal dopamine receptors. Nature 275:453–455
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niznik, H.B., Grigoriadis, D.E., Pri-Bar, I. et al. Dopamine D2 receptors selectively labeled by a benzamide neuroleptic: [3H]-YM-09151-2. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 329, 333–343 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00496365
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00496365