Abstract
Effects of suramin and five analogs or fragments of suramin were studied on contractions of the rat vas deferens elicited by α,β-methylene ATP (α,β-McATP; mediated by P2X-purinoceptors), relaxations of the carbachol-precontracted guinea-pig taenia coli elicited by adenosine 5′-O-(2-thiodiphosphate) (ADPβS; mediated by P2Y-purinoceptors), and the degradation of ATP by rat vas deferens tissue. One compound, NF023, differed from suramin by removal of two p-methylbenzamido groups, whereas another, BSt101, differed from NF023 by additional removal of the three sulphonate residues from one of the terminal naphthalene rings.
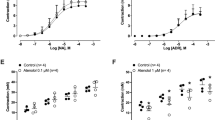
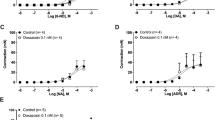
The compounds all shifted the concentration-response curve of α,β-MeATP in the rat vas deferens to the right and simultaneously increased the maximum of the curve. Where three concentrations were tested, the Arunlakshana-Schild regression was linear, and the slope did not differ from 1. The apparent K d values were between 1 and 3672 μM. In the guinea-pig taenia coli, the compounds shifted the concentration-response curve of ADPβS to the right in a parallel manner, but in the one case where three concentrations were tested, the slope of the Arunlakshana-Schild regression was lower than 1. Apparent K d values were between 10 and 786 μM. The removal of ATP from the medium by vas deferens tissue was decreased only by suramin, NF023 and BSt101, with IC25% values between 170 and 590 μM.
The results indicate that P2X-purinoceptor affinity, P2Y-purinoceptor affinity and the ecto-nucleotidase effect all increase with the size of the molecule. BSt101 resembled NF023 in potency at all three sites, indicating that the possession of a second naphthalene-trisulphonate group is not a prerequisite for relatively high affinity. NF023 is interesting because it is P2X- versus P2Y-selective and, in addition, the compound with the highest P2X- versus ecto-nucleotidase-selectivity presently available.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arunlakshana O, Schild HO (1959) Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol 14:48–58
Beukers MW Kerkhof CJM, van Rhee MA, Ardanuy U, Gurgel C, Widjaja H, Nickel P, Uzerman AP, Soudijn W (1995) Suramin analogs, divalent cations and ATPγS as inhibitors of ecto-ATPase. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 351:523–528
Blakeley AGH, Brockbank JE, Kelly SS, Petersen SA (1991) Effects of suramin on the concentration-response relationship of α,β-methylene ATP on the mouse vas deferens. J Auton Pharmacol 11:45–49
Bültmann R, Starke K (1993) Evans blue blocks P2X-purinoceptors in rat vas deferens. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 348:684–687
Bültmann R, Starke K (1994) P2-purinoceptor antagonists discriminate three contraction-mediating receptors for ATP in rat vas deferens. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 349:74–80
Bültmann R, Trendelenburg M, Starke K (1994) Trypan blue blocks P2X-purinoceptors in rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol 113:349–354
Bültmann R, Dudeck O, Starke K (1996a) Evaluation of P2-purinoceptor antagonists at two relaxation-mediating P2-purinoceptors in guinea-pig taenia coli. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 353:445–451
Bültmann R, Pause B, Wittenburg H, Kurz G, Starke K (1996b) P2-Purinoceptor antagonists: I. Blockade of P2-purinoceptor subtypes and ecto-nucleotidases by small aromatic isothiocyanato-sulphonates. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 354:481–490
Burnstock G, Fischer B, Hoyle CHV, Maillard M, Ziganshin AU, Brizzolara AL, von Isakovics A, Boyer JL, Kendall Harden T, Jacobson KA (1994) Structure activity relationships for derivatives of adenosine-5′-triphosphate as agonists at P2 purinoceptors: heterogeneity within P2X and P2Y subtypes. Drug Dev Res 31:206–219
Cusack NJ (1993) P2 Receptor: subclassification and structure-activity relationships. Drug Dev Res 28:244–252
Den Hertog A, Nelemans A, van den Akker J (1989) The inhibitory action of suramin on the P2-purinoceptor response in smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig taenia caeci. Eur J Pharmacol 166:531–534
Dudeck O, Bültmann R, Starke K (1995) Two relaxation-mediating P2-purinoceptors in guinea-pig taenia coli. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 351:107–110
Dunn PM, Blakeley AGH (1988) Suramin: a reversible P2-purinoceptor antagonist in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol 93:243–245
Furchgott RF (1972) The classification of adrenoceptors (adrenergic receptors). An evaluation from the standpoint of receptor theory. In: Blaschko H, Muscholl E (eds) Catecholamines. Handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol 33. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 283–335
Hoyle CHV, Knight GE, Burnstock G (1990) Suramin antagonizes responses to P2-purinoceptor agonists and purinergic nerve stimulation in the guinea-pig urinary bladder and taenia coli. Br J Pharmacol 99:617–621
Khakh BS, Michel A, Humphrey PPA (1994) Estimates of antagonist affinities at P2x purinoceptors in rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol 263:301–309
Khakh BS, Surprenant A, Humphrey PPA (1995a) A study on P2X purinoceptors mediating the electrophysiological and contractile effects of purine nucleotides in rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol 115:177–185
Khakh BS, Michel AD, Humphrey PPA (1995b) Inhibition of ectoATPase and Ca-ATPase in rat vas deferens by P2 purinoceptor antagonists. Br J Pharmacol 115:2P
Kurz AK, Bültmann R, Driessen B, von Kagelgen I, Starke K (1994) Release of ATP in rat vas deferens: origin and role of calcium. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 350:491–498
Lambrecht G, Niebel B, Ziyal R, Ardanuy U, Bäumert HG, Nickel P, Mutschler E (1996) P2-Purinoceptor heterogeneity in guinea-pig taenia coli and rabbit vas deferens. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 353:R42
Mallard N, Marshall R, Sithers A, Spriggs B (1992) Suramin: a selective inhibitor of purinergic neurotransmission in rat isolated vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol 220:1–10
Motulsky HJ, Ransnas LA (1987) Fitting curves to data using non-linear regression: a practical and nonmathematical review. FASEB J 1:365–374
Nickel P, Haack HJ, Widjaja H, Ardanuy U, Gurgel U, Düwel D, Loewe H, Raether W (1986) Potentielle Filarizide. Arzneim Forsch 36:1153–1157
Trezise DJ, Kennedy I, Humphrey PPA (1994) The use of antagonists to characterize the receptors mediating depolarization of the rat isolated vagus nerve by α,β-methylene adenosine 5′-triphosphate. Br J Pharmacol 112:282–288
Urbanek E, Nickel P, Schlicker E (1990) Antagonist properties of four suramin-related compounds at vascular purine P2X receptors in the pithed rat. Eur J Pharmacol 175:207–210
van Rhee AM, van der Heijden MPA, Beukers MW Uzerman AP, Soudijn W Nickel P (1994) Novel competitive antagonists for P2 purinoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol 268:1–7
von Kügelgen I, Bültmann R, Starke K (1990) Interaction of adenine nucleotides, UTP and suramin in mouse vas deferens: suraminsensitive and suramin-insensitive components in the contractile effect of ATP. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 342:198–205
Waud DR (1976) Analysis of dose-response relationships. In: Narahashi T, Bianchi CP (eds) Advances in general and cellular pharmacology, vol 1. Plenum, New York London, pp 145–178
Wittenburg H, Bültmann R, Pause B, Kurz G, Nickel P, Starke K (1996a) Blockade by suramin congeners of P2-purinoceptor subtypes and ecto-nucleotidases. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 353:R41
Wittenburg H, Bültmann R, Pause B, Ganter C, Kurz G, Starke K (1996b) P2-Purinoceptor antagonists: II. Blockade of P2-purinoceptor subtypes and ecto-nucleotidases by compounds related to Evans blue or trypan blue. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 354:491–497
Ziyal R, Pfaff O, Windscheif U, Bo X, Nickel P, Ardanuy U, Burnstock G, Mutschler E, Lambrecht G (1994) A novel P2-purinoceptor ligand which displays selectivity for the P2X-subtype. Drug Dev Res 31:336
Ziyal R, Ralevic V Nickel P, Ardanuy U, Mutschler E, Lambrecht G, Bumstock G (1996) NF023, a novel and selective P2-purinoceptor antagonist for P2X-purinoceptors in rat and hamster mesenteric arterial beds. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 353:R41
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bültmann, R., Wittenburg, H., Pause, B. et al. P2-purinoceptor antagonists: III. Blockade of P2-purinoceptor subtypes and ecto-nucleotidases by compounds related to suramin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 354, 498–504 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168442
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168442