Abstract
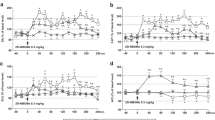
The antipunishment properties of diazepam (DZP) were investigated in mice treated acutely, or following nine daily treatments with either DZP (5 mg/kg, PO) or its vehicle. Acutely, or following chronic vehicle treatment, DZP produced a dose-related increase in activity punished by footshock. Following chronic DZP, test doses of DZP given 24 or 48 h following the last chronic treatment were no longer, or less effective in enhancing punished activity. Effects on unpunished activity were unaffected. In a study of the time course of tolerance development, tolerance was not seen after one or three daily treatments but was present after 6 days. Following establishment of tolerance by 9 days' treatment, the antipunishment activity of DZP reappeared after 8 days' withdrawal and was restored to acute levels after 16 days. Tolerance was not associated with changes in benzodiazepine (BZ) receptor affinity or numbers, but the ability of GABA to enhance BZ binding was increased. There was no change in the ability of DZP or the convulsant β-carboline DMCM to modulate 35S-TBPS binding. The mechanism of tolerance to the antipunshment properties of DZP therefore remains unknown.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernasconi R, Maitre L, Martin P, Raschdorf F (1982) The use of inhibitors of GABA-transaminase for the determination of GABA turnover in mouse brain regions: an evaluation of aminooxyacetic acid and gabaculine. J Neurochem 38:57–66
Boissier JR, Simon P, Aron C (1968) A new method for the rapid screening of minor tranquillisers in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 4:145–150
Braestrup C, Nielsen M (1983) Benzodiazepine receptors. In: Iversen LL, Iversen SD, Snyder SH (eds) Handbook of Psychopharmacology Vol. 17 Plenum, New York, pp 285–384
Braestrup C, Schmiechen R, Neef G, Nielsen M, Petersen EN (1982) Interaction of convulsive ligands with benzodiazepine receptors. Science 216:1241–1243
Browne TR, Penry JK (1973) Benzodiazepines in the treatment of epilepsy: a review. Epilepsia 14:277–310
Committee for the Review of Medicines (1980) Benzodiazepines. Drug Ther Bull 18:97–98
Costa E, Guidotti A (1979) Molecular mechanisms in the receptor action of benzodiazepines. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 19:531–535
Demellweek C, Goudie AJ (1983) Behavioural tolerance to amphetamine and other psychostimulants: the case for considering behavioural mechanism. Psychopharmacology 80:287–307
File SE (1981) Rapid development of tolerance to the sedative effects of lorazepam and triazolam in rats. Psychopharmacology 73:240–245
File SE (1984) Behavioural pharmacology of benzodiazepines. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol Psychiatry 8:19–31
File SE (1985) Tolerance to the behavioural actions of benzodiazepines. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 9: (in press)
Frey HH, Philippin HP, Scheuler W (1984) Development of tolerance to the anticonvulsant effect of diazepam in dogs. Eur J Pharmacol 104:27–38
Gallager DW, Lakoski JM, Gonsalves SG, Rauch SL (1984a) Chronic benzodiazepine treatment decreases postsynaptic GABA sensitivity. Nature 308:74–77
Gallager DW, Rauch SL, Malcolm LK (1984b) Alterations in a low affinity GABA recognition site following chronic benzodiazepines. Eur J Pharmacol 98:159–160
Greenblatt DJ, Shader RI (1978) Dependence, tolerance, and addiction to benzodiazepines: clinical and pharmacokinetic considerations. Drug Metab Rev 8:13–28
Greenblatt DJ, Shader RI, Harmatz JS, Georgotas A (1979) Selfrated sedation and plasma concentrations of desmethyldiazepam following single doses of chlorazepate. Psychopharmacology 66:289–290
Haefely W, Kulcsar A, Möhler H, Pieri L, Polc P, Schaffner R (1975) Possible involvement of GABA in the central actions of benzodiazepines. In: E. Costa, P. Greengard (eds) Mechanism of action of benzodiazepines. Raven Press, New York pp 131–151
Lader MH (1980) The present status of benzodiazepines in psychiatry and medicine. Arzneimittelforsch 30:851–916
Lister RG, File SE (1983) Changes in regional concentrations of 5-HT and 5-HIAA during development of tolerance to the sedative action of chlordiazepoxide. J Pharm Phamacol 35:601–603
Margules DL, Stein L (1968) Increase of antianxiety activity and tolerance to behavioral depression during chronic administration of oxazepam. Pschopharmacology 13:74–80
Martin IL, Candy JM (1979) Facilitation of benzodiazepine binding by sodium chloride and GABA. Neuropharmacology 17:993–998
Nielsen M, Honore T, Braestrup C (1985) Radiation inactivation of brain 35S-TBPS binding sites reveals complicated molecular arrangements of the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor chloride channel complex. Biochem Pharmacol (in press)
Overstreet DH, Yamamura HI (1979) Receptor alterations and drug tolerance. Life Sci 25:1865–1878
Rago LK, Sarv KA, Allikmets LK (1983) Effect of a ten-day course of fenibut and diazepam on GABA and benzodiazepine receptors in mouse brain. Bull Exp Biol Med 96:1708–1709
Rosenberg HC, Smith S, Chiu TH (1982) Benzodiazepine-specific and nonspecific tolerance following chronic flurazepam treatment. Life Sci 32:279–285
Sepinwall J, Cook L (1980) Mechanism of action of the benzodiazepines: behavioral aspects. Fed Proc 39:3024–3031
Sepinwall J, Grodsky FS, Cook L (1978) Conflict behavior in the squirrel monkey: effects of chlordiazepoxide, diazepam and N-desmethyldiazepam. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 204:88–102
Siegel S, MacRae J (1984) Environmental specificity of tolerance. Trends Neurosci 7:140–144
Squires RF, Casida JE, Richardson M, Saederup E (1983) [35S]-t butylbicyclophosphorothionate binds with high affinity to brain-specific sites coupled to λ-aminobutyric acid A and ion recognition sites. Mol Pharmacol 23:326–336
Stephens DN, Kehr W (1985) β-carbolines can enhance or antagonize the effect of punishment in mice. Psychopharmacology 85:143–147
Stephens DN, Kehr W, Schneider HH, Braestrup C (1984) Bidirectional effects on anxiety of β-carbolines acting as benzodiazepine receptor ligands. Neuropharmacology 23:879–880
Supavilai P, Karobath M (1983) Differential modulation of [35S]-TBPS binding by the occupation of benzodiazepine receptors with its ligands. Eur J Pharmacol 91:145–146
Tallman JF, Thomas JW, Gallager DW (1978) GABAergic modulation of benzodiazepine binding site sensitivity. Nature 274:383–385
Vellucci SV, File SE (1979) Chlordiazepoxide loses its anxiolytic action with long-term treatment. Pschopharmacology 62:61–65
Wise CD, Berger BD, Stein L (1972) Benzodiazepines: anxiety reducing activity by reduction of serotonin turnover in the brain. Science 177:180–183
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stephens, D.N., Schneider, H.H. Tolerance to the benzodiazepine diazepam in an animal model of anxiolytic activity. Psychopharmacology 87, 322–327 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00432715
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00432715